![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the boundaries of the femoral triangle in the horse?
What are the structures located within the femoral triangle? |
Cranial boundary – Sartorius m.
Caudal boundary – Pectineus m. Dorsal boundary – Vascular lacuna Femoral a. Femoral v. Saphenous n. Deep inguinal lnn. |
|
|
What are the boundaries of the femoral triangle in the ruminant?
What are the structures located within the femoral triangle? |
Cranial boundary – Sartorius m.
Caudal boundary – Sartorius m. Dorsal boundary – Vascular lacuna Femoral a. Femoral v. Saphenous n. Deep inguinal lnn. |
|
|
What is the continuation of deep femoral a. in the horse?
|
medial circumflex femoral a.
|
|
|
What does the saphenous a. run with in the horse?
What does it connect with over the tarsus? What does it continue as? |
It course with the saphenous n. and medial saphenous v on the medial side of the pelvic limb.
It anastomoses with the caudal tibial a. at the loop on the plantar aspect of the tarsus. Saphenous a. continues as the medial and lateral plantar aa. |
|
|
What bones make up the tarsal canal in the horse?
|
Central tarsal bone, 3rd tarsal bone and 4th tarsal bone.
|
|
|
What vessels arise from the proximal deep plantar arch in the horse?
|
The medial and lateral plantar metatarsal aa.
|
|
|
Where do you get the arterial blood sample from in the horse? It is the main blood supply to the digit.
Where does it course between? |
Dorsal metatarsal a. III (or the great metatarsal a)
Courses between metatarsals III and IV |
|
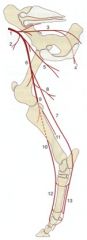
ID these bovine arteries
|
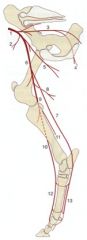
Deep circumflex iliac a. (2)
Deep femoral a. -Pudendoepigastric trunk -Medial circumflex femoral a. (5) Femoral a. (6) -Lateral circumflex femoral a. -Saphenous a. (7) --Plantar aa. – medial and lateral (13) ---Plantar common digital aa. -Descending genicular a. -Distal caudal femoral a. (8) Popliteal a. (9) -Cranial tibial a. (10) --Dorsal metatarsal aa. (12) -Caudal tibial a. (11) |
|
|
What forms the tarsal canal in the ox?
|
2nd and 3rd fused tarsal bone, fused metatarsal 3 and 4, and fused 4th and central tarsal bones
|
|
|
What is clinically relevant about the dorsal common digital vein III of the ruminant?
|

In the ox, this vein can be raised to administer intravenous anesthesia.
|
|
|
What nerves form the lumbosacral plexus of the pelvic limb?
|
Ventral branches of L4-S2
|
|
|
What nerves come together to form obturator n?
|
ventral branches of L4, L5, and L6
|
|
|
What muscles does femoral n. innervate?
What nerve does femoral n. give rise to? What does that nerve innervate? |
Iliopsoas m. (flex hip)
Quadriceps femoris m. (flex hip, extend stifle) Gives rise to the saphenous n. Innervates sartorius m. (and possibly pectineus m. in the Ruminant) Supplies cutaneous innervation to the craniomedial aspect of the thigh, crus and metatarsus as far distally as the fetlock joint |
|
|
What muscles does obturator n. innervate?
What is their action? |
Innervates:
External obturator m. Pectineus m. Gracilis m. Adductor m. All are adductor |
|
|
What muscles does cranial gluteal n. innervate?
What is their action? |
Superficial gluteal m. (Horse)
Middle gluteal m. Deep gluteal m. Tensor fascia latae m. Primary actions: abduct the hip and flex the hip |
|
|
What muscles does caudal gluteal n. innervate?
What is their action? |
Superficial gluteal m. (Horse)
Semitendinosus m. Biceps femoris m. (Horse) Gluteobiceps m. (Ruminant) Middle gluteal m Primary action: extend the hip |
|
|
What muscles does sciatic n. innervate?
What is their action? What nerves does sciatic n. divide into? |
Internal obturator m. (Horse)
Gemelli mm. Quadratus femoris m. Biceps femoris m. (Horse) Gluteobiceps m. (Ruminant) Semimembranosus m. Semitendinosus m. Lots of actions - lateral rotators, extend stifle, extend hock Branches into: common peroneal/fibular and tibial n. |
|
|
What is another name for deep peroneal n.?
