![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
231 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Automated observation |
Is obtained from an automated surface weather observing system that prepares the meteorological reports for transmission without a certified weather observer |
|
|
|
Augmented observation |
Is an automated surface weather observing system that prepares the meteorological reports for transmission with certified weather observers signed on to the system to add information to the observation |
|
|
|
Manual observation |
Is taken by a certified weather observer who is responsible for meteorological observation |
|
|
|
Aviation routine weather report(metar) |
Is the primary onservation code used in the United states (and worldwide) for reporting surface meteorological data. |
|
|
|
once per hour |
How often is a METAR transmitted |
|
|
|
Body and Remarks |
A metar has two major sections: what are they? |
|
|
|
Aviation selected special weather report(SPECI) NOTE: see appendix A at end of lesson |
Is an unscheduled report taken when certain criteria have been observed. |
|
|
|
Evaluating the event |
SPECI criteria are only applicable to stations which have the capability of_____? |
Visually evaluated elements are not applicable to non staffed automated stations |
|
|
METAR |
A SPECI contains all of the data elements found in a _____? |
|
|
|
Special report |
If the report is a SPECI, announce it as ______? |
|
|
|
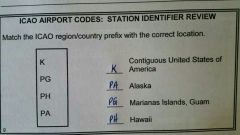
Station identifier |
The_____ is included in all reports to identify the station to which the coded report applies. |
|
|
|
ICAO |
The _____ airport codes have a regional structure, are not duplicated, and are comprehensive |
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Date and time(utc) |
The _____ of report is the actual time of the report or when the criteria for a SPECI was met or noted |
|
|
|
Day of the month |
The first two digits of report coding format is: |
|
|
|
The hour |
The 3rd and 4th digits of report coding format is: |
|
|
|
The minute |
The final two digits of report coding format is: |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Last two |
If a special report os the most recent observation available, follow the location with the words"special report, ((first two/last two) digits of the time) observation" |
|
|

|
Examples of date and time phraseology |
|
|
|
AUTO |
The report modifier,_____, identifies the METAR/SPECI as a fully automated report with no human intervention or oversight |
|
|
|
COR |
in the event of a corrected METAR or SPECI, the report modifer,_____,is substituted in place of AUTO |
|
|
|
Automated;corrected |
Announce AUTO as: Announce COR as: |
|
|

|
Examples of report elements phraseology |
|
|
|
1: zero five five three observation 2: oklahoma city automated (one five five four observation) 3:oklahoma city corrected (two three five five observation) 4: special report zero one onservation 5:oklahoma city, automated,special report, one niner observation 6:oklahoma city, corrected, special report three eight observation |

|
|
|
|
Wind |
The horizontal motion of the air past a given point |
|
|
|
1:the wind direction relative to true north coded in tens of degrees using three digits 2:VRB 3: the wind speed in knots 4: G followed by 2 or 3 digits which indicate the max wind speed gust |
The WIND Group coding format is: 1:The first 3 digits indicate? 2: _____is coded if the wind direction is variable and the speed os 6 kts or less 3:the next two(or 3) digits indicate? 4: if the wind is gusty what is coded? |
|
|

|
Decoding wind group |
|
|
|
V
Example : 180V250 |
If the wind direction is variable and the speed is greater than 6 knots, a variable wind group consisting of the extremes of the wind directions seperated by a ___ will follow the wind group |
|
|
|
1: wind calm 2:wind variable at five 3:wind zero one zero at eight 4: |

Use correct phraseology |
|
|
|
Prevailing visibility |
Visibility considered representative of conditions at the station; the greatest distance that can be seen throughout at least half the horizon circle(180degrees), not necessarily continuous. |
