![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
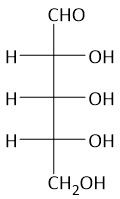
|
Ribose |
¹⁵
|
|
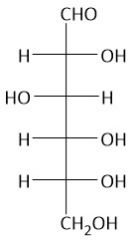
|
Glucose |
|
|
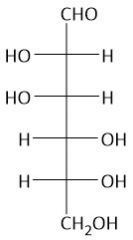
|
Mannose |
The two OH groups form the head of a man |
|
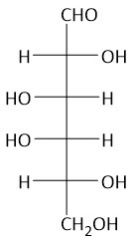
|
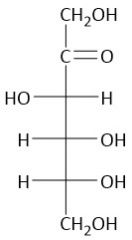
Galactose |
The symmetrical bond is the bending the galaxy |
|
|
Fructose |
|
|
|
|
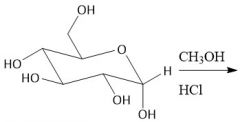
Glycoside Formation (27.7A): Forms both α-glycoside, β-glycoside |
|
|
|
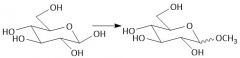
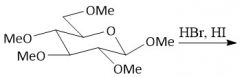
Acidic Ether Hydrolysis (27.8): Will only hydrolyze at the anomeric carbon Use EXCESS water |
|
|
|
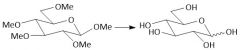
Complete Acidic Ether Hydrolysis (notes): |
|
|
|
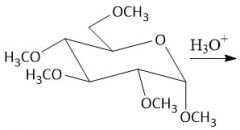
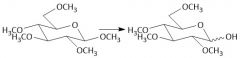
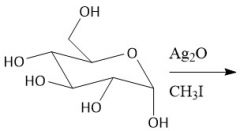
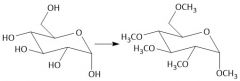
Etherification (27.8): All OH groups are converted to ethers by treatment with base Mechanism in notes Does not form anomers |
|
|
|
Acetalation w/ Dione (27.8): Does not form anomers |
|
|
|
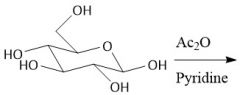
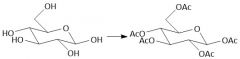
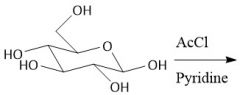
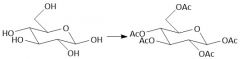
Acytlation w/ Acid Chlorides (27.8): Does not form anomers |
|
|
|
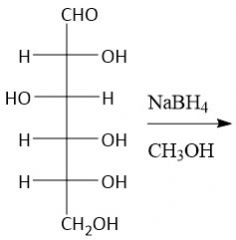
NaBH₄ Reduction (27.9A) |
|
|
|
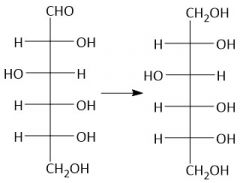
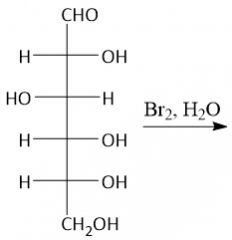
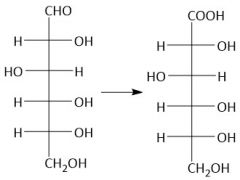
Aldonic Acid Formation (27.9B): DON'T use Tollens Reagent, Benedict's Reagent or Fehling's reagent |
|
|
|
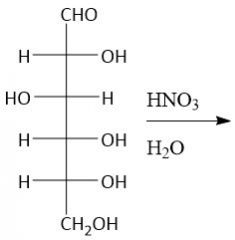
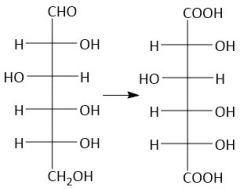
Aldaric Acid Formation (27.9B): Oxidizes 1° alcohols and aldehydes but not 2° |
|
|
|
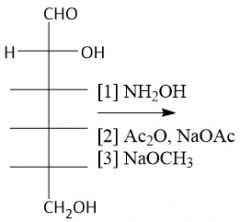
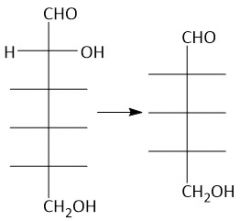
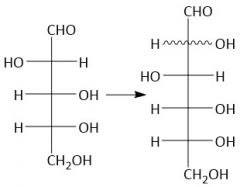
Wohl Degradation (27.10): (Shortens Aldose chain by one carbon) [1] Oxime (aq. hydroxylamine) [2] Cyanohydrin (acteyl group) [3] Aldehyde (sodium methoxide) |
|
|
|
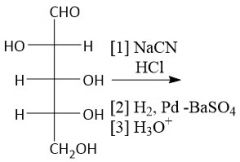
Kiliani-Fischer Synthesis (27.10): (Lengthens Aldose chain by one) [1] Cyanohydrin [2] Imine [3] Aldehyde |
|
|
|
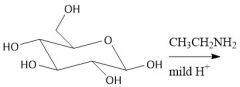
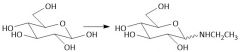
N-Glycosidos Formation (27.14B): Top: α-N-glycoside Bottom: β-N-glycoside |
|
|
|
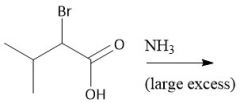
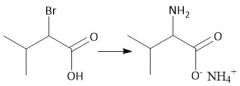
