![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the polyene antifungals still used?
|
Amphotericin B
Nystatin |
|
|
What is the MOA of the polyenes?
|
Insert into fungal cytoplasmic membrane and binds ergosterol. Pores form w/ leakage of K+ and other studd leading to cell death
the crossreactivity for cholesterolk is what causes the toxic SE |
|
|
What are the sites of Antifungals?
|
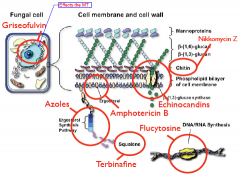
|
|
|
What are the forms of Amphoteracin B?
|
Only IV formulations. Insoluble in water so...
1. Na deoxycholate (micellare dispersion) in D5W to prevent preciptiation |
|
|
What are the pharmacodynamics of Amphoteracin B?
|
90% bind plasma proteins
No distribution to CNS or adipose Kinetics are non linear & 2-5% excreted in urine w/ little metabolism |
|
|
What can we use amphoteracin B for?
|
Wide spectrum activity - Yeast, Molds, Dimorphics
Some are Inherantly resistant (dont need to know) |
|
|
SE of amphoteracin? Shorter,? Long term?
|
Infusion related (give test dose) - fever & chills, phlebitis (inflammatory), arrhythmias
- Renal toxicity (Infuse large amounts Saline post administration, monitor electrolytes) - K/Mg wasting & renaltubular acidosis, renal dysfunction, anemia (decreased EPO) |
|
|
What are the benefits and downfalls of the newer Amphoteracin formulations?
|
Liposomal amphoteracin B
Reduced renal toxicity but more expensive and requires a higher dose |
|
|
What is Nystatin used to treat?
|
Topically for (never systemic)
-oral candiasis -vaginal candidiasis -cutaneous candidiasis |
|
|
What are the 2 groups of Azoles and the rxs in each?
|
Large and water insoluble
-itraconazole, posaconazole Small and water soluble -Fluconazole, voriconazole |
|
|
What is the MOA of azoles?
|
binds heme moitey to block demethylation of lanosterol a ergosterol precursor
- disrupts the cell membrane |
|
|
Profiles of 4 azoles
|
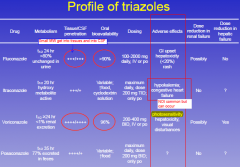
|
|
|
What are the drug interaction risks in azoles?
|
Azoles metabolized by and inhibit CYP450, the CYP3A4 which leads to bidirectional interactions
*Rifampin induce CYP (antifungal lose fx) *Grapefruit inihbits CYP3a4 (Increase SE from overdosed) *Increase Warfarin levels (coagulopathy-bleed) *Increases statin levels (rhabdomyolsis) |
|
|
Compare small and large azoles and the benefit of the small compounds.
|
The small and water soluble azoles have beter oral bioavailability and better tissue/CSF penetration
|
|
|
Compare azoles activity against various yeasts.
|
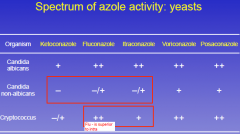
|
|
|
How can we ger resistance to azole?
|
intirinsic - absed on properties of fungi
Acquired - when repeated exposures through multiple MOA such as alteration 14a-demethylase or efflux pumps |
|
|
Echinocandins
|
Large and no oral absorption
Hepatic metabolism and poor fx for UTI (fungal) Good for candida |
|
|
What is the MOA of ecchinocanfins?
|
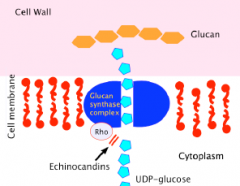
Inhibit synthesis cell wall 1,3 Beta
|
|
|
What is the common ecchinocandin?
|
micafungin
|
|
|
What is the MOA of Terbinafine?
|
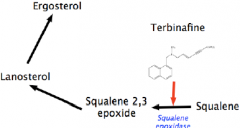
Only allylamine available (lamisol) for dermatophytes (ring worm)
|
|
|
What are the properties of Terbinafine?
|
PO or Topical - !! 24weeks of treatment !!
Highly lipophilic which increases fx in skin (highly lipidous) -onchomycosis (toe nail fungus) -Tinea capitis -Sporotrichosis |
|
|
What is Flucytosine (5-FC)
|
Never use alone otherwise fungi become resistant
- only use for 1 infection type (amphoteracin B) - Multiple enzymes can mutate |
|
|
What is the MOA of 5FC?
|
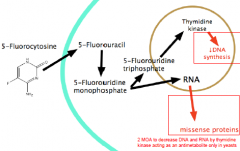
Antimetabolite at the DNA and RNA level
|
|
|
What yeasts is 5FC active against? What is it used for clinically?
|
Clinically used to tx cryptococcal meningitiss in conjunction w/ amphoteracin B (MUST monitor renal fx)
dependent on renal excretion and renal toxic = dangerous |
|
|
What is the Pharmacology of 5FC? SE?
|
90% eliminated in urine not metabolized, short t1/2 (4h)
- Effects rapidly growing cells, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bone marrow toxic, elevated ALT/AST (all dose related and can be monitored) |
|
|
What are the properties of Griseofulvin?
|
Binds fungal tubulin to inhibit mitosis
Rapid fungicidal Water insoluble - take w/ fatty meal |
|
|
What is Griseofulvin used for?
|
PO for dermatophytes(NOT candida or deep mycoses). Rarely used.
|
|
|
What is MOA of Griseofulvin?
|
Microtubule disruption interferes with cell division
|
|
|
Nikkomycin Z
|
competive inhibitor of fungal chitin synthesis. NOT currently clinically available
|
|
|
Summary of antifungal USE
|
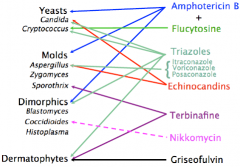
|
|
|
Amphoteracin B renal issues
|
Seen in just about EVERY pt over the course of tx
and thus obvious reasons, amphotericin B is limited to progressive, life-threatening fungal infections |
|
|
How does resistance in fungi compare to bacteria?
|
Similar MOresistance in general. In fungi methods for determining are variable
-Missing any analog to beta lactamases -able to alter synthetic pathways -use altered binding site -use efflux pumps (more common in fungi) |
|
|
What azoles are used for CSF penetration or good bioavailabilty? What are each SE?
|
Small MW and water soluble Triazoles
Fluconazole - GI upset / hepatotoxic / rash Voriconazole - photosensitivity / hepatotoxic / hallucination |
|
|
Azole metabolism issue? Some interactions he mentioned?
|
metabolized by and inhibit **CYP3A4** and CYP2C9
Rifampin - accelerate metabolism Grapefruit - inhibits metabolism Warfarin - will increase levels (bleed) Statin - increase levels -> rhabdomyolysis |
|
|
Echinocandins delivery issue? What are they used to treat?
|
Large size, must give IV
Candida Most common is Micafungin |