|
|
|
M1/4SM or "visibility less than one quarter" |
What is the lowest visibility that can be reported by an automated station? |
|
|
|
10SM or "visibility one zero" |
What is the highest visibility an automated station can report? |
|
|

|
Examples of visibility phraseology |
|
|
|
Runway visual Range(RVR) |
Is an instrumentally derived value, based on standard calibrations, that represents the horizontal distance a pilot may see down the runway from the approach end. |
|
|
|
Visibility is 1SM or less and/ or RVR for designated instrument runway is 6,000 feet or less |
RVR is reported when: |
|
|
|
M; LESS THAN |
If the RVR is less than its lowest reportable value, the group is preceded by an ____ and spoken as _____ |
|
|
|
P; MORE THAN |
If the RVR is greater than its highest reportable value, the group is preceded by a ____ and spoken as _____ |
|
|
|
V |
When RVR is variable, both the lowest and highest values are coded with a _____ between them. |
|
|
|
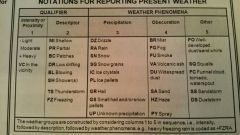
Present weather group |
The _____ specifies any weather phenomena occuring at, or in the vicinity or, the station |
|
|
|
Precipitation |
Is any of the forms of water particles, whether liquid or solid, that fall from the atmosphere and reach the ground |
|
|
|
Obscuration |
Is any phenomenon in the atmosphere, other than precipitation, that reduces horizontal visibility |
|
|
|
VC "vicinity" |
The proximity qualifier "___" indicates weather phenomena between 5 and 10 statute miles from the points of observation |
|
|
|
SHALL |
When more than one type of present weather are reported at the same time, present weather _____ be reported in the following order: •Tornado •thunderstorm •Present weather in order of dominance |
|
|
|
Notations for reporting present weather |
|
|
|
Showers |
Descriptors are spoken before the weather phenomenon except for _____ which is spoken after the precipitation |
|
|
|
Do not |
When multiple precipitation types are encoded, DO/DO NOT speak the word "and" between them |
|
|
|
Sky condition |
Is the state of the sky in terms of such parameters as sky cover, layers and associated heights, ceiling, and cloud types |
|
|
|
Sky cover |
Is the amount of celestial dome (sky) which is hidden by clouds and/ or obscurations |
|
|
|
Layer |
Is an array of clouds and/or obscurations whose bases are at approximately the same level |
|
|
|
Summation layer amount |
Is a categorization of the amount of sky cover at and below each reported layer |
|
|
|
Ceiling |
Is the lowest layer aloft reported as broken or overcast; or the vertical visibility into an indefinite ceiling |
|
|
|
Vertical visibility |
Is vertical distance into a surface-based obscuration that an observer would be able to see |
|
|
|
Indefinite ceiling |
Is the ceiling classification applied when the reported ceiling value represents the vertical visibility upward into a surface based obscuration |
|
|
|
SKC |
Is the abbreviation used by manual stations to indicate no layers are present |
|
|
|
CLR |
Is the abbreviation used by automated stations to indicate no layers are detected at or below 12,000 feet above the surface |
|
|
|
Temperature |
Is a measure of the hotness or coldness of the air as measured by a thermometer |
|
|
|
Dew point |
Is the temperature to which the air must be cooled at constant pressure and constant water-vapor content in order for saturation to occur |
|
|
|
Altimeter setting |
Is the pressure value to which an aircraft altimeter scale is set so that it will indicate the altitude above mean sea level of an aircraft on the ground at the location for which the value was determined |
|
|
|
Remarks |
Are plain language or coded data added to the body of the METAR/SPECI to report significant information not provided for in the body of the report |
|
|
|
RMK |
Remarks are seperatedfrom the body of the report by the contraction ____ |
|
|
|
DSNT |
Indicates weather phenomena beyond 10 SM of the points of observation |
|
|
|
