![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
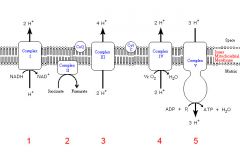
Identify the enzyme class for step 1 of the electron transport chain
|
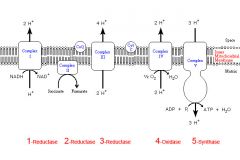
Step 1 utilizes Reductase
|
|
|
Identify the enzyme class for step 2 of the electron transport chain
|
Step 2 utilizes Reductase
|
|
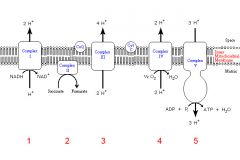
Identify the enzyme class for step 2 of the electron transport chain
|
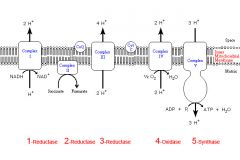
Step 2 utilizes Reductase
|
|
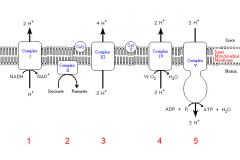
Identify the enzyme class for step 3 of the electron transport chain
|
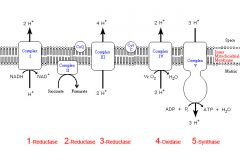
Step 3 utilizes Reductase
|
|
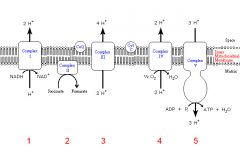
Identify the enzyme class for step 4 of the electron transport chain
|
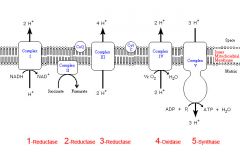
Step 4 utilizes Oxidase
|
|
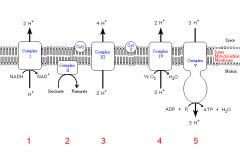
Identify the enzyme class for step 5 of the electron transport chain
|
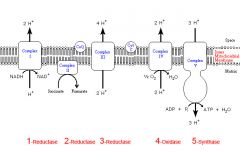
Step 5 utilizes Synthase
|
|
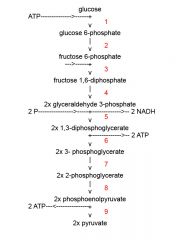
Identify the enzyme class for step 1 of glycolysis
|
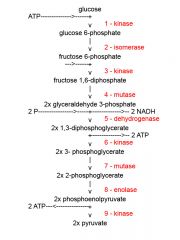
Step one of glycolysis utilizes Kinase
|
|
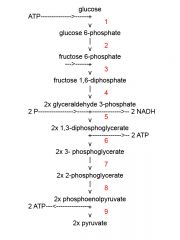
Identify the enzyme class for step 2 of glycolysis
|
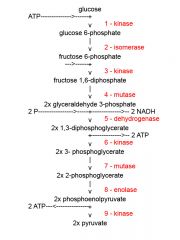
Step one of glycolysis utilizes Isomerase
|
|
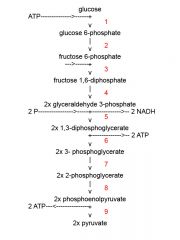
Identify the enzyme class for step 3 of glycolysis
|
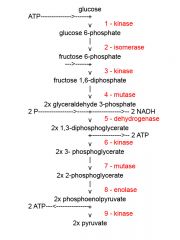
Step 3 of glycolysis utilizes Kinase
|
|
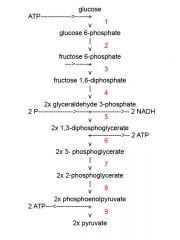
Identify the enzyme class for step 4 of glycolysis
|
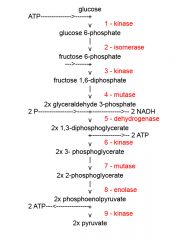
Step 4 of glycolysis utilizes Mutase
|
|
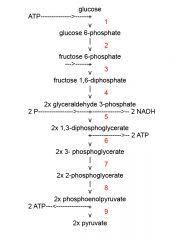
Identify the enzyme class for step 5 of glycolysis
|
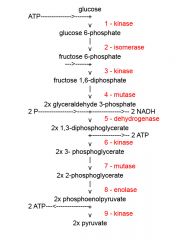
Step 5 of glycolysis utilizes Dehydrogenase
|
|
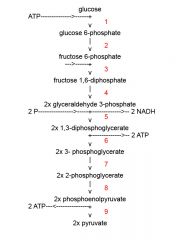
Identify the enzyme class for step 6 of glycolysis
|
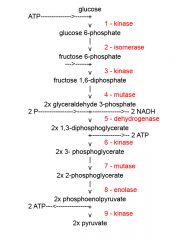
Step 6 of glycolysis utilizes Kinase
|
|
