![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
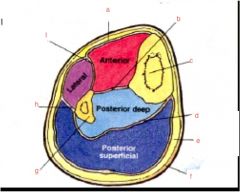
Label the muscles of the legs and understand compartments
|
a. interosseus membrane
b. tibia c. transverse septum d. superficial fascia e. skin f. fibula g. posterior septum h. anerior septum i. deep crural fascia |
|
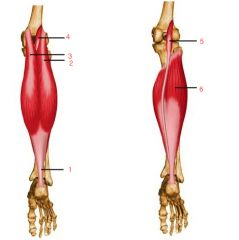
What are some of the posterior leg muscles shown? Innervation?
Where these distally attach and what layer are they? |
All innervated by Tibial nerve (L4-S1)
Distally attach calcaneus 1. Achilles tendon 2. gastrocnemius lateral head 3. gastrocnemius medial head 4. plantaris 5. plantaris 6. Soleus |
|
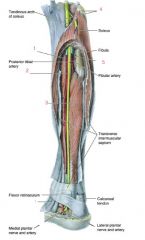
Label these 5 markers... What are the four muscles that make up the deep posterior compartment of the leg?
What are innervations? |
1. Flexor digitorum longus (FDL)
2. Tibial nerve 3. Flexor hallucis longus 4. Popliteus 5. Tibialis posterior (TP) 1,3,4,5 all innervated by tibial nerve (L5-S1) |
|
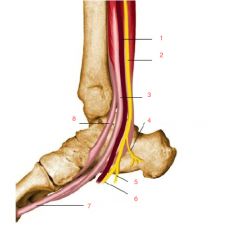
What are we looking at?
|
1. posterior tibial artery
2. posterior tibial nerve 3. flexor digitorum longus 4. medial calcaneal nerve 5. lateral plantar nerve 6. medial plantar nerve 7. flexus hallucis longus 8. tibialis posterior |
|
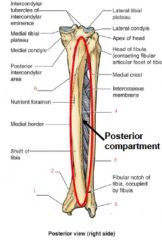
Mark the spots in the posterior compartment of the leg that the muscles attach to...
|
1. medial malleolus
2. groove for tibialis posterior tendon 3. posterior border 4. interosseous border 5. lateral malleolus 6. Soleal line |
|
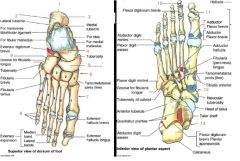
What are the markers on the foot?
|
1. calcaneal tuberosity (posterior surface)
2. Calcaneus 3. groove for flexion hallucis longus 4. talus 5. navicular 6. 3 cuneiforms 7. 5 metatarsals 8. 14 phalanges 9. Cuboid 10. flexor digorum longus 11. flexor longus 12. tibialis posterior 13. groove for flexor hallucis longus |
|
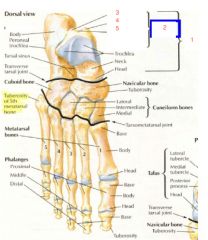
What are the areas of the posterior process of foot?
|
1. talus
2. posterior process 3. lateral tubercle 4. medial tubercle 5. groove for flexor hallicus longus tendon |
|
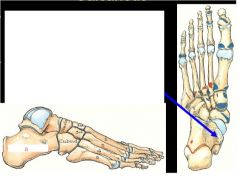
What is the name of the longest and strongest bone of the foot where does it lie below?
What does the arrow point to? |
1. Calcaneus lies below the talus
2. forms the heel of the foot Arrow points to shelf like medial projection called sustenaculum tali |
|
|
What is the role of the sustentaculum tali?
|
supports head of the talus and has a groove on its inferior surface for flexor hallucis longus tendon
|
|
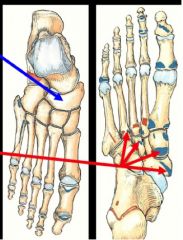
What is the bone pointed with the left pointer?
What does the picture on the right show and what is attached? |
navicular bone- lies between head of talus and three cuneiform bones
- navicular tuberosity- attaches tibialis posterior |
|
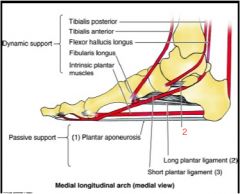
What is the name of the spring ligament?
|
plantar calcaneonavicular
|
|
|
What divides the posterior compartment into two parts and what are those parts?
|
tranverse septa
deep and superficial |
|
|
What nerve/ vessels are deep to the transverse crural intermuscular septum?
|
tibial nerve
|
|
|
Explain aspects of the medial and lateral head of the gastrocnemius?
|
1. medial-
- superior to medial femoral condyle - medial head slightly larger 2. lateral- - lateral aspect superior to lateral femoral condyle |
|
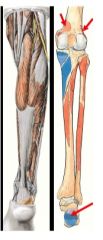
Where do the medial and lateral aspects of the gastrocnemius lie?
What is there primary function? |
1. medial-
- superior to medial femoral condyle - medial head slightly larger 2. lateral- - lateral aspect superior to lateral femoral condyle Plantar flexion and flexes leg at knee joint |
|
|
What sesamoid bone may lie close to proximal attachment of gastrocnemius and what problems could that cause?
|
fabella
- fabellar stress may cause severe pain and a total knee replacement may be needed |
|
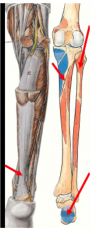
Where does the soleus attach and insert?