What does this nerve course with? What does it innervate? |
Fibular n.
Courses deep with cranial tibial a. Innervates: Lateral digital extensor, long digital extensor, cranial tibial, peroneus tertius mm. Peroneus longus, short digital extensor mm. (Ruminant) |
|
|
What is another name for fibular n.?
What does this nerve course with? What does it innervate? |
Deep peroneal n.
Courses deep with cranial tibial a. Innervates: Lateral digital extensor, long digital extensor, cranial tibial, peroneus tertius mm. Peroneus longus, short digital extensor mm. (Ruminant) |
|
|
What are the two additional nerves that you have to block in the pelvic limb of the horse than in the thoracic limb?
|
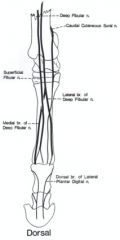
Branches off of deep peroneal/fibular n.
Medial br. – medial dorsal metatarsal n. Innervates: short digital extensor m. Sensory innervation to the joint capsule of the hock and to the skin on the medial surface of the metatarsus and fetlock to the level of p3 Lateral br. – lateral dorsal metatarsal n. Innervates: short digital extensor m. Courses with the dorsal metatarsal III a. Sensory to the skin on the lateral surface of the metatarsus and fetlock to the level of p3 |
|
|
How do you block the deep and superficial peroneal and fibular n?
|
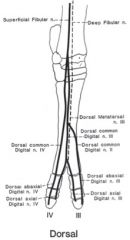
Deep peroneal / fibular n.
Continues as dorsal metatarsal n. III in the metatarsal region Provides deep innervation to the interdigital space Anesthesia: Dorsolateral surface of the hock region at the level of the tuber calcanei between the long digital extensor tendon and the peroneus longus tendon Insert needle to bone (approx. 1 inch) and inject Superficial peroneal / fibular n. Dorsal common digital nn. Provides innervation of the dorsal aspect of the digits Anesthesia: After blocking deep peroneal n., before withdrawing the needle, inject subcutaneously |
|
|
What does tibial n. innervate in the pelvic limb of the large animals?
What does it divide into? |
Gluteobiceps m. (Ruminant)
Gastrocnemius m. Popliteus m. Soleus m. Superficial digital flexor m. Deep digital flexor m. Divides into medial (6’’) and lateral (6’’’) plantar nn. |
|
|
What nerve provides the cutaneous innervation of the medial aspect of the tarsus and metatarsus of the horse?
What does this nerve continue as? |
Medial plantar n.
(from tibital) Continues in the digit as medial plantar digital n. |
|
|
What nerve innervates interosseus in the horse?
What does this nerve continue as? |
Deep br. of lateral plantar n. of tibial n.
Continues in the digit as lateral plantar digital n. |
|
|
Where do you block tibial n. in the ox?
|
Medial side of common calcaneal tendon approximately 4 inches proximal to tuber calcanei
Nerve is palpable subcutaneously |
|
|
What are the cutaneous autnomous zones of the pelvic limb in the horse?
|
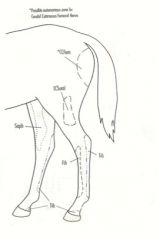
CCFem – Caudal cutaneous femoral n.
LCSural – Lateral cutaneous sural n. -From common peroneal (fibular) n. Saph – Saphenous n. -From femoral n. Tib – Tibial n. Fib – Peroneal / fibular n. |
|
|
What are the five pelvic limb nerve blocks in the horse?
|
Plantar digital (heel) block
Medial and lateral plantar digital nn. (not including dorsal brs.) Abaxial sesamoidean block Medial and lateral plantar digital nn. (including dorsal brs.) Low plantar, 4-point Medial and lateral plantar nn. Medial and lateral plantar metatarsal nn. Medial dorsal metatarsal n. Lateral dorsal metatarsal n. High plantar, 4-point Medial and lateral plantar nn. Medial and lateral plantar metatarsal nn. Peroneal and tibial nerve block |
|
|
What are the landmarks for the plantar digital nerve block (heel block) in the horse? What does it anesthetize and block?
|
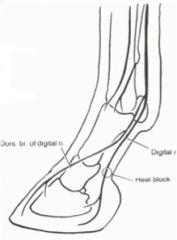
Landmarks: on the plantar aspect of the pastern, medially and laterally, midway between the fetlock and the coronet; just plantar to the plantar digital v. and a.
