![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What if the difference in offspring that are Asexually reproduced and those Sexually reproduced? |
Asexual = Clones Sexual- Traits from both parents |
|
|
An adaptive trait can spread more quickly through which form of reproduction? |
Sexual |
|
|
Somatic cells are? |
Body cells |
|
|
What are Alleles? |
different forms of the same gene |
|
|
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of.... |
Gametes (from two parents) |
|
|
Gametes come from? |
The division of germ cells ( immature reproductive cells) |
|
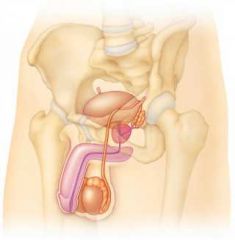
Male or female reproductive organ? |
Male (Testis) |
|
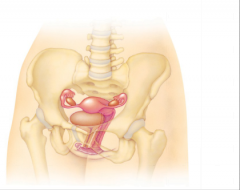
Male or female reproductive organ? |
Female |
|

Explain plant sexual reproduction. |
Meiosis produces haploid germ cells inside anthers and ovaries. These cells divide by mitosis to give rise to gametes (sperm and eggs). |
|
|
Gametes have a single set of chromosomes meaning they are? |
Haploid (n) |
|
|
What happens in meiosis II? |
sister chromatids are separated |
|
|
what happens in meiosis I? |
each duplicated homologous chromosome is separated from its partner |
|
|
When is diploid chromosome # restored? |
At fertilization |
|
|
Egg and sperm fuse and form what? |
A zygote (First cell of a new individual) |
|
|
Meiosis help maintain? |
Chromosome number ( without it the chromosome # would double each generation) & organism health |
|
|
Describe Prophase I |
Homo-Chromosomes condense, pair, and swap segments Spindle microtubules attach to condensed chromosomes |
|
|
Describe Metaphase I |
Homo-Chromosome pairs align between spindle poles Microtubules attach to each pair |
|
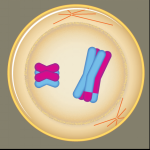
What phase is this? |
Prophase I |
|
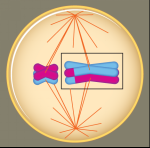
What phase is this? |
Metaphase I |
|
|
Describe Anaphase I |
Homologous chromosomes separate and begin heading toward spindle poles |
|
|
Describe Telophase I |
A complete set of chromosomes clusters are at both ends of the cells A nuclear envelope forms around each set, forming two haploid (n) nuclei |
|
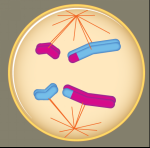
What phase is this? |
Anaphase I |
|
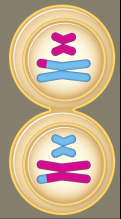
What phase is this? |
Telophase I |
|
|
Describe Prophase II |
Chromosomes condense Spindle microtubules attach to each sister chromatid as the nuclear envelope breaks up |
|
|
Describe Metaphase II |
Chromosomes align between spindle poles |
|
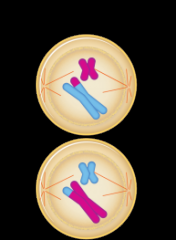
What phase is this? |
Prophase II |
|
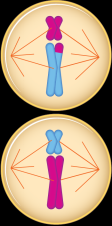
What phase is this? |
Metaphase II |
|
|
Describe Anaphase II |
Sister chromatids separate and begin heading toward spindle poles |
|
|
What happens during Telophase II? |
A nuclear envelope forms around each set, so four haploid (n) nuclei form |
|
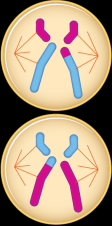
What phase is this? |
Anaphase II |
|
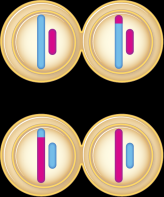
what phase is this? |
Telophase II |
|
|
What is Crossing Over? |
The process where a chromosome & it's homo partner exchange heritable info |
|
|
When does crossing over happen? |
Condensation in Prophase I |

