![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Attempts to measure likelihood of variability of future returns from proposed investment
|
Risk Analysis
|
|
|
7 Approaches to Risk Assesment
|
1. Informal Method
2. Risk adjusted discount rates 3. Certainty equivalent adjustments 4. Simulation analysis 5. Sensitivity analysis 6. Monte Carol technique 7. Capital Asset Pricing Model |
|
|
NPVs are calucated and apparently less risky project is chosen
|
Informal method
|
|
|
Technique adjust rate of return upward as investment becomes riskier
|
Risk-adjusted discount rates
|
|
|
Forces decision maker to specify at what point firm is indifferent to choice between certain sum of money and ecpected value of risky sum
|
Certain equivalent adjustments
|
|
|
Computer is used to generate many examples of results based upon various assumptions
|
Simulation Analysis
|
|
|
Forecast of many calculated NPVs under various assumptions are compared to see how sensitive NPV is changing conditions. (What-if technique)
|
Sensitivity Analysis
|
|
|
Technique is often used in simulation to generate the individual values for random variable
|
Monte Carol Technique
|
|
|
Method is derived from use of portfolio theory. More sensitive an asset's rate of return is to change in market's rate of return, the riskier the asset.
|
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
|
|
|
Return on Investment (ROI)
|
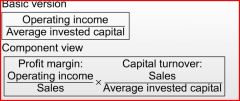
|
|
|
Residual Income
|
Net Income - (Average Total Assets * Target rate of return)
|
|
|
Return on assets (ROA)
|
Net Income/Average Total assets
|
|
|
Return on common equity (ROCE)
|
(Net Income - Preferred dividends)/ Average common equity
|
|
|
Economic Value Added (EVA)
|
After tax OI= After tax WACC*(Total assets - current liabilities)
|
|
|
Firm's ability to pay its noncurrent obligations as they come due and thus remain in business in long run
|
Solvency
|
|
|
Capital structure ratios
|
1. Total debt to total capital
2. Debt to equity 3. Long term debt to equity 4. Debt to total assets |
|
|
The excess of the amount of the ROI over a targeted amount equal to an imputed interest charge on invested capital
|
Residual income
|
|
|
Profitability index
|
PV of future net cash flows or NPV of project/Initial investment
|
|
|
Types of real options
|
1. Abandonment of project (exceeds NPV of future cash flows)
2. Option of follow up investment (NPV of project b/c of inefficient scale) 3. Wait,learn 4. Flexibility 5. Capacity 6. Geographical market 7. New product option |
|
|
A firm earning a profit can increase its return on investment by
|
A firm earning a profit can increase its return on investment by
|

