![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Light? |
Electromagnetic energy that, in certain wave-lengths, stimulates the eyes and brain. |
|
|
What is Ambient Light? |
Light all around us in our world. |
|
|
What is value (tone)? |
Lightness/darkness within a hue. |
|
|
What is achromatic? |
White and black (the value extremes), with the continuum of grey tones in between. |
|
|
What is chromatic? |
Lighter, darker, or different values of a color. |
|
|
What is a hue? |
It is another word for color. Pure state of color in the spectrum. |
|
|
What is chiaroscuro? |
Light-dark gradations that can depict objects in space. Italian for "light-dark". |
|
|
Color is visible in refracted light. True or false? |
True! Color is visible in refracted light. |
|
|
What is refracted light? |
A range of colors that is visible when a prism breaks a light beam into a spectrum of colors (a rainbow). |
|
|
What is a spectrum? |
A breakdown of white light into components of ROYGBIV. |
|
|
What is reflected light? |
The brightness and color of light that is bounced off of objects in the enviroment. |
|
|
What is shade? |
Adding black to a color. |
|
|
Tint |
Adding white to a color. |
|
|
Intensity |
Brightness and dullness of color. |
|
|
What are colors? |
Components of light that affects us directly by modifying our thoughts, our moods, our actions, and our health. |
|
|
What is the additive color system? |
Color that is created by mixing light rays. |
|
|
What is the subtractive color system? |
Any system of color mixing which the addition of more colors gives a duller result. |
|
|
What are pigments? |
Powdered substances ground into oil, acrylic polymer, or others to make paint. |
|
|
Primary colors are... |
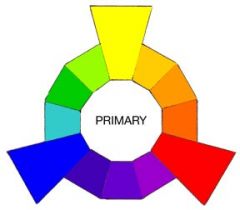
Colors combined that produce the largest number of new colors. |
|
|
Secondary colors are... |
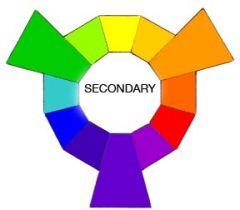
Color results when any two colors are mixed.
|
|
|
Tertiary colors are... |
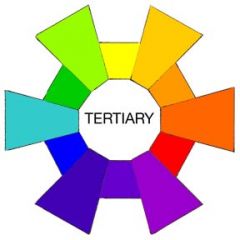
Colors that result from the mixing of one primary color that neighbors the secondary color. |
|
|
Analogous colors are... |
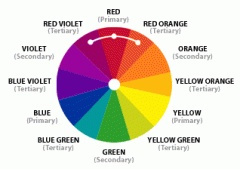
Colors that are next to each other on the color wheel. |
|
|
Complementary colors are... |
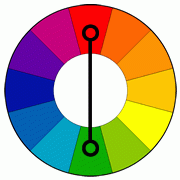
Hues that are located directly opposite of each other on the color wheel. |
|
|
What is a color wheel? |
A circular arrangement of the hues of the spectrum. |
|
|
What is the relativity of color perception? |
Seeing colors differently depending on the enviroment/surrounding. |
|
|
What are textures? |
A surface characteristic that is tactile (touchable) or visual. |
|
|
What is Tactile Texture? |

