![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mass spectrometer |
Powerful instrumental technique used to do find the relative mass of elements and compounds |
|
|
Ionisation |
Electrospray ionisation-sample is dissolved in a solvent and pushed through a nozzle at high pressure.HIgh voltage is applied causing each particle to gain H+ ions. Solvent is removed =gas Electron impact ionisation -sample is vaporised , electron is used to fire high energy electrons. This knocks one electron off=+1ions |
|
|
Acceleration |
Positive ions are accelerated by electric field Electric field gives the same kinetic energy to all ions Lighter ions = greater acceleration |
|
|
Ion drift |
No electric field Same speed Lighter ions drifting at higher speeds |
|
|
Detection |
Lighter ions reach detector first Detecter detects the current created by th ions |
|
|
Electron configurations |
Copper and chromium are special-donate one 4s electron to the 3D sub shell because they are fully stable Cu:1s22s22p63s23p64s13d10 Cr:1s22s22p63s23p63d54s1 |
|
|
Ionisation |
The energy needs to remove the first electron is called the first ionisation energy Ex O(g)➡️O(g)+e- |
|
|
Ionisation |
The energy needs to remove the first electron is called the first ionisation energy Ex O(g)➡️O(g)+e- |
|
|
Factors affecting ionisation energy |
Nuclear charge Distance from the nucleus Shielding |
|
|
Ionisation trends down group 2 |
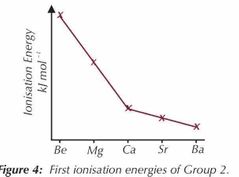
Ionisation energy decreases. Easier to remove outer electrons .Provides evidence that electron shells exist. 1Going down group 2 each each element has an extra shell to the one above ,the inner electrons will shield the outer from the attraction of the nucleus 2outer electrons are further away from the nucleus so the nucleus attraction is reduced |
|
|
Ionisation energy across period 3 |

Ionisation energy increase Number of protons increased extra electrons are at roughly the same energy level-extra shielding or distance to lessen the attraction |

