![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood is composed of two major components; What are they?
|
Plasma and suspended cells
|
|
|
Plasma contains:
|
H2O, Inorganic salts, organic matter, gases, proteins and antibodies
|
|
|
Cells contain:
|
Leukocytes (white blood cells)
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) Thrombocytes (platelets) |
|
|
how many leukocytes circulating in the bood stream?
|
3,500 to 12,500
|
|
|
Leukocytes are catergorized into two groups, these are ... ?
|
Agranulocytes and Granulocytes
|
|
|
Granulocytes include .. ?
|
neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
|
|
|
Agranulocytes include ...?
|
Lymphocytes and monocytes
|
|
|
Thrombocytes appear as ...?
|
small cell fragments
|
|
|
what are the most frequent cell type?
|
erythrocytes
|
|
|
what are erythrocytes responsible for?
|
transport of oxygen to tissues and the transport of carbon dioxide t the lungs
|
|
|
where do erythrocytes usually originate and mature?
|
in the bone marrow
|
|
|
what happens to an erythrocyte when it matures?
|
the size of the cell decreases and the nucleus disappears.
|
|
|
In certain disease state, RBC's can also be produced by ... ?
|
liver and spleen
|
|
|
What is the smallest blood cell?
|
A mature RBC at about 7 um in diameter
|
|
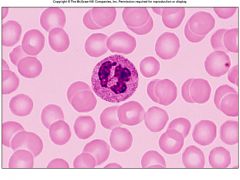
Name this white blood cell
|
Neutrophil
|
|
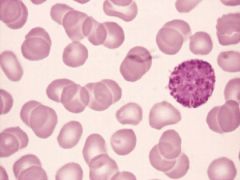
Name this white blood cell
|
Eosinophil
|
|
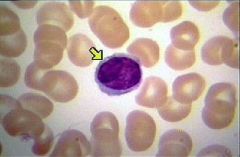
Name this white blood cell
|
Basophil
|
|
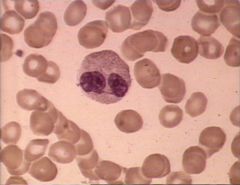
Name this white blood cell
|
Lymphocyte
|
|
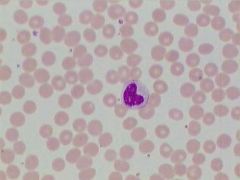
Name this white blood cell
|
Monocyte
|
|
|
Thrombocytes (or platelets)
|
small, irregularly shaped cell fragments that have broken away from larger cells in the bone marrow (megakaryocytes)
|
|
|
the two upper chambers are the ...
|
right and left ATRIA
|
|
|
the two lower chambers are the ...?
|
right and left VENTRICLES
|
|
|
what do the ventricles do?
|
they form the bulk of the heart and are the discharging chambers that push blood to various places in the body.
|
|
|
Interatrial or Interventricular septum
|
the wall of tissue that separates the right and left chambers longitudinally
|
|
|
Deoxygenated blood comes TO the heart and is drained into the right atrium though one of two major vessels... what are they?
|
the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava
|
|
|
superior vena cava
|
drains blood from the upper body (head, neck, and forelimbs)
|
|
|
inferior vena cava
|
drains blood from the trunk and lower body
|
|
|
Tricuspid Valve
|
a valve with three flaps found between the right and left atrium and ventricle.
|
|
|
Chordae Tendinae
|
fibrous strands that attach the tricuspid valves to the muscular wall of the right ventricle
|
|
|
Pulmonary Trunk
|
this divides into two pulmonary artieries that convey the blood to the lungs for gas exchange
|
|
|
semi-lunar valve
|
a valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk that prevents the backflow of blood.
|
|
|
how does oxygenated blood return to the heart?
|
through two pulmonary veins
|
|
|
Bicuspid valve, or the mitral valve
|
a valve with two flaps; between the left atrium and left ventricle, its a chamber to prevent the backflow of blood.
|