Volcanic eruption |
Is an explosion caused by the intense heating of subterranean rock which expels lava,steam,ashes,etc through vents in the earths crust |
|
|
|
Funnel cloud |
Is a violent, rotating column of air which does not touch the surface, usually appended to a cumulonimbus cloud |
|
|
|
Tornado |
Is a violent, rotating column of air touching the ground |
|
|
|
Waterspout |
Is a violent, rotating column of air that forms over a body of water, and touches the water surface; tornado that touches a body of water |
|
|
|
Peak wind speed |
Is the maximum instantaneous wind speed that exceeded 25 knots since the last METAR |
|
|
|
Wind shift |
Is a change in the wind direction of 45 degrees or more in less than 15 minutes with sustained wind speeds of 10 knots or more throughout the wind shift |
|
|
|
Surface visibility |
Is the prevailing visibility determined from the usual point of observation |
|
|
|
Tower visibility |
Is the prevailing visibility determined from the airport traffic control tower (ATCT) when the surface visibility is determined from another location |
|
|
|
Variable prevailing visibility |
Is a condition when the prevailing visibility is less than 3 statute miles and rapidly increases and decreases by 1/2 mile or more during the period of observation |
|
|
|
Sector visibiltlity |
Is the visibility in a specified direction that represents at least a 45 degree arc of the horizon circle |
|
|
|
Lightning |
Generally any and all forms of cisible electrical discharge produced by a thunderstorm |
|
|
|
A: Occasional,OCNL, less than 1 flash a minute B: Frequent,FRQ, about 1 to 6 flashes a minute C: Continuous, CONS, more than 6 flashes a minute |
What are the frequencies of lightning ? |
|
|
|
Cloud to ground |
Lightning occuring between cloud and ground |
|
|
|
In-cloud |
Lightning which takes place within the cloud |
|
|
|
Cloud-to-cloud |
Streaks of lightning reaching from one cloud to another |
|
|
|
Cloud-to-air |
Streaks of lightning which pass from a cloud to the air, but do not strike the ground |
|
|
|
Virga |
Is visible wisps or strands of precipitation falling from clouds that evaporate before reaching the surface |
|
|
|
It could indicate the beginning of a dry microburst; it can consist of supercooled water droplets and be an icing hazard at altitude |
What 2 things make virga important? |
|
|
|
Variable ceiling |
Is a ceiling of less than 3,000 feet which rapidly increases or decreases in height during the period of onservation |
|
|
|
PRESRR;PRESFR |
At designated stations, when pressure is rising or falling rapidly at the time of observation, the remark____ (rising rapidly) or _____(rapidly falling) is included in the report |
|
|
|
Appendix A-D will help!!!! |
NOTE :USE PAGES 78-89 IN LESSON PLAN 24 |
|
|
|
Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere,exosphere |
The earths atmosphere is divided into 5 layers what are they? |
|
|
|
Troposphere |
The lowest layer of the earths atmosphere is _____? |
|
|
|
Troposphere |
Most air traffic happens in this layer of the earths atmosphere |
|
|
|
Inversion |
An increase in temperature with altitude is abnormal and is defined as what? |
|
|
|
Tropopause |
The tranisition boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere is called ? |
|
|
|
Stratosphere |
In this layer temperature increases with altitude making it a stable layer, generally devoid of significant weather except for thunderstorm tops which extend into it |
|
|
|
Standard atmosphere |
A hypothetical vertical distribution of the atmospheric temperature, pressure, and density, which by international agreement is considered to be representative of the atmosphere for pressure-altimeter calibrations and other purposes |
|
|

|
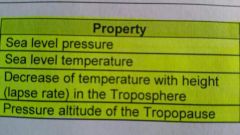
Name units of measure for each property of standard atmosphere |
|
|
|
Jet stream |
Relatively strong winds concentrated within a narrow, horizontal band in the upper troposphere |
|
|
|
Polar jet stream; subtropical jet stream |
Rwo jet streams are commonly identified: |
|
|
|
Polar |
