![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What force keeps the lungs inflated? What figures should you know in relation to this?
|
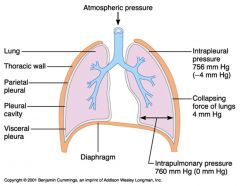
Negative pressure keeps the lungs inflated. At sea level, intrapleural pressure is at approximately 756 mm Hg, and the intrapulmonary pressure is at approximately 760 mm Hg - the difference between these values, 4 mm Hg, is the collapsing force of lungs and is what allows them to expand.
|
|
|
Describe the sequence of events necessary for inspiration
|
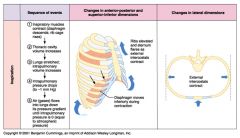
1. Inspiratory muscles contract (diaphragm descends, rib cage rises)
2. Thoracic cavity volume increases 3. Lungs stretched, intrapulmonary volume increases 4. Intrapulmonary pressure drops (to -1 mm Hg) 5. Air (gases) flows into lungs down its pressure gradient until intrapulmonary pressure reaches 0 (equal to atmospheric pressure) |
|
|
Describe the sequence of events necessary for expiration.
|
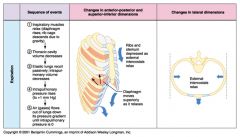
1. Inspiratory muscles relax (diaphragm rises, rib cage descends due to gravity)
2. Thoracic cavity volume decreases 3. Elastic lungs recoil passively; intrapulmonary volume decreases 4. Intrapulmonary pressure rises (to +1 mm Hg) 5. Air (gases) flows out of the lungs down its pressure gradient until intrapulmonary pressure is 0. |
|
|
What three pressure values are measured during inspiration and expiration - how do they change during these two acts?
|
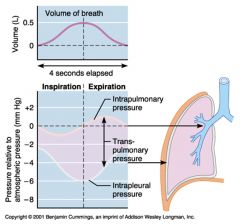
Intrapulmonary pressure descends from 0 to -1 mm Hg, then rises back to 0 mm Hg during inspiration, and rises from 0 to 1 mm Hg, the descends back to 0 mm Hg during expiration
Transpulmonary pressure is a measure of the pressure between the lung and the pleural space Intrapleural pressure descends from about -2 to -6 mm Hg during inspiration, and rises from -6 to -2 mm Hg during expiration |
|
|
What is IRV? How is it measured or calculated? What is a normal value for this for a healthy adult male?
|

IRV = Inspiratory Reserve Volume
It is the additional amount of air that may be inhaled beyond normal resting breathing (IE deep inhalation) A healthy adult male has an IRV of about 3100 ml |
|
|
What is TV? How is it measured or calculated? What is a normal value for this for a healthy adult male?
|
TV = Tidal Volume
It is the normal amount of air exchanged during normal resting breathing A healthy adult male has an TV of about 500 ml |
|
|
What is TV? How is it measured or calculated? What is a normal value for this for a healthy adult male?
|

TV = Tidal Volume
It is the normal amount of air exchanged during normal resting breathing A healthy adult male has an TV of about 500 ml |
|
|
What is ERV? How is it measured or calculated? What is a normal value for this for a healthy adult male?
|

ERV = Expiratory Reserve Volume
It is the amount of air that may be exhaled beyond the that exhaled during normal resting breathing (IE deep exhalation) A healthy adult male has an ERV of about 1200 ml |
|
|
What is RV? How is it measured or calculated? What is a normal value for this for a healthy adult male?
|

RV = Residual Volume
It is the amount of air that remains in the lungs even after deep exhalation A healthy adult male has an RV of about 1200 ml |
|
|
What is IC? How is it measured or calculated? What is a normal value for this for a healthy adult male?
|

IC = Inspiratory Capacity
It is the total amount of air that may be inhaled, equal to the Tidal Volume (TV) plus the Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) A healthy adult male has an IC of about 3600 ml |
|
|
What is FRC? How is it measured or calculated? What is a normal value for this for a healthy adult male?
|

FRC = Functional Residual Capacity
It is equal to the Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) plus the Residual Volume (IRV) A healthy adult male has an IC of about 2400 ml |
|
|
What is VC? How is it measured or calculated? What is a normal value for this for a healthy adult male?
|

VC = Vital Capacity
It is equal to the Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) plus Tidal Volume (TV) plus the Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) - another way of thinking of it is that it's all of the air you can move between a deep inhalation and a deep exhalation A healthy adult male has an VC of about 4800 ml |
|
|
What is TLC? How is it measured or calculated? What is a normal value for this for a healthy adult male?
|

TLC = Total Lung Capacity
It is equal to the Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) plus Tidal Volume (TV) plus the Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) plus the Residual Volume (RV) - another way of thinking of it is that it's all of the air in your lungs after a deep inhalation A healthy adult male has an TLC of about 6000 ml |