Anesthetizes: plantar digital nerves, not including the dorsal brs. Blocks: plantar one-third of the foot |
|
|
What are the landmarks of the abaxial sesamoidean nerve block of the pelvic limb in the horse? What does it anesthetized/block?
|
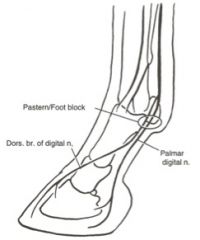
Landmarks: at the level of the proximal sesamoids, medially and laterally
Anesthetizes: plantar digital nerves including dorsal branches Blocks: the foot distal to the fetlock, not including the fetlock |
|
|
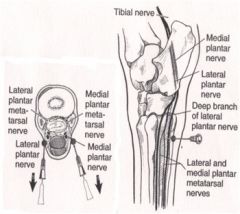
Where is the low plantar (4 point) block done in the pelvic limb of the horse?
Where does it block? |
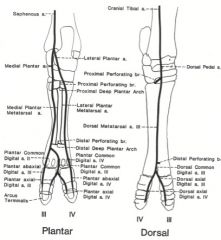
Medial and lateral plantar nerves (9, 9’)
Between the interosseus (5) and deep digital flexor tendon (6) Medial and lateral plantar metatarsal nerves (10) Between the interosseus (5) and splint bones (2, 3) Medial dorsal metatarsal nerve (11) Block at the middle of metatarsal III (1) on the dorsomedial aspect, just medial to the long digital extensor tendon (4) Lateral dorsal metatarsal nerve (8) Block at the middle of metatarsal III (1) on the dorsolateral aspect, in the groove between metatarsals III and IV. Courses with the dorsal metatarsal a. III (great metatarsal a.) (8) Blocks fetlock and everything distal to fetlock |
|
|
What are the landmarks for performing the high plantar (4 point) block? What does it block?
|
Landmarks: just distal to the tarsometatarsal joint and axial to the fourth metatarsal bone
Nerves blocked: Medial and lateral plantar nerves Medial and lateral plantar metatarsal nerves Blocks: flexor tendons, interosseus, metatarsals II, III and IV Cutaneous innervation still present due to lateral and medial dorsal metatarsal nn. |
|
|
What are the landmarks for performing the peroneal and tibial nerve blocks?
When is this block used? |
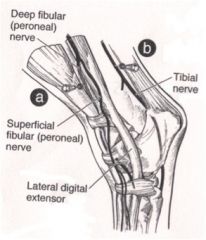
Deep and superficial peroneal / fibular nerves
Landmarks: In the groove formed by the lateral digital extensor and long digital extensor tendons Tibial nerve Landmarks: 10 cm proximal to the tuber calcanei Cranial to the common calcaneal tendon Caudal to the deep digital flexor tendon Used for diagnosing hock lameness |
|
|
What are the lymph nodes of the horse pelvic limb?
|
Popliteal lnn.
No superficial popliteal lnn. Deep popliteal lnn. are located caudal to the origin of the gastrocnemius m., between biceps femoris and semitendinosus mm. Afferents from distal part of limb Efferents course mainly to the deep inguinal lnn. (located in the femoral triangle in the horse) Subiliac lnn. Afferents from the skin of the pelvis, thigh and stifle |
|
|
What are the lymph nodes of the ruminant pelvic limb?
|
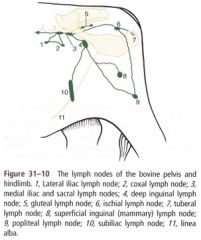
Popliteal ln. (9)
Afferents from the skin of the lateral and caudal portions of the leg and from the distal part of the limb Efferents course to the deep inguinal lnn. (4) and ischial lnn. (6) which drain to the medial iliac lnn. (3) Subiliac ln. (10) Afferents from the skin of the thigh, stifle and flank Efferents course mainly to the deep inguinal lnn. (4) |