This jet stream is located between 30 degrees and 60 degrees latitude |
|
|
|
Subtropical |
This jet stream is located between 20 and 40 degrees latitude |
|
|
|
Clear air turbulence |
Jet streams often produce this |
|
|
|
Troposphere |
Which layer of the atmosphere contains almost all clouds and precipitation? |
|
|
|
Stratosphere |
Whixh layer of the atmosphere is stable and generally devoid of significant weather? |
|
|
|
29.92 (two niner niner two) |
What is the value of sea level pressure in the standard atmosphere |
|
|
|
Polar and subtropical |
Which two jets streams are commonly identified? |
|
|
|
Water vapor |
Water in the invisible gaseous form |
|
|
|
Evaporation |
The change of liquid water to water vapor |
|
|
|
Sublimation |
The change of ice to water vapor |
|
|
|
Water vapor |
This is the raw material for clouds and precipitation |
|
|
|
Temperature |
A measurenof hotnessnor coldness of the air |
|
|
|
More |
Warm air can hold more/less water vapor than cold air? |
|
|
|
Saturation |
The maximum possible quantity of water vapor that a parcel of air can hold at any given temperature and pressure |
|
|
|
Unsaturated |
Means that a parcel of air can hold more water vapor |
|
|
|
Saturated |
Means an air parcel contains all the water vapor it can hold |
|
|
|
Dew point |
The temperature to which a given parcel of air must be cooled at constant pressure and constant water vapor content in order for saturation to occur |
|
|
|
Relative humidity |
The ratio usually expressed as a percentage of water vapor actually in the air compared to the amount of water vapor the air could hold at a particular temperature and pressure |
|
|
|
Zero; saturated |
When the temperature-dew point spread decreases to____, the air becomes______, and condensation will form dew or fog |
|
|
|
Condensation |
The change of water vapor to liquid water |
|
|
|
Water vapor |
What is the raw material for clouds and precipitation? |
|
|
|
Unsaturated |
A parcel of air that has the capacity to hold more water vapor is? |
|
|
|
Temperature-dew point spread; saturated |
When the _______decreases to zero, the air becomes______, and condensation will form dew, foh, or clouds |
|
|
|
Clouds |
A visible mass of tiny water droplets an/or ice particles in the atmosphere above the earths surface |
|
|
|
Cooled, saturated |
Clouds form when air is ______ to its dew point and becomes______? |
|
|
|
Stratiform |
-Consists of a featureless low layer that can cover sky -often produces widespread IFR weather -little or no turbulence, but can produce icing |
|
|
|
Cirriform |
-high level clouds which form above 20,000ft -usually composed of ice crystals -typically thin and white in appearance -contains no significant icing |
|
|
|
Cumuliform |
-resembles white fluffy cotton balls or heaps -indicates upward vertical motion or thermal uploft of air -tops. An reach over 60,000ft |
|
|
|
Rising |
A parcel of ______air expands and cools as pressure decreases with height |
|
|
|
Sinking |
A parcel of ______air warms as it encounters increasing pressure and is compressed |
|
|
|
Wind |
Air in motion relative to the surface of the earth |
|
|
|
High |
A maximum of atmospheric pressure on a surface weather chart; also kjown as an anti-cyclone |
|
|
|
Diverges;Clockwise |
Air flow around a high______in a ______motion and sinks |
|
|
|
Low |
a minimum of atmospheric pressure on a surface weather chart; also known as a cyclone |
|
|
|
Converges, counterclockwise |
Air flow around a low ______in a _______motion and rises |
|
|
|
Converges, rises |
air flow around a low______ in a counterclockwise motion and _______causing the air to cool and eventually condense into clouds and prexipitation |
|
|
|
Air mass |
A large body of air that has similar horizontal temperature and moisture characteristics |
|
|
|
Air mass source region |
Region where air masses originate and acquire their properties of temperature and moisture. These properties are acquired by prolonged contact(days to weeks) with the underlying surface |
|
|
|
Arctic |
An extremely deep cold air mass which develops mostly in winter over arctic surfaces of ice and snow |
