![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ganglia
|
clusters of neurons
|
|
|
sensory neurons
|
transmit information from sensors that detect external stimuli or internal conditions
|
|
|
interneurons
|
make local connections (mostly in the brain)
|
|
|
peripheral nervous system
|
PNS. the rest of the nervous system (not in the CNS)
|
|
|
presynaptic cell
|
the neuron that is transmitting a signal
|
|
|
postsynaptic cell
|
the neuron that is recieving the signal
|
|
|
glia
|
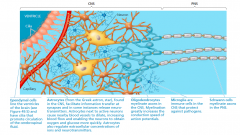
supporting cells that nourish neurons. today we know about furter influenceof the glia.
|
|
|
hyperpolarization
|
the increase in magnitude of the membrane potential
|
|
|
depolarization
|
the reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential (pos inside, neg outside)
|
|
|
action potential
|
a massive change in membrane voltage - a wave down the neuron
|
|
|
threshold
|
Action potentials occur whenever a depolarizationincreases the membrane voltage to a particular value,called the threshold
|
|
|
refactory period |
the downtime following an action potential when a second action potential can not be initiated (when its recovering) |
|
|
oligodendrocytes
|
myelin sheath section in the CNS
|
|
|
schwann cells
|
myelin sheath sections in the PNS
|
|
|
Nodes of Ranvier
|
gaps between the myelin sheath
|
|
|
myelin sheath |
The electrical insulation that surrounds vertebrate axons. they insulate the axon and speed up the signal
|
|
|
synaptic terminal
|
the end of the neuron - sends neurotransmitters
|
|
|
How does a nerve impulse travel? (long)
|
sodium starts moving in, then to make up for it, potassium starts to move out but in a delayed fassion. then once the impulse goes through, the sodium needs to come back in using sodium pumps which require energy. the potassium then slowly comes back in, comes in too much, then leaks out.
|
|
|
saltatory conduction
|
signal "jumping" form node to node in myelinatedaxons.
|
|
|
Acetylcholine
|
Acetylcholine is vital for nervous system functions thatinclude mainly muscle stimulation and also memory formation and learning.
|
|
|
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
|
fight or flight response
|
|
|
Dopamine
|
Affects sleep, mood, attention and learning. lack of it causes parkinson's. excess causes schizophrenia
|
|
|
Serotonin
|
affects sleep, mood, attention and learing. cause of depression
|
|
|
EPSP |
Excitatory postsynaptic potential. a synapse that cause the ligand-gated ion channel to be permeable to both K+ and Na+. cause depolarization of the postsynaptic cell. |
|
|
IPSP |
Inhibitorypostsynaptic potential. cause hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell. |
|
|
GABA |
is the neurotransmitter at most inhibitory synapses in the brain. Binding of GABA to receptors in postsynaptic cells increases membrane permeability to Cl-, resulting in an IPSP. |
|
|
Astrocytes |
glia called astrocytes participate in formation of the blood-brain barrier, a specialization of the walls of brain capillaries that restricts the entry of most substances from theblood into the CNS. |
|
|
Microglia |
immune cells in theCNS that protectagainst pathogens. a glia cell. |
|
|
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) |
the neurotransmitter at most inhibitory synapses in thebrain. Binding of GABA to receptors in postsynaptic cellsincreases membrane permeability to Cl-, resulting in anIPSP. |
|
|
glutamate |
An amino acid that functions asa neurotransmitter in the central nervoussystem. |