Consists of physical surface variations that can be perceived through touch. |
|
|
Visual Textures are... |
Rendering of illusionary texture on a surface or ground. |
|
|
Simulated textures are... |
Textures mimicking reality. |
|
|
Abstracted textures are... |
Textures that have been distorted, simplified, or exaggerated from an actual texture. |
|
|
Invented textures are... |
An imaginary surface quality (texture) created by the artist. |
|
|
What are patterns? |
An arrangement with repeated visual forms. |
|
|
What are natural patterns? |
Patterns that occur all around us. |
|
|
What are geometric patterns? |
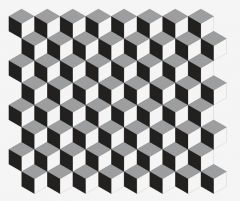
Patterns that have regular elements spaced at regular intervals. |
|
|
What is Surrealism? |
Surrealism in an art movement during the early 20th century in Europe, that was influenced by the work of Sigmund Frued. |
|
|
What are shapes? |
They are 2d visual forms. |
|
|
What are Regular Shapes/Geometric Shapes? |
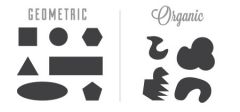
Geometric 2d visual forms with names like circle, square, triangle, etc. |
|
|
What are Irregular Shapes? |
Geometric 2d visual forms that are unique and have no simple defining name. |
|
|
What is Volume? |
An area of occupied space. |
|
|
Perspective is... |
A group of methods for creating the illusion of depth on a flat picture plane. |
|
|
Atmosphere Plane (Aerial Perspective) is... |
Light, bleached out, fuzzy handling of distant forms to make them seem far away. |
|
|
Linear Perspective is... |
Parallel lines that appear to converge as they recede. |
|
|
Horizon Line is... |
Viewers eye level in a picture, determining what the viewer perceives as "above" or "below". |
|
|
One-point Perspective is... |
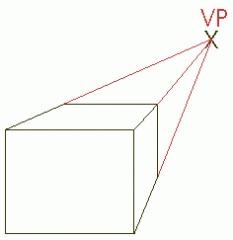
A drawing in which all front-facing planes are shown as parallel to the picture plane, and all other planes recede to a single point. |
|
|
Two-point Perspective is... |
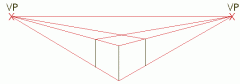
A drawing in which no planes are parallel to the picture plane, but all recede to one of two points on the bottom. |
|
|
Three-point Perspective is... |
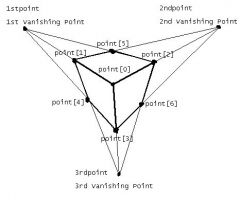
A drawing in which only one point of each volume is closest to the viewer, and all planes recede to one of three points. |
|
|
What is Isometric Perspective? |
A perspective system for rendering 3d objects on a 2d surface by drawing all horizontal edges at a 30 degree angle from horizontal base. |
|
|
What is oblique perspective? |
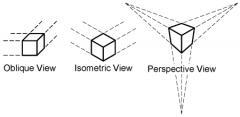
When a 3d object is rendered with the front and back panel.
|
|
|
What is Multipoint Perspective? |
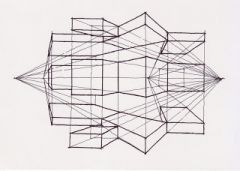
A type of drawing that depicts forms in space as receding to two or more vanishing points, but not on the same horizontal line. |
|

What is the name of this painting and who is the artist? |
"The Morning Anxiety" by Giorgio de Chirico |
|

What is this the name of this art and who is it by? |
"Black Rainbow" by Cai Guo-Qiang |
|

What is this the name of this art and who is it by? |
"Nude Descending Staircase (No. 2)" by Marcel Duchamp |
|
|
What is composition? |
Arrangement of the formal elements in a work of art. |
|
|
What is balance? |
Results from placing elements so that their visual weights seem evenly distributed. |
|
|
What is Symmetrical Balance? |
Visual weight that is evenly distributed throughout the composition. |
|
|
What is Asymmetrical Balance? |
The careful distribution of uneven elements. |
|
|
What is Radial Balance? |
All elements in the composition that visually radiate outward from a central point. |
|
|
Rhythm is... |
The repetition of carefully placed elements separated by intervals. |
|
|
Regular Rhythm is... |
Some visual elements that are systematically repeated with a standard interval in between. |
|
|
Alternating Rhythm is... |
Different elements that are repeatedly placed side by side, which produces a regular and anticipated sequence. |
|
|
Eccentric Rhythm is... |
A perceived pattern that has irregular repetition of elements or irregular spacing between elements. |
|

What is the name of this art? |
"Churning of the Ocean Milk" |
|
|
What is proportion? |
The size of one part in relation to another within an artwork. |
|
|
What is scale? |
The size of something in relation to what we assume to be normal. |
|
|
What is emphasis? |
One or more focal points in an artwork. |
|
|
What are accents? |
Lesser focal points in an artwork. |
|
|
What is unity? |
When the artist organizes all the compositional elements so that they visually work together as a whole. |
|
|
What is variety? |
Different visual elements in a composition that add interest without disturbing its unity. |
|