α-Halo Amidification (28.2A) |
|
|
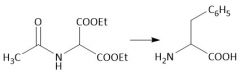
|
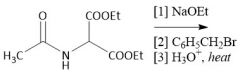
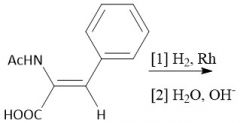
Diethyl Malonate Derivative Alkylation (28.2B): Uses diethyl acetamidemalonate |
|
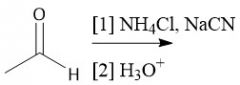
|
|
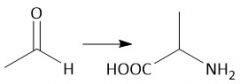
Strecker Synthesis (28.2C): [1] α-amino nitro [2] Cyano to carboxyl hydrolysis |
|
|
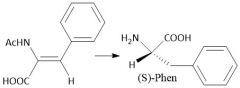
|
Enantioselective Amino Acid Synthesis (28.4): BINAP and rhodium moieties |
|
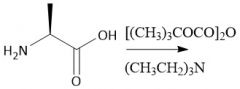
|
|
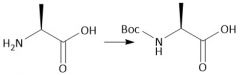
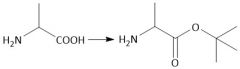
Boc Protecting group (28.7): [Boc/OtBu] Deprotect with CF₃CO₂H, HCl, HBr Carbamates |
|
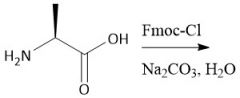
|
|
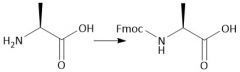
Fmoc Protecting group (28.7): [Fmoc/OMe] Deprotect with piperidine |
|
|
|
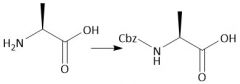
Cbz Protecting Group (notes): Cbz/OBn |
|
|
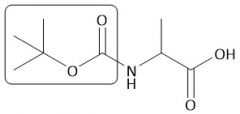
Boc Group |
|
[Boc/OtBu]: P: (t-BuOCO)₂O, Et₃N D: H+, H₂O |
|
|
OtBu Group |
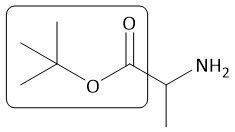
|
[Boc/OtBu]: P: Isobutene, H+ D: HCl |
|
|
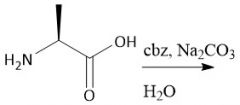
Cbz Group |
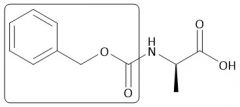
|
[Cbz/OBzn]: P: BnOCOCl, Na₂CO₃, H₂O D: HBr or H₂/Pd |
|
|
OBzn Group |
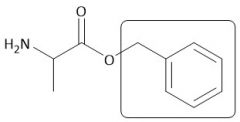
|
[Cbz/OBzn]: P: PhCH₂OH, H+ D: H₂, Pd/C or OH⁻, H₂O |
|
|
Fmoc Group |
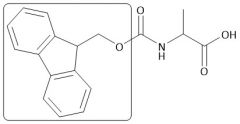
|
[Fmoc/OMe]: P: Fmoc-Cl, Na₂CO₃, H₂O D: Piperidine |
|
|
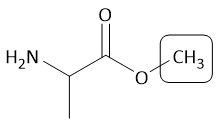
OMe Group |
|
[Fmoc/OMe]: P: CH₃OH, H⁺ D: OH⁻, H2O |
|
|
|
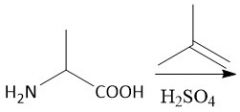
OtBu Protecting Group (notes): |
|
|
|
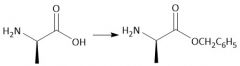
Carboxyl Protecting Group (28.7): Deprotect: [Cbz/OBn] CH₃COOH (hydrolysis) H₂, Pd/C (hydrogenolysis) |
|
|
|
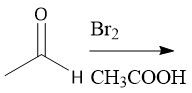
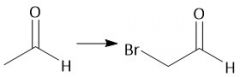
Alpha-halogenation (28) |
|
|
|
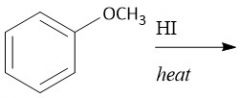
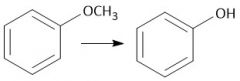
Anisole to Phenol (28) |
|
|
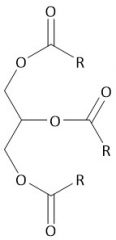
Triacylglycerol |
|
Energy storage |
|
|
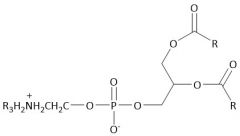
Phosphoacylglycerol |
|
Phospholipid |
|
|
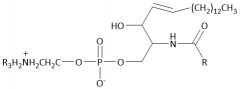
Sphingomyelin |
|
Phospholipid |
|
|
Non-hydrolyzables |
Eicosanoids, Fat-soluble vitamins, Terpenes, Steroids |
|
|
|
Wax |
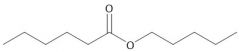
|
Repellant |
|
|
|
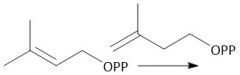