What 2 things is it influential in forming does it form? What are its intended actions? |
proximal horshoe shaped- plantarflexion
1. soleal line of tibia 2. posterior head of fibula and superior 1/4 of posterior fibula Distal 1. surface of calcaneus via tendo calcaneus (achilles tendon) with gastrocnemius "triceps surae" and calf prominence |
|
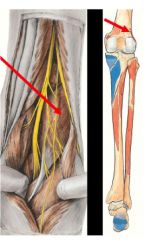
What muscle does this point to and what is action? What is interesting about it?
What are attachments? |
PLANTARIS
Weak plantar and leg flexion high amount of proprioceptive receptors for foot position Lateral end of lateral supracondylar lin, in between gastrocnemius and soleus and posterior surface of calcanael tendon |
|
|
What is mostly likely the cause of the injury?
a. violent ankle movment or sudden dorsiflexion (usually seen in sprinters, ballet dancers and basketball players)? |
torn plantaris muscle
|
|
|
What tendon is commonly used in reconstructive surgery of hand tendons?
|
plantaris long tendon
|
|
|
What are the four muscles in the deep posterior crural compartment?
|
1. popliteus
2. flexor hallucis longus 3. Flexor digitorum long 4. Tibialis posterior |
|
|
What are the arteries of the popliteal fossa?
|
1. genicular (superior medial, superior later, inferior medial, inferior lateral)
|
|
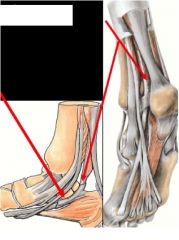
What are the attachments of this muscle?
|
flexor hallucis longus-
- shallow groove on posterior surface of sustenaculum tali of calcaneus -approaches great toe - distal attachment- base of distal phalanx of great toe action- flexes great to plantar flex foot at ankle |
|
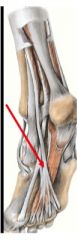
What is muscle and where does it go?
|
flexor digitorum longus
- diagonally in sole of foot, divides into 4 tendons as it goes towards distals phalanx Action- flexes lateral four digits, plantarflex foot at ankle joint |
|
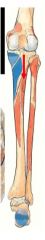
What muscle attaches here and where is here?
|
tibialis posterior deepest posterior crural muscle
interosseus membrane, posterior tibia inferior to soleal line and posteromedial surface of fibula |
|
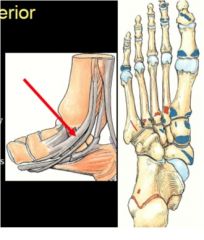
What is arrow pointing to and what function does this have?
|
tibialis posterior tendon
- inversion plantar flexion |
|
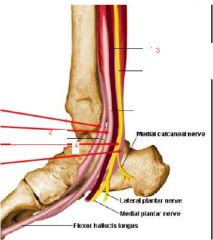
Tom dick an harry means?
|
from anterior to posterior on the medial mediolus
1. Tibialis posterior 2. flexor Digitorum longus 3. posterior tibial Artery 4. tibial Nerve 5. flexor Hallucis longus |
|
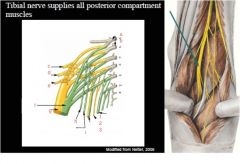
Memorize this and understand
|
a + b. lumbosacral trunk
c. superior gluteal nerve d. inferior gluteal nerve e. nerve to piriformis f. tibial portion of sciaic g. common fibular portion of sciatic h. Quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus i. Obturator internus and superior gemellus 1. Pudendal nerve 2. perforating cutaneous 3. posterior femoral cutaneous |
|
|
Where does the following pass to and leave?
a. tibial nerve |
a. deep to soleus muscle and posterior to tibialis posterior
- leaves posterior compartment via deep to flexor retinaculum between medial malleolus and calcaneus - ends by dividing into medial and lateral planter nerves |
|
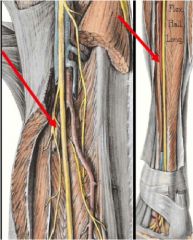
What does arrow point to and what is pathway of structure?
|
posterior tibial artery
1. starts inferior to popliteus---->fibular artery---> deep to flexor (does posterior and laterla compartments) (retinaculum---> divides into medial and lateral planter arteries |
|
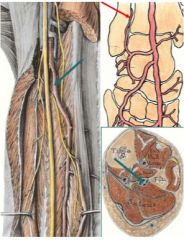
What is this artery where does it come from and where does it go?
|
fibular artery, largest branch of posterior tibial artery
- descends toward fibula under Flexor hallucis longus - ends by piercing interosseus membrane and anastomosing with anterior lateral malleolar artery |
|
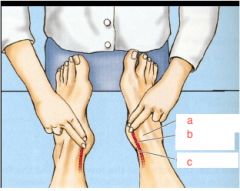
What are we feeling for here?
Why do have the person invert and point toes? |
a. medial malleolus
b. posterior tibial artery c. calcaneal tendon Posterior tibial pulse relax flexor retinaculum, and allows to feel around tom dick an harry |
|
|
What types of conditions do you need to make sure they have posterior tibial pulse?
What is the condition caused by ischemia of leg muscles due to narrowing or occlusion of leg arteries often characterized by leg cramps and pain during walking and disappears after rest? |
1. occlusive peripheral arterial disease (intermittent claudication)
2. intermittent claudication |