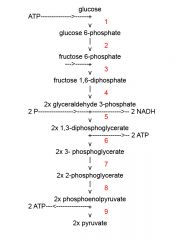
Identify the enzyme class for step 7 of glycolysis
|
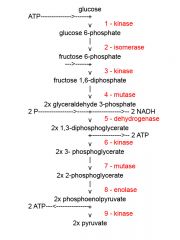
Step 7 of glycolysis utilizes Mutase
|
|
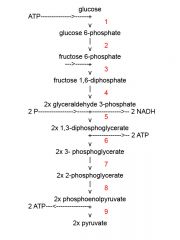
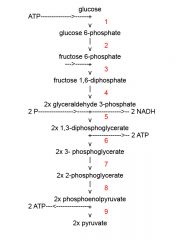
Identify the enzyme class for step 8 of glycolysis
|
Step 8 of glycolysis utilizes Enolase
|
|
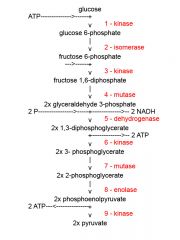
Identify the enzyme class for step 9 of glycolysis
|
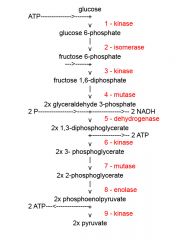
Step 9 of glycolysis utilizes Kinase
|
|

Identify the enzyme class for step 1 of the kreb cycle (pyruvate to Acetyl COA)
|
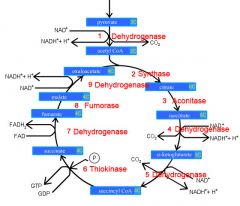
Step 1 of the kreb cycle utilizes Dehydrogenase
|
|
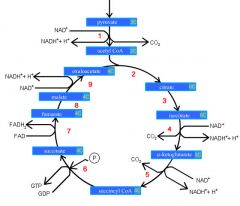
Identify the enzyme class for step 2 of the kreb cycle (Acetyl COA to Citrate)
|
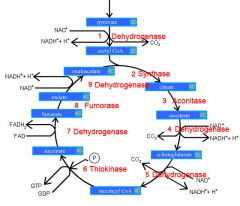
Step 2 of the kreb cycle utilizes Synthase
|
|
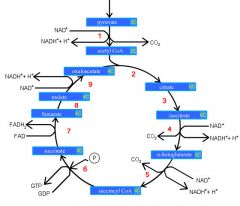
Identify the enzyme class for step 3 of the kreb cycle (Citrate to Isocitrate)
|
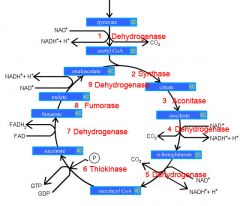
Step 3 of the kreb cycle utilizes Aconitase
|
|
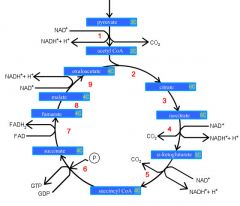
Identify the enzyme class for step 4 of the kreb cycle (Isocitrate to a-ketoglutarate)
|
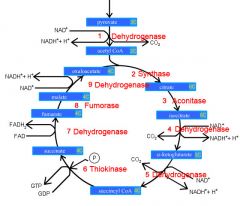
Step 4 of the kreb cycle utilizes Dehydrogenase
|
|
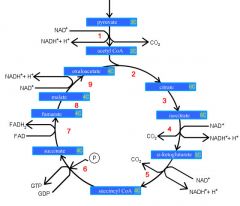
Identify the enzyme class for step 5 of the kreb cycle (a-ketoglutarate to succincyl CoA)
|
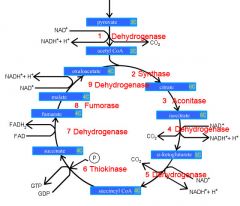
Step 5 of the kreb cycle utilizes Dehydrogenase
|
|
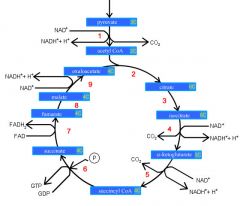
Identify the enzyme class for step 6 of the kreb cycle (succincyl CoA to succinate)
|
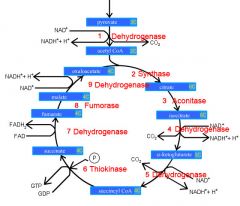
Step 6 of the kreb cycle utilizes Thiokinase
|
|
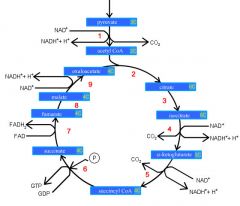
Identify the enzyme class for step 7 of the kreb cycle (succinate to fumerate)
|
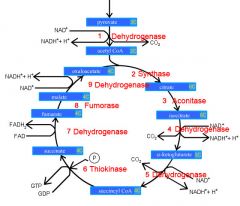
Step 7 of the kreb cycle utilizes Dehydrogenase
|
|
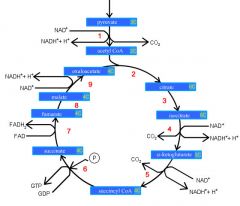
Identify the enzyme class for step 8 of the kreb cycle (fumerate to malate)
|
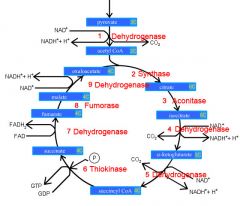
