![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
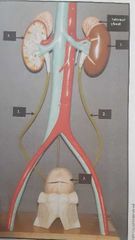
|
1. Kidneys 2. Ureters 3. Urinary bladder 4. Urethra |
|
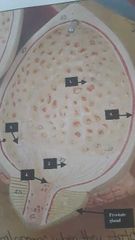
|
Urinary bladder 1. Mucosa layer with Rugae 2. Trigone 3. Ureteral opening 24. Urethral opening 15. Detrusor muscle aka Muscularis layer Serosa layer (outer layer) |
|
|
About urethra |
Female is 1.5inch Stratified squamous epithelial Male is 8inch Pass through prostate Urogenital diaphragm is external muscle for penis to hang to Sphincters carry urine out body Internal urethral sphincter External urethral sphincter Involuntary smooth muscle External urethral sphincter Voluntary skeletal muscle Voluntary skeletal muscle |
|
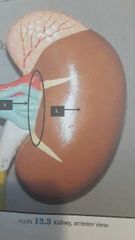
Kidney location 3 membranes are what |
Retroperitoneal 2. Renal capsule Adipose capsule Renal fascia 1. Hilus |
|
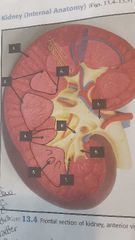
|
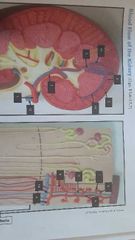
1. Renal cortex 2. Renal medulla 3. Renal pelvis drain to ureter 4. Renal column 5. Renal pyramid urine is formed 6. Renal papillae (tip) 7. Renal sinus 8. Major calyce drains in renal pelvis 9. Minor calyce drains in major calyce |
|
|
1. Renal artery 12. Renal vein 2. Segmental artery 3. Interlobar artery 11. Interlobar vein 4. Arcuate artery 10. Arcuate vein 5. Interlobular artery 9. Interlobular vein 6. Afferent arteriole (big one) in Efferent arteriole (small one) out 7. Glomerular capillaries 8. Peritubular capillaries |
|

|
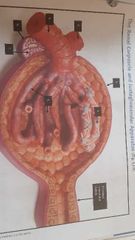
1. Renal corpuscle= Glomerular (bowman's) capsule and Glomerular capillaries 2. Proximal convoluted tubule= reabsorption 3. Loop of henle 4. Descending limb 5. Ascending limb 6. Distal convoluted tubule 7. Collecting tubule 8. Papillary duct |
|
|
Renal corpuscle 1. Glomerular Bowmans capsule 2. Glonerular capillaries (glomerulus) 3. Podocytes 4. Afferent arteriole 5. Efferent arteriole Juxtaglomerular apparatus Juxtaglomerular cells for Low BP 6. Distal convulated tubule 6. Macula dense cells |
|
|
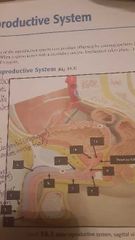
Penis 1. Glans penis 2. Prepuce (foreskin) 3. Corona 4. Crus of penis 5. Bulb of penis 6. Corpora cavernosa 7. Corps spongiosum Urethra 8. Spongy urethra 9. Membranous urethra 10. Prostatic urethra 11. Ejaculatory duct |
|
|
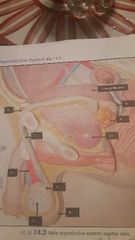
1. Scrotum 3. Testes 4. Epididymis (sperm maturation) 5. Inguinal canal 6. Spermatic cord (sperm run through) 7. Ductus vascular deferens (sperm stored) 8. Ampulla of ductus Reproductive glands 9. Seminal vesicles 10. Prostate gland |
|
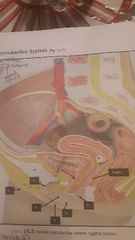
External genitalia |
Vulva 1. Mons pubis 2. Labia majora 3. Minor majora 4. Clitoris 5. Vaginal opening 6. Urethral opening Vestibule (space btw labia minora) |
|
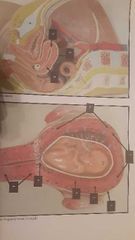
Uterus layers and regions |
Layers 1.Perimetrium -connective tissue 2.Myometrium -smooth muscle 3.Endometrium -stratum basalis Regions 4. Cervix 5. Isthmus 6. Body 7. Fundus Perineum Region btw pubis symphysis/ coccyx Obstetrical perineum Btw vaginal opening and anus |
|
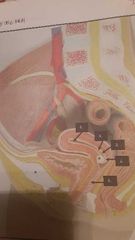
Uterine passageway |
1. Vagina 2. External os 3. Cervical canal 4. Internal os 5. Uterine cavity |
|
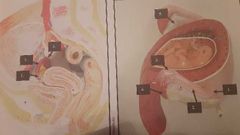
Uterine tube . Oviduct. Fallopian tubes |
1. Isthma passageway to uterus 2. Ampulla fertilization occurs 3. Infundibulum 4. Fimbriae sweep egg into oviduct 5. Ovary holds eggs |
|
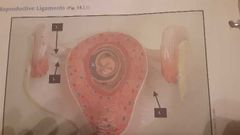
|
1. Broad ligament suspends uterus from side wall of pelvis
2. Ovarian ligament Anchors ovary to uterus
5. Mesovarium ligament Btw ovary and fallopian tube |
|
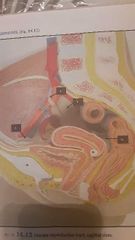
|
1. Broad ligament Suspends uterus from side wall of pelvis 3. Round ligament Attaches ovaries to inguinal canal 4. Suspensory ligament Cover blood supply to ovaries and passes under fallopian tube 5. Uterosacral ligament |
|
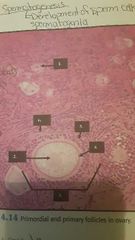
Ovary |
1. Primordial follicle 2. Primary oocyte 3. Primary follicle 4. Zona pellucida 5. Granulosa cells of primary follicle 6. Theca folliculi |
|
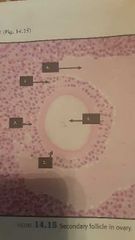
Secondary follicle |
1. Primary oocyte 2. Zona pellucida radiata 4. Granulosa cells of 2ndary follicle 3. Corona radiata 4. Granulosa cells of 2ndary follicle 5. Theca folliculi 6. Antrum filled with follicular fluid 5. Theca folliculi 6. Antrum filled with follicular fluid |
|
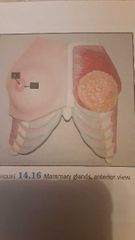
Mammary glands |
1. Nipple 2. Areola Mammary ducts- Lactiferous sinus- storage Lobules -secrets milk Mammary ducts-Lactiferous sinus- storage Lactiferous duct- out through nipple Lactiferous duct- out through nipple |
|
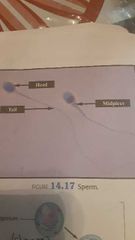
Sperm |
Head DNA, acrosomes (enzymes) Midpiece Mitochondria to form ATP Tail Flagellum used for locomotion |
|
|
Spermatogenesis |
-Spermatogonium is stem cells -Development of sperm cells from spermatogonia -formations from mitosis and meiosis - 23 chromosomes (haploid) |
|

|

|
|
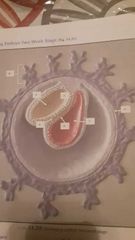
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|

