![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The simple sequence of amino acids describes what protein structure?
a. Primary b. Secondary c. Tertiary d. Quaternary |
a. Primary |
|
|
When a protein binds to another protein, what is changed? a. Primary structure b. Secondary structure c. Tertiary structure d. Quaternary structure e. Color |
d. Quaternary structure |
|
|
Which amino acid is not chiral? |
Glycine, the alpha, central carbon binds to two hydrogen atoms. A chiral carbon must be bound to four separate groups. |
|
|
Which of these amino acids is most hydrophobic?
a. Glycine b. Alanine c. Phenylalanine d. Serine e. Methionine |
While Methionine is often considered a hydrophobic (non-polar) amino acid, the fact that it contains a sulfur atom means there will be some polar characteristics. Phenylalanine, on the other hand, has only hydrogen and carbons in its side chain and therefore has no polar characteristics. |
|
|
Draw the structure of methionine. |

|
|
|
Where is proline most likely to be found?
a. In an alpha helix b. In a beta sheet c. In a hydrophobic stretch of amino acids d. In a region of a protein without secondary structure |
In a region of a protein without secondary structure
Because of its unique ring structure, proline is not readily formed into either an alpha helix or a beta sheet. Rather, it is more likely to disrupt these secondary structures. It is, however, a critical component of the three amino acid chains which wind around one another to form collagen. |
|
|
In an alpha helix, hydrogen bonding that stabilizes this structure is found:
a. Between separate chains of amino acids b. Between neighboring amino acids c. Between amino acids in the same chain separated by other amino acids d. Between the peptide bond and neighboring side chains e. Between side chains with polar groups |
Between amino acids in the same chain separated by other amino acids
Remember, one amino acid in an alpha helix forms a hydrogen bond to the amino acid located four downstream in the same peptide chain. |
|
|
Because of the complex hydrogen bonding arrangement in anti-parallel strands of a beta sheet, only two such strands are able to form next to one another.
a. True b. False |
b. False We have numerous examples of proteins formed with multiple strands forming a beta sheet in both the parallel and the anti-parallel conformation. |
|
|
Because of the needs for hydrogen bonding, a beta sheet is unlikely to be located within the hydrophobic interior of a protein.
a. True b. False |
b. False
It is the side chains not the secondary structure that determines the position of a beta sheet within the protein. |
|
|
Where would you expect the following peptide to be located within a protein if it were involved in a beta sheet? (a separate answer for each peptide) |
a. Phe-Leu-Met-lle-Trp (Because all amino acids are hydrophobic, this peptide would be most likely located within the hydrophobic interior of the protein) b. Phe-Ser-Met-Asp-Trp (Because the amino acids alternate between hydrophobic and hydrophilic, this beta sheet would most likely be located on the surface for the protein, with the hydrophobic amino acids oriented towardsthe interior of the nrntein.) |
|
|
What charge will the free amino acid aspartic acid have at neutral pH? a. Positive b. Negative c. No charge |
b. Negative |
|
|
Which amino acid has a pKa nearest to neutral pH? |
Histidine |
|
|
In an alpha helix, the amino acid side chains: |
Extend outward from the center of the helix |
|
|
If the following peptide were part of an alpha helix, where would you expect this peptide to be located relative to the rest of the protein? Phe, Leu, ser, Asp, Val, Ile, Arg, Glu |
On the surface of the protein |
|
|
There can be no more than 3 peptides associated with a single beta sheet |
False |
|
|
The most rigid keratin structure is formed by: |
alpha helical proteins with cysteine |
|
|
The center portion of the alpha helix is: |
Filled with the hydrogen atoms attached to the alpha carbon. |
|
|
If each of these peptides were part of a beta sheet, which would you expect to be most likely to be located on the surface of the protein? |
Phe, Ser, Ile, Arg |
|
|
If each of these peptides were part of a beta sheet, which would you expect to be most likely to be located on the surface of the protein? |
Phe, Ser, Ile, Arg |
|
|
If the pkA of the an amine group is 10, what proportion of the molecules will be charged at pH7.0? |
1000 charged for every uncharged |
|
|
What will the above charge be? |
Positive |
|
|
What is a Zwitterion? |
A molecule or ion having separate positively and negatively charged groups. |
|
|
A peptide bond: |
Is rigid |
|
|
Write the Gibbs equation and explain each of its components. |

|
|
|
What is unusual about proline? |
Its cyclic nature |
|
|
Which of the above amino acids is strictly non-polar: |
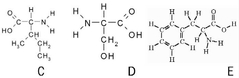
C & E |
|
|
What is the name of amino acid B? |
Cysteine |
|
|
Under what conditions does an –SH bond in an amino acid become involved in a disulphide bond to stabilize protein structure? (What condition is always the case?) |
Under oxidizing conditions |
|
|
If the free carboxylic acid group of an amino acid has a pKa of 4.0, what approximate ratio of these groups would be negatively charged compared to uncharged at pH 7.0? |
1000 charged for every uncharged |
|
|
The amino acid sequence of a protein is considered its: |
Primary sequence |
|
|
If the above peptide were part of an extended alpha helix. What molecular group would the oxygen atom (indicated by double arrows) hydrogen bond to? (all possible answers indicated by single arrows) |
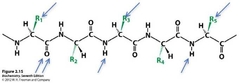
The nitrogen farthest to the right. |
|
|
Which if these describes the peptide bond? |

|
|
|
If a random mutation occurred in the DNA coding a protein, which structure(s) of the protein might be altered? |

|
|
|
At neutral pH which of the following is true of an amino acid? |

|

