![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) |
GDP is the value of all goods/services produced in an economy in a one-year period. |
|
|
The expenditure approach |
Adds up the value of all the expenditure in the economy. This includes consumption, government spending, investment by firms and net exports. |
|
|
The income approach |
Adds up the rewards for the factors of production used. This includes wages, rent, interest from capital and profit. |
|
|
Nominal GDP |
The actual value of all goods/services produced in an economy in a one-year period. There has been no adjustment for inflation. |
|
|
Real GDP |
The value of all goods/services produced in an economy in a one-year period - and adjusted for inflation |
|
|
GDP per capita |
GDP / the population, it shows the mean wealth of each citizen in a country. This is useful to compare standards of living. |
|
|
Gross National Income (GNI) |
Measures the income earned by citizens operating outside of the country as well as the GDP |
|
|
Gross National Product (GNP) |
GDP and income from abroad sent by non-residents |
|
|
Purchasing Power Parities (PPP) |
A conversion factor that can be applied to GDP,GNI and GNP. It calculates the relative purchasing power of different currencies. |
|
|
Limitations of GDP |
Quality of goods/services, does not measure inequality, does not measure unpaid/voluntary work, does not measure environmental factors affecting standard of living. |
|
|
Inflation |
The sustained increase in the average price level of goods/services in an economy |
|
|
Deflation |
Occurs when there is a fall in the average price level of goods/services in an economy |
|
|
Disinflation |
Occurs when the average price level is still rising, but at a lower rate than before |
|
|
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) |
A 'household basket' of 700 goods/services that an average family would purchase is compiled on an annual basis.Each month, prices for these goods/services are gathered from 150 locations across the UK and is used to measure inflation. |
|
|
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) equation |
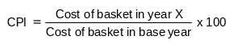
|
|
|
Limitations of CPI |
Doesn't measure product quality changes, ignores regional differences, errors in data collection |
|
|
The Retail Prices Index (RPI) |
The retail price index (RPI) is calculated in exactly the same way as the CPI. Certain goods/services that are excluded from the CPI are included with the RPI such council tax, mortgages etc. |
|
|
Demand Pull Inflation |
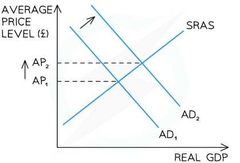
Caused by excess demand in the economy. |
|
|
Cost Push Inflation |
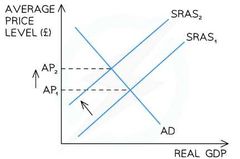
Caused by increases in the costs of production in an economy |
|
|
Impacts of Inflation |
Uncertainty due to rapid price changes, decrease in purchasing power, decrease in the real value of savings, fall in real income, higher wages. |
|
|
Unemployment |
Someone is considered to be unemployed if they are not working but actively seeking work. |
|
|
Underemployed |
Someone is underemployed when they want to work more hours than they currently work , or they are working in a job that requires lower skills than they have |
|
|
Cyclical unemployment |
Unemployment caused by a fall in AD in an economy which causes firms to lay off workers. |
|
|
Structural unemployment |
Unemployment cause by a mismatch between jobs and skills as the structure of an economy changes. |
|
|
Frictional unemployment |
Occurs when workers are betwen jobs |
|
|
Real wage unemployment |
Occurs when wages are inflexible at a point higher than the free-market equilibrium wage |
|
|
Balance of Payments |
A record of all the financial transactions that occur between a country and the rest of the world |
|
|
The current account |
All transactions related to goods/services along with payments related to the transfer of income |
|
|
The finacial and capital account |
All transactions related to savings, investment and currency stabilisation (intervention from government to influence currency price) |
|
|
A current account defecit |
Occurs when the value of the outflows is greater than the value of the inflows Usually occurs when the imports is higher value than exports. |
|
|
A current account surplus |
Occurs when the value of the inflows is greater than the value of the outflows Usually occurs when imports is lower value than exports. |