|
|
|
Polar |
A relatively shallow cool to cold air mass which develops over high latitudes |
|
|
|
Tropical |
A warm to hot air mass which develops over low latitudes |
|
|
|
Continental (c) |
A dry air mass which develops over land |
|
|
|
Maritime(m) |
A moist air mass which develops over water |
|
|

|
When classification is applied the five air masses may be applied |
|
|
|
Unstable |
Cold air mass moving over a warm surface produces ______air associated with turbulence, good visibilty,cumuliform clouds and showers |
Snow plow |
|
|
Stable |
A warm air mass moving over a cold surface often produces______air associated with smooth air, poor visibility, stratiform clouds, fog, and drizzle |
Drunk with shovel |
|
|
Front |
A boundary or tansition between two air masses of different density, and thus,(usually) of different temperature |
|
|
|
Cold front |
A front that moves in such a way that colder air replaces warmer air |
|
|
|
Warm front |
A front that moves in a such a way that a warmer air replaces colder air |
|
|
|
Stationary front |
A front which is stationary or nearly so. |
|
|
|
Occluded front |
A composite of two fronts as a cold front overtakes a warm front or stationary front |
|
|
|
Cold fronts |
Have a steep slope and air is forced upward abruptly |
|
|
|
Warm fronts |
Typically have a gentle slope so the air rising along the frontal surface is gradual |
|
|
|
Warm, moist |
a maritime tropical(mT) air mass is _____and _____ |
|
|
|
Cold, warm |
A ______air mass moving over a ______surface often produces unstable air associated with turbulence, good visibility, cumuliform clouds and showers |
|
|
|
Warm front |
Which front moves in such a way that warmer air replaces colder air? |
|
|
|
Cold front |
What type of front has a steep slope which often leads to a narrow band of showers and thunderstorms if the rising air is unstable |
|
|
|
Precipitation |
Any forms of water particles, whether liquid or solid, that fall from the atmosphere and reach the ground |
|
|
|
Water vapor, lift, growth process |
Precipitation formation requires the following: |
|
|
|
Snow (SN) |
Pre ipitation of snow crystals, mostly beanched in the form of six-pointed stars |
|
|
|
Ice pellets |
Precipitation of transparent or translucent pellets of ice, which are round or irregular, rarely conical, and which have a diameter of 0.2 inch(5mm) or less |
|
|
|
Ice pellets |
Occur when there is a shallow layer aloft with above freezing temperatures, with deep layer of below freezing air based at the surface |
|
|
|
Freezing rain (FZRA) |
Rain that freezes on contact with the ground or exposed objects |
|
|
|
Freezing rain |
Occurs when there is a deep layer aloft with above freezing temperatures, with a shallow layer of below freezing air at the surface |
|
|
|
Rain(RA) |
Precipitation, either in the form of drops larger than .02 inches, or smaller drops, which in contrast to drizzle are widely seperated |
|
|
|
Water vapor |
The three necessary ingredients for precipitation formation are _____lift, and a growth pocess |
|
|
|
Freezing rain |
Which precipitation type occurs when there is a deep layer aloft with above freezing temperatures, with a shallow layer of below freezing air at the surface? |
|
|
|
Center weather service units(cwsu) |
Are NWS offices located in every air route traffic control center (artcc), providing meteorological consultation, forecasts, and advice to ARTCCs and other FAA facilities weather impact |
|
|
|
Aviation weather hazard |
Is an armospheric condition which, when encountered in flight, can potentially cause damage to the aircraft, personal injury, a crash, or death |
|
|
|
Adverse wind |
Is responsible for most weather -related accidents |
|
|
|
Takeoff and landing |
_____and _____ are the most critical periods of any flight and are most susceptible to adverse wind |
|
|
|
Crosswind |
When used in aviation refers to a wind that is not parallel to the runway or path of an aircraft |
|
|
|
Perpendicular;degrades |