Biological Synthesis of Geranyl Diphosphate (29.7) |
|
|

|
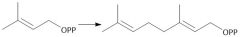
Biological Synthesis of Farnesyl Diphosphate (29.7) |
|
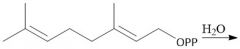
|
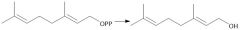
|
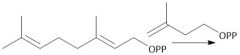
Diphosphate Hydrolysis (29.7) |
|
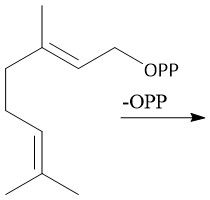
|
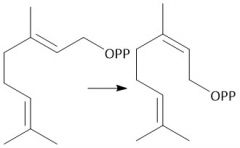
|
Isomerization (29.7): [1] Geranyl diphosphate [2] Linalyl Diphosphate [3] Neryl Diphosphate [4] Cyclization |
|
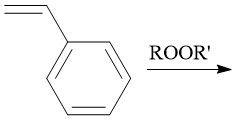
|
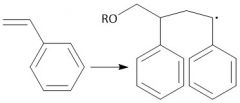
|
Radical Polymerization (30.1): [1] Initiation [2] Propagation [3] Termination Disproportionation |
|
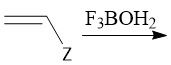
|
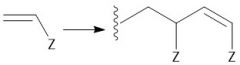
|
Cationic Polymerization (30.2C): [1] Initiation: Alkene abstracts proton from LBC [2] Propagation [3] Termination: Loss of a proton |
|
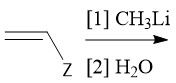
|
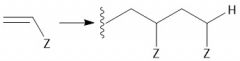
|
Anionic Polymerization (30.2C): Terminates with acid-base reaction Requires a stabilizing EWG Living polymerization (polymerization will begin again if more monomer is added) |
|
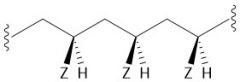
|
Isotactic Polymer |
Chiral |
|
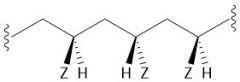
|
Syndiotactic Polymer |
Meso Compound (achiral) |
|
|
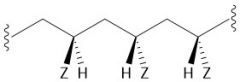
Atactic Polymer |
Random Z pattern Lower melting point |
|
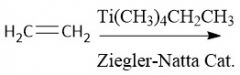
|
|
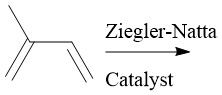
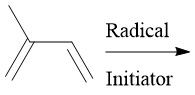
Ziegler-Natta Polymerization (30.4): Coordination polymerization Forms HDPE (unbranched) β-Elimination |
|
|
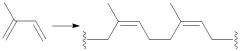
|
Natural Rubber Synthesis (30.5): Z-Configuration |
|
|
|
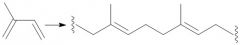
Gutta-Percha Synthesis (30.5): E-Configuration |
|
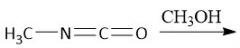
|
|
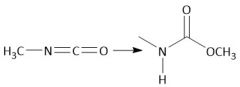
Urethane (carbamate) Synthesis (30.6C): From Isocyanate |
|
|
|
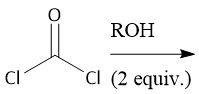
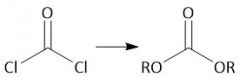
Polycarbonate Synthesis (30.6D): Phosgene + ROH = Lexan |
|
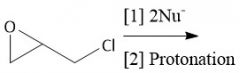
|
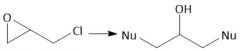
|
Epoxy Resin Synthesis (30.6E): Two consecutive ring openings Add NH₂(CH₂)2NH(CH₂)2NH₂ |
|
|
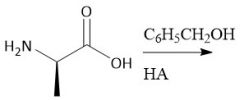
Amino Acid Resolution |
[1] (CH3CO)2O [2] Add chiral amine [3] Seperate [4] Hydrolyze amide |
(28.3A) |
|
|
Cellulose |
1→4,β-glycosidic linkage Linear |
|
|
|
Amylose |
1→4, α-glycosidic linkage Helical |
|

