![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe how drugs are absorbed via filtration.
|
Drug passes cell membrane via aqueous channels
|
|
|
What factors determine how quickly drugs are distributed to tissue?
|
Blood flow (very high in brain)
Capillary permeability (higher in liver than in brain because of BBB) |
|
|
What factors determine the tissue/blood ratios at equilibrium?
|
-Dissolution of lipid-soluble drugs in adipose tissue
-Binding of drugs to intracellular sites -Plasma protein binding |
|
|
What is volume of distribution?
Equation. |
Space drug will end up in during equilibrium
Vd = Dose injected/C0 C0 = concentration measured in plasma |
|
|
Plasma half-life is directly proportional to ____ and indirectly proportional to _____.
|
Plasma half-life is directly proportional to Vd (volume of distribution)
Indirectly proportional to total clearance |
|
|
Vd: 0.05-0.1 L/kg body weight
Compartment? Drug? |
Limited to plasma
Heparin |
|
|
Vd: 0.1-0.2 L/kg body weight
Compartment? |
Limited to Plasma
Not penetrating cell membrane |
|
|
Vd: 0.2-0.4 L/kg body weight
Compartment? |
Distributed in ECF
Not quite in interstitial space |
|
|
Vd: 1-2 L/kg body weight
Compartment? |
In total body water
Passes BBB, CNS fx |
|
|
Vd: 2-5 L/kg body weight
Compartment? |
In total body water;
Pass BBB! Central fx. |
|
|
What is bioavailability?
Equation? |
Fraction of dose that gets into systemic circulation (if drug delivered IV, it's 100% available because it's in plasma, but not the case for other routes for administration).
bioavailability= AUCpo/AUCiv x 100 (AUC = area under curve of Cp vs Time) |
|
|
Why would a drug have a low oral availability?
|
Drugs can be almost completely cleared by hepatic metabolism in one pass and never make it to plasma.
|
|
|
What is biotransformation? Effect on pharmacological activity?
|
Elimination of drug by chemical modification of molecule (spontaneous, enzyme catalyzed); product may have greater, lesser, or different pharmacological activity from parent compound
Mostly due to enzyme activity (highest in liver) Variations among individuals due to genetics, age, disease, environmental factors |
|
|
Biotransformation:
Phase I vs Phase II |
Phase I: first step with formation of product susceptible to phase II reactions
Often catalyzed by cyt p450 enzymes Reactions include: Oxidations, Reductions, Hydrolysis Phase II Reactions: Coupling of drug or its oxidized metabolite to endogenous coupling agent Requires energy to form activated conjugating agent Product is usually more water soluble and more readily excreted into urine/bile (bile secreted via stool) Reactions: any sort of transferase! |
|
|
Biotransformation:
Enzyme Inducers vs Enzyme Inhibitors 1 Example of Each |
Inducers increase metabolism of drugs (need higher doses): phenobarbital, ethanol
Inhibitors slow metabolism of drugs (needs slower doses): cimetidine |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
What is the formula for determining half-life?
|
t1/2 = (.693/Cl total)Vd
Cl total = sum of clearances by all routes of elimination |
|
|
What is the relationship between total clearance and plasma half-life?
|
When total clearance decreases, plasma half-life INCREASES.
|
|
|
What three factors determine renal clearance?
|
Glomerular filtration
Proximal tubular secretion Distal tubule reabsorption |
|
|
What transporters are required for secretion of acid drugs? Basic drugs?
What drug type doesn't require a transporter? |
Acid drugs require anion transporter
Basic drugs require cation transporter Lipid-soluble, unionized drugs are passively reabsorbed (not secreted; longer half-life) |
|
|
An acid drug in _____ urine has increased excretion.
|
Acid drug in alkaline urine has increased excretion and vice versa
|
|
|
Clearance of inulin is an indicator of _____.
Normal clearance for a 70 kg man? |
GFR; no secretion and no reabsorption
C inulin = 120 ml/min |
|
|
Clearance of PAH is an indicator of ______.
Normal clearance for a 70 kg man? |
RPF (and glomerular filtration, no reabsorption)
C PAH = 650 ml/min |
|
|
Under what conditions would penicillin and probenicid be co-administered?
|
If difficult to maintain effective plasma levels of penicillin, administer probenicid.
Probenicid, like PCN, is an acid drug and will compete for organic anion transporter in proximal tubules; thus, less PCN will be secreted and it will be present in the plasma for longer. |
|
|
What is a steady-state concentration?
Formula? How would you determine the loading dose? |
Steady state is a drug infusion designed such that input = output (maintains constant plasma level)
Css = K0/Cl total Where K0 = infusion rate constant Loading dose: D = Css x Vd = Css Vd/f Where f = fraction of dose absorbed |
|
|
Formula for steady-state concentration average?
|
Css average = f(D/t)/Cl total
Where f = fraction of dose absorbed D/t = dosing rate Note f(D/t) = input rate Output = Vd x Css |
|
|
Drug accumulation is dependent on _______ and ______.
|
Drug accumulation is dependent on dosing interval and elimination half-life.
|
|
|
Formula for drug accumulation.
|
R = C max ss/Co
Where R = accumulation C max ss = maximal plasma concentration of drug at steady state C0 = plasma concentration after first dose |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
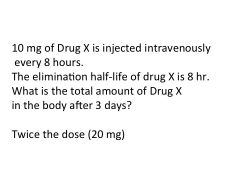
|