As wind turns more _____to the runway to become a crosswind, airplane performance gradually______? |
|
|
|
Gust |
A sudden, brief increase in the speed of the wind |
|
|
|
Tailwind |
Any wind more than 90 degrees to the longitudinal axis of the runway |
|
|
|
Gust |
This can cause an airplane to bounce on the runway and possibly lead to a crash |
|
|
|
Longer takenoff roll; longer landing roll,smaller initial rate of climb |
A tailwind can be hazardous during both takeoff and landing because why? |
|
|
|
Variable wind |
Wind direction is considered to be variable when, during the 2 minute evaluation period, it fluctuates by 60 degrees or more and the wind speed is more than 6 knots. |
|
|
|
Wind shift |
Is a term applied to a change in wind direction of 45 degrees or more which takes place in less than 15 minutes and has sustained winds of 10 knots or more throughout the wind shift |
|
|
|
Bounce on the runway |
When an airplane is taking off into a headwind, gusts may cause it to |
|
|
|
Quickly becomes a crosswind or tailwind |
A variable wind can be hazardous on takeoff and landing because it could______. |
|
|
|
Larger airplanes |
Which type of aircraft will perform better in adverse wind conditions, due to its higher takeoff and approach speeds? |
|
|
|
IFR weather |
Weather conditions below the minimum for flight under visual flight rules |
|
|
|
Continued visual flight into IFR weather |
What is the single greatest cause of fatal accidents? |
|
|
|
Vertigo |
The feeling that you or your environment is moving or spinning |
|
|
|
Ceiling |
The lowest layer aloft reported as broken or overcast; or the vertical visibility into an indefinite ceiling |
|
|
|
Indefinite ceiling |
The ceiling classification that is applied when the reported ceiling value represents the veryical visibility upward into a surface based onscuration |
|
|
|
Indefinite;equal |
An______ceiling is more hazardous than an _____ceiling caused by a layer aloft |
|
|
|
Fog |
A visible aggregate of minute water dropleys based at the Earths surface and reducing horizontal visibility to less than 5/8 statute mile. |
|
|
|
Fog |
_____is the most common and persistent weather hazard encountered in aviation. |
|
|
|
Precipitation |
Any of the forms of water particles, whether liquid or solid, that fall from the atmosphere and reach the ground |
|
|
|
Blowing snow |
Snow lifted from the surface of the earth by the wind to a height of 6 feet or more above the ground and blow about in such quantities that the reported horizontal visibility is reduced to less than 7 statute miles |
|
|
|
Volcanic ash |
Fine particles of rock or powder that oroginate from a volcano and that may remain suspended in the armosphere for long periods |
|
|
|
Mountain obscuration |
Weather phenomena causing the obscuration of mountain peaks caused by clouds, precipitation, smoke, haze, mist or fog. |
|
|
|
Are not instrument rated |
Most aircraft accidents related to instrument weather invole pilots who_____ |
|
|
|
Rain, drizzle, snow |
Which precipitation types most commonly produce instrument weather? |
|
|
|
Aircraft turbulence |
Irregular motion of an aircraft in flight, especially when characterized by rapid up and down motion, caused by a rapid variation of atmospheric wind velocities |
|
|
|
Convective turbulence |
Turbulent vertical morions that result from convective currents and the subsequent rising and sinking of air. |
|
|
|
Warm summer afternoons |
Convective currents are most active on _______when winds are light |
|
|
|
Mechanical turbulence |
Turbulence caused by obstructions, such as trees, buildings, mountains, etc. |
|
|
|
Mountain wave |
An armospheric wave disturbance formed when stable air flow passes ober a mountain or mountain range |
|
|
|
Wind shear |
A change in wind speed and/or wind direction in a short distance resulting in a shearing effect |
|
|
|
Temperature inversion |
A layer in which temperature increases with altitude |
|
|
|
Frontal zone |
The interface or transition zone between two air masses of different density. |
|
|
|
Clear air turbulence (CAT) |