Step 8 of the kreb cycle utilizes Fumorase
|
|
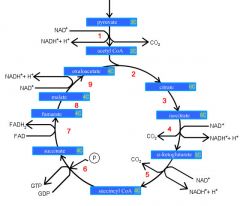
Identify the enzyme class for step 9 of the kreb cycle (malate to oxaloacctate)
|
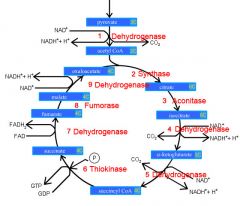
Step 9 of the kreb cycle utilizes Dehydrogenase
|
|
|
What are the inputs and outputs in Glycolysis?
|
Glycolysis
Glucose + 2 ATP > 2 Pyruvate + 4 ATP |
|
|
What are the inputs and outputs in the kreb cycle?
|
Kreb Cycle
2 Pyruvate > 6 CO2 + 2 FADH2 + 8 NADH + 2 ATP |
|
|
What are the inputs and outputs of the electron transport chain?
|
Electron Transport Chain
O2 + NADH + FADH2 > ATP + H2O |
|
|
What are the water soluble vitamins?
|
Water soluble
Dissolves in water (polar) - Bs, C - Not stored in body, excess is peed out |
|
|
What are the fat soluble vitamins?
|
Fat soluble
Dissolves in fat (non-polar) - A, D, E, K - Excess stored in body fat |
|
|
What is meant by aerobic metabolism?
|
Aerobic - with O2
|
|
|
What is meant by anaerobic metabolism? How does this relate to vitamins?
|
Anerobic - without O2 - Glycolysis -> lactic acid -> only 2 ATP per cycle
Vitamin B1 required for Pyruvate dehydrogenase to start Kreb Cycle, without, cannot perform aerobic metabolism |
|
|
How does the kreb cycle relate to fat?
|
If burning fat, can enter kreb cycle directly, bypass glycolysis and skip necessity of B1 - most fat ends up in kreb cycle, but some fat enters liver, which makes it into ketones (bad, waste product)
|
|
|
What is meant by the body being in an absorptive state?
|
Absorptive State - Absorbing nutrients (when eating)
- burn for ATP - store them for later = ____-"genesis"; lipogenesis (store fat), glycogenesis (store glycogen), protein genesis (store protein) - build stuff |
|
|
What is meant by the body being in a post-absorptive state?
|
Post Absorptive State - Hungry (after eating, running out of food)
- take out of storage = ____-"lysis"; lipolysis (break down fat), glycogenolysis (break down glycogen; different from glycolysis), protein lysis |
|
|
What special function does the cecum serve in digestion?
|
Cecum - start of large intestine - bacterial housing - digest non-digestable food - give gas & vitamins
|

