![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|

|
|
|
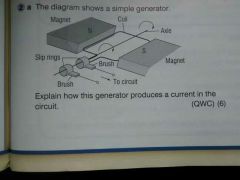
Define the generator effect |
The induction of a potential difference in a wire which is experiencing a change in magnetic field |
|
|
Define the motor effect |
When a wire carrying an electric current is placed in a magnetic field, and experiences a force |
|
|
What type of ring commutator does a motor have? |
Split-ring commutator |
|
|
What does the commutator on a motor do? |
Reverses the direction of the current around the coil every half turn, to keep the coil rotating in the same direction |
|
|
What is the activity of a radioactive source? |
The number of nuclei that decay per second |
|
|
What is the half life of a radioactive source? |
The time taken for the count rate from the original isotope to halve The time taken for the number of unstable nuclei in a sample of the isotope to halve |
|
|
Use of: radio waves |
Radio, mobile phone, and TV signals |
|
|
Use of: microwaves |
Satellite signals (can pass through the atmosphere) |
|
|
Use of: infrared rafiation |
TV remote signals, can be transmitted along optical fibres (optical fibre communication) |
|
|
Use of: Ultraviolet radiation |
Detecting forged bank notes. Makes some chemicals emit light - they absorb UV light and emit visible light as a result |
|
|
Use of: X-Rays |
Medical imaging, detecting internal cracks in metal objects |
|
|
Use of: Gamma rays |
Killing cancer cells, sterilising surgical equipment, killing bacteria in food |
|
|
Dangers of: microwaves |
Penetrate skin, absorbed by internal body tissue. Causes heating of organs which may damage them. |
|
|
Dangers of: radiowaves |
Penetrate skin, absorbed by internal body tissue. Causes heating of organs which may damage them. |
|
|
Dangers of: infrared radiation |
Is absorbed by skin - can cause burns |
|
|
Dangers of: UV radiation |
Harmful to human eyes - can cause blindness Can cause skin cancer |
|
|
Define transverse wave |
A wave created when the direction of energy transfer is perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels |
|
|
Define longitudinal wave |
A wave that is created when the direction of energy transfer is parallel to the direction in which the wave travels |
|
|
Describe nuclear fission |
A neutron is absorbed by uranium-235 or plutonium-239 A larger nucleus is formed The larger nucleus is unstable The larger nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei 2 or 3 nuclei are emitted for each fissioned nucleus, which can go on to cause further fissions Energy is released |
|
|
Describe nuclear fusion |
Two light nuclei are brought together at high speeds (to overcome the repulsive forces from their positive nuclei) The two nuclei collide A single larger nucleus is formed Energy is released |
|
|
Why does fusion normally occur in stars? |
The core of a star is hot enough to contain a 'plasma' of bare nuclei (without electrons) The hot temperature caused the bare nuclei to collide at very high speeds |
|
|
What are the requirements for a fusion reactor? |
A magnetic field around the edge, to prevent the positive nuclei from hitting the wall and losing energy The plasma is heated to a very high temperature by passing an electric current through it |
|
|
Define plasma |
A very hot gas consisting of bare nuclei (atoms without electrons) |
|
|
Define resultant force |
The single force that would have the same effect on the object as all the original forces acting together |
|
|
Define the law of conservation of momentum |
In a closed system The total momentum before an interaction is equal to the total momentum after the interaction |
|
|
Define stopping distance |
Thinking distance + braking distance |
|
|
Define thinking distance |
The distance traveled in the car during driver's reaction time |
|
|
Define braking distance |
Distance traveled by a vehicle during the time its brakes act |
|
|
Which factors increase breaking distance? |
Slippery roads Worn tires Worn brakes High speed |
|
|
Which factors increase thinking distance? |
A tired driver An intoxicated driver High speed |
|
|
Define Hooke's law |
The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied to it, as long as its limit of proportionality is not exceeded |
|
|
When will an object become unstable? |
When the line of action of a weight,(which acts through the object's centre of mass) Lies outside the base of an object Causing a resultant moment |
|
|
Define centripetal force |
The resultant force which acts on an object toward the centre of a circle. As it is a resultant force, it cause the object to accelerate If it did not act, the object would continue to move in a straight line at a tangent to the circle, (so the object would be accelerating) |
|
|
What causes the centripetal force needed to keep an object performing circular motion to increase? |
Increased mass of object Increased speed of object Decreased radius of circle F=(mv^2)/r |