A higher altitude(20,000 to 50,000ft) turbulence phenomenon occuring in cloud-free regions, associated with wind shear, particularly between the core of a jet stream and the surrounding air |
|
|
|
Light, moderate, severe, extreme |
Name 4 intensities of turbulence |
|
|
|
Light |
What type of turbulence momentarily causes slight erratic changes in altitude and/or attitude(pitch,yaw,roll) |
|
|
|
Extreme |
During what type of turbulence is the aircraft violently tossed about and practically impossible to control? |
|
|
|
Convective |
When the air is too dry for cumuliform clouds to form,______currents caused by uneven surface heating can still be active and cause turbulence |
|
|
|
Rotor cloud |
Which type of cloud would provide visual proof that a mountain wave exists? |
|
|
|
Wind shear |
What generates turbulence between two wind currents of differing wind directions and/or speeds |
|
|
|
High density altitude |
A condition of the atmosphere that reduces an aircrafts performance capability below a level od standard performance at a specified altitude |
|
|
|
Icing |
In general, an deposit of ice forming on an object |
|
|
|
Structural icing |
Is ice that sticks to the outside of an airplane |
|
|
|
Rime, clear, mixed |
What are 3 types of icing? |
|
|
|
Rime ice |
Rough, milky, opaque ice formed by the instantaneous freezing of small supercooled water droplets after they strike the aircraft |
|
|
|
Clear ice |
A glossy, clear, or translucent ice dormed by the relatively slow freezing of large supercoolex water droplets |
|
|
|
Mixed ice |
A mixture of clear and rime ice |
|
|
|
Trace, light, moderate, severe |
Name 4 types of icing: |
|
|
|
Supercooled water |
liquid water at temperatures below the freezing point |
|
|
|
Structural icing |
Most dangerous thing about icing is? |
|
|
|
Reduces |
High density altitude _____an aircrafts power and thrust |
|
|
|
Rime |
Although,______is the most common type of icing, it is the least serious because it is easier to remove |
|
|
|
Light |
With______ice,the rate of accumulation may create a problem if flight is prolonged(over 1 hour). Occasional use of de-icing equipment removes/prevents accumulation |
|
|
|
Pilot rating |
Aircraft icing potential is NOT depedant upon____ A:aircraft type and design B:pilot rating C:meteorological factors |
|
|
|
Increased Weight |
Which adverse effect of structural icing is LEAST significant to an aircraft? |
|
|
|
Thunderstorm cell |
The convective cell of a cumulonimbus cloud having lightning and thunder |
|
|
|
Towering cumulus stage,mature stage,dissipating stage |
Name the 3 distinct stages of a thunderstorm cell: |
|
|
|
Downburst |
a strong downdraft which induces an outburst of damaging winds on or near the ground. Damaging winds, either straight or curved, are highly divergent. |
|
|
|
Microburst |
A downburst that covers an area up to 2.5 miles along a side with peak winds as high as 150 knots that lasts 2 to 5 minutes |
|
|
|
Macroburst |
A downburst that covers an area greater than 2.5 miles up to 10 miles along a side with peak winds as high as 120 knots that last 5 to 30 minutes |
|
|
|
Water vapor |
Thunderstorm cell formation requires______,unstable air, and lift |
|
|
|
A microburst |
It may be impossible to recover from ______encountered at low altitude. |
|
|
|
Low level wind shear (llws) |
A wind shear of 10 knots or more per 100 feet in a layer more than 200 feet thick which occurs within 2,000 feet of the surface |
|
|
|
Headwind; tailwind |
While an aircraft is on approach, a shear from a ____to a _____causes airpseed to decrease, nose to pitch down, aircraft to drop below the glideslope |
|
|
|
Tailwind;headwind |
A shear from a _____to a _____ causes airspeed to increase, nose to pitch up, aircraft to rise upward above glideslope |
|
|
|
During takeoff and landing |
Wind shear is especially dangerous when it is encountered _______ |
|
|
|
Increase, up,rise upward above |
While an aircraft is on approach, a shear from a tailwind to a headwind causes airspeed to _____, the nose to pitch_____, and the aircraft to _____the glideslope |
|