What is the name of this art and who is it by? |
"Electronic Superhighway: Continental US, Alaska, Hawaii" by Nam June Paiks |
|
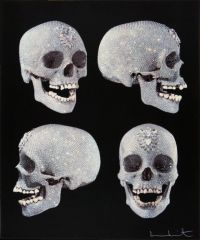
What is the name of this art and who is it by? |
"For the Love of God" by Damien Hirst |
|
|
What are Silverpoints? |
Drawings that are produced by a thin stylus made of silver that leaves marks on paper/wood coated with layers of gesso as a ground. |
|
|
What is Printmaking? |
The process of making multiple artworks, usually on paper, using a printing plate, woodblock, stone or stencil. |
|
|
What are etchings? |
Creating of lines on an area (plate), using acid that eats into exposed surfaces. |
|
|
What is Lithography? |

A form of printmaking invented in the 19th century, based on the principle that water and oil do not mix. |
|
|
What is Seriography? |

Screen printing. |
|

What is the name of this art and who is it by? |
"Marylin Monroe" by Andy Warhol |
|
|
What is Monotype? |

A printmaking process involving drawing or painting directly on a plate, resulting in only one impression of an image. |
|
|
What is a binder? |
A substance which pigments are blended into and holds the components together once it dries. |
|
|
What are the key principles of composition? |
Unity, variety, balance, emphasis, contrast, repetition, rhythm, scale and proportion. |
|
|
Design addresses the basic human needs for meaning and order. True or False? |
True! Design addresses the basic human needs for meaning and order. |
|
|
Who is Jacob Lawrence? |
The first African-American painter who created dynamic cubism art that portrayed African-American life. |
|

What is the name of this art and who is it by? |
"Going Home" by Jacob Lawrence |
|
|
What are installations? |
Mixed media that is organized or placed in a specific space. |
|
|
Who is Nam June Park? |
A Korean-American artist who is the father of video art. He artworks involved using the power of broadcasting and media art. |
|
|
Who is M.C. Esher? |
A Dutch graphic artist who is known for his often mathematically inspired woodcuts, lithographs, and mezzotints. |
|
|
What are mezzotints? |

A method of engraving on copper or steel by burnishing or scraping away a uniformly roughened surface. |
|
|
Who is Syd Mead? |

A "visual futurist" and a neofuturistic concept artist. He is best known for his designs for science-fiction films such as Blade Runner, Aliens and Tron. |
|
|
What are organic shapes/biomorphic shapes? |
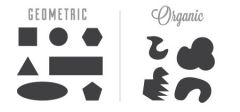
A shape that seems to be drawn from nature or that is like nature; not geometric. |
|
|
What are actual lines? |

Lines that physically exist. Can be broad, thin, straight, jagged, and so on. |
|
|
What are implied lines? |
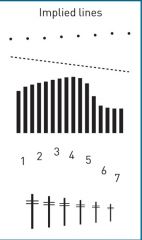
Lines that do not physically exist, yet they seem quite real to viewers. Can be dotted, broke, or have pointing action. |
|
|
What is direction? |
The course of movement, as in horizontal, vertical, or diagonal. |
|
|
What is line quality? |
Lines that can express a range of emotions: |
|
|
What are gesture lines? |
Lines that are rapid, sketchy marks that mimic movement of the human eyes when examining a subject. |
|
|
What is an outline? |

Line that follows the outer edges of the silhouette of a 3d form with steady line thickness. |
|
|
What are contour lines? |
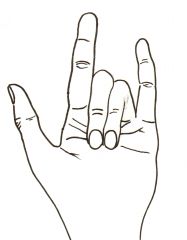
Lines that mainly mark the outer edges of a 3d object, but with varying line thickness with some inner detail. |
|
|
What are cross-contour lines? |
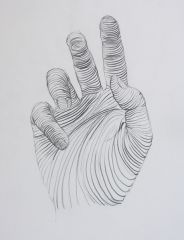
Repeated lines that go around an object to express its 3d form. |
|
|
What is hatching? |
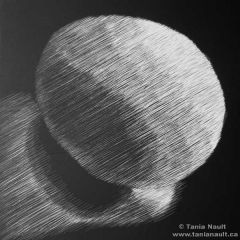
Parallel lines that produce tones or values on a 3d object. |
|
|
What is cross-hatching? |

Parallel lines in superimposed layers that produce tones or values on a 3d object. |

