![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
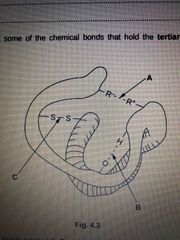
These are chemical bonds that hold the tertiary structure of a protein together. Name A B & C |
A - ionic B - hydrogen C - disulfide bridge |
|
|
Put an X next to each incorrect statement 1. The DNA molecule unwinds 2. Hydrogen bonds between the base pairs break 3. Free RNA nucleotides join your vases on exposed DNA strand 4. Both polypeptide strands act as a template 5. Hydrogen bonds form between complementary bases 6. 3 hydrogen bonds form between A&T 7. DNA polymerase links the new nucleotides 8. Covalent bonds form between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the pentose sugar of the next nucleotide |
3,4 and 6 are incorrect |
|
|
Complete the passage: Variation can be described as the differences in characteristics between ........................................................ . The type of variation that is caused by differences in DNA is known as ........................................................ variation. Variation can also be caused by the ........................................................ . Variation between members of the same species is known as ........................................................ variation. Evolution depends on variation and ........................................................ of the best adapted individuals. |
Variation can be described as the differences in characteristics between individuals . The type of variation that is caused by differences in DNA is known as genetic variation. Variation can also be caused by the environment. Variation between members of the same species is known as intraspecific variation. Evolution depends on variation and the survival of the best adapted individuals. |
|
|
State the number of DNA nucleotide bases that code for a single amino acid |
3 |
|
|
There is a maximum of 64 different base combinations in DNA that could each code for an amino acid, how is this number calculated? |
4x4x4 |
|
|
20 different amino acids are commonly used for protein synthesis, this would in theory only need 20 different base combinations. Explain the uses of the remaining 44 (2) |
- several triplets code for one amino acid - some are used as stop/start |
|
|
Which nucleotide bases are common to both DNA and RNA? |
- adenine - cytosine -guanine |
|
|
Describe how a nucleotide bases sequence in a gene is used to synthesis a polypeptide (7) |
TRANSCRIPTION -DNA/gene copied into mRNA -free nucleotides line up by complementary base-pairings to one template DNA strand, catalysed by RNA polymerase TRANSLATION - mRNA moves out of nucleus to ribosomes -tRNA binds to mRNA -anticodon bind to codons -specific amino acid attached to tRNA -formation of peptide bond between amino acids |
|
|
How many hydrogen bonds between A&T and C&G |
2 between A&T 3 between C&G |
|
|
A gene is a section of DNA that codes for the production of a ... |
Polypeptide |
|
|
The molecule that copies a gene and carries the information to a ........ is called RNA |
Ribosome |
|
|
State two ways in which a diagram of an RNA molecule would appear different from a DNA molecule |
- would be single stranded - would have Uracil instead of Thymine |
|
|
Why is DNA replication considered to be semi-conservative? (2) |
-one strand from original DNA and one strand newly formed - original strand acts as template for new strand |
|
|
Why complementary base-pairing is important in DNA replication (2) |
- so DNA can be replicated without error - reduces occurrence of mutations - allows reformation of hydrogen bonds |
|
|
Suggest 3 precautions that Meselson and Stahl would have taken in order to ensure that the centrifugation part of their investigation produced valid results |
- same concentration of sugar solution in each tube - same Volume of solution in each tube - spin all tubes for same amount of time - soon all tubes at same speed |
|
|
Glucose is a hexose sugar and is a monomer in many carbohydrates. Name the precise group of carbohydrate molecules of which glucose is an example |
Monosaccharide |
|
|
Draw a B glucose molecule |
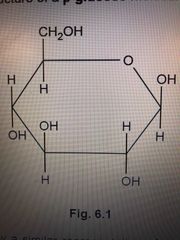
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is a structural difference between a & B glucose |
Inversion of OH and H on 1st carbon atom |
|
|
State and explain two ways In which a glucose molecule is well suited to its function in living organisms |
- soluble so can be easily transported around organism - small so can diffuse across membranes - quickly/easily broken down to release energy - molecules can join to produce polysaccharide glycogen using a condensation reaction |
|
|
Structure of cellulose |
- insoluble - B glucose - only 1-4 bonds - straight chain - contains C, H & O - long chains x |
|
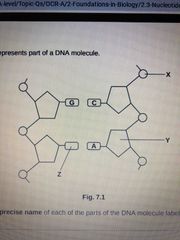
State the precise name of X Y & Z |
X - phosphate Y - deoxyribose sugar X - thymine |
|
|
Describe how the DNA molecule replicates |
- semi-conservative replication - double helix unwinds - hydrogen bonds between bases break - each strand acts as template - free nucleotides align with exposes bases - complementary base pairings - hydrogen bonds reform - sugar-phosphate backbone forms - DNA polymerase joins backbone/strands - each new molecule has 1 old and 1 new strand |
|
|
Suggest how non-competitive inhibitors that stop formation of complex during RNA production may lead to the death of an organism (2) |
- inhibits production of mRNA - prevents protein synthesis |
|
|
State the meaning of the term primary structure |
- sequence of amino acids |
|
|
These are chemical bonds that hold the tertiary structure of a protein together. Name A B & C |
A - ionic B - hydrogen C - disulfide bridge |
|
|
When proteins are heated to a high temperature, their tertiary structure is disrupted. Explain how this occurs (3) |
- increased kinetic energy - protein molecule vibrates - bonds break - change in 3D shape or protein - denatures |
|
|
Suggest why information gained from studying model organisms such as fruit flys and mice can be applied to humans (2) |
- similar cells/genes - similar development - shared ancestry |
|
|
Suggest two characteristics that researchers should look for when choosing an organism for research into how genes control development (2) |
- small - short life cycle - easy to keep/breed - cheap to buy/keep - readily available |
|
|
Describe how the information coded on genes is used to synthesise polypeptides and how these polypeptides control the physical development of an organism (8) |
Synthesis - DNA copied into mRNA - transcription, one strand copied - complementary base pairings - codon 3 bases, base sequence determines amino acid sequence - translation - ribosomes Roles - structural proteins/enzymes - hormones - receptor proteins - apoptosis - homeobox genes |
|
|
Which apply to DNA, RNA, or both 1. Contains thymine 2. Contains ribose 3. Consists of two chains connected to eachother with hydrogen bonds 4. Has a sugar-phosphate backbone 5. Has 4 different nitrogenous bases 6. Contains a pentose sugar 7. Is found in the nucleus and cytoplasm |
1. Contains thymine - DNA 2. Contains ribose - RNA 3. Consists of two chains connected to eachother with hydrogen bonds - DNA 4. Has a sugar-phosphate backbone - DNA & RNA 5. Has 4 different nitrogenous bases - DNA & RNA 6. Contains a pentose sugar - DNA & RNA 7. Is found in the nucleus and cytoplasm - RNA |
|
|
Suggest how information obtained by DNA analysis can be useful to taxonomists (2) |
- info used to decide which group an organism fits into - can compare DNA or proportion of bases - more similar the DNA, closer the relationship |
|
|
State two types of evidence that are used by taxonomists when classifying organisms |
- fossil records - anatomy - embryology - biochemical evidence |
|
|
Suggest why some people may be concerned about plans to introduce species from other areas to their area |
- may bring disease - may not be adapted to local conditions - may outcompete native population |
|
|
State one visual way to distinguish between DNA and mRNA |
- mRNA is shorter - mRNA is single stranded, DNA double stranded - mRNA not helical |
|
|
Give further differences in structure between DNA and RNA |
- RNA constrains ribose, DNA deoxyribose - RNA contains uracil, DNA thymine - more than one form of RNA |
|
|
Suggest why DNA is not able to leave the nucleus |
- too big to fit through pore in nuclear envelope |
|
|
Explain why the mRNA molecule is shorter than a DNA molecule |
- only copies one gene not the whole strand - DNA compromises of many genes |
|
|
Explain how amanitin stops the formation of an enzyme-substrate complex during RNA production (2) |
- non-competitive inhibitor - fits into allosteric site - causes conformational change in active site - substrate no longer complementary to active site |
|
|
State the components of a DNA molecule |
- deoxyribose sugar - phosphate group - nitrogenous base |
|
|
Describe how the structure of RNA differs from that DNA |
- has ribose sugar - uracil instead of thymine - single stranded - 3 forms |
|
|
Describe how a DNA molecule is replicated (7) |
- unwinds by gyrase - unzips by helicase - H bonds break - both strands act as a template - free nucleotides join - complementary base pairings - hydrogen bonds reform - sugar-phosphate back bone forms - using phosphodiester bonds - semi conservative replication |
|
|
State what a gene coded for |
- polypeptide/protein |
|
|
Suggest how changing the sequence of DNA nucleotides could affect the final product the DNA codes for (2) |
- different sequence of amino acids - makes protein fold differently/different tertiary structure - protein no longer functions correctly |
|
|
State the role of a gene |
- Codes for one or more polypeptide |
|
|
Explain how the structure of DNA allows replication (5) |
- double stranded - both strands act as a template - hydrogen bonds easily break/form between bases - complementary base pairings - purine binds to pyrimidines - 3 H bonds between C & G and 2 H bonds between A & T |
|
|
State the role of mRNA |
- transfers genetic information - out of nucleus - transfers it to ribosome - for protein synthesis |

