![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Scientific method |
1. Observation 2. Question about observation 3. Hypothesis(educated guess that answers your question) 4. Conduct experiment 5. Analyse the data |
|
|
Independent variable |
Parameters of your experiment that you, as the experimenter , will ADJUST. |
|
|
Control |
Parameters of your experiment that will be used to compare to the treatments. |
|
|
Dependent variable |
What is measured by the investigator. |
|
|
Constant variable |
Must be controlled and standardized. |
|
|
Experimental error |
Difference between a measurement and the true value or between two measured values. |
|
|
Scientific data are presented? |
Data graph Line graph Bar graph Pie graph |
|
|
Scientific notation |
A way scientists easily handle very large numbers or very small numbers. ex. 20045 = 2.0045 x 10🔝4 |
|
|
Metric system |
Based on basic units. Length: meters Volume: liters Mass: grams |
|
|
Common metric prefixes |

|
|
|
Light Microscope parts |
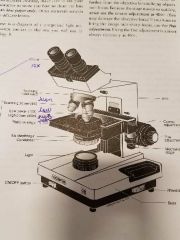
Objective lense: magnifies the specimen by the number on the lens. Coarse adjustment: moves the stage either closer or farther from the objective lens to bring objects into focus. Fine adjustment: brings image into sharp focus. Magnification: determined by multiplying the magnification of the ocular lens. |
|
|
Phases of the cell cycle |

1. Interphase (collectively G1, S, G2) 2. G1 3. S 4.G2 5. Mitosis(prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) 6. Cytoplasmic division |
|
|
DNA Replication |
1.Unzipping •Double-helix of DNA is separated. •Each single-strand is used to make template for new DNA. 2.Base pairing •Once separated the nitrogen base floating in the nucleus pair up with the base on each half of the DNA. •Moves in a 5' to 3' direction. •A bonds with T and G with C. |
|
|
Enzymes necessary for DNA replication? |
DNA polymerase. |
|
|
DNA direction replication? |
5' - 3' |
|
|
DNA replication takes place in? |
Nucleus. |
|
|
When does DNA replication take place? |
S phase in interphase. |
|
|
Transcription |
Process of converting the information found in DNA into RNA format. |
|
|
Transcription takes place in? |
Nucleus |
|
|
When does transcription take place? |
G1 in interphase. |
|
|
Translation |
Converting the information found in RNA into a protein format. |
|
|
Translation takes place ? |
Cytoplasm. |
|
|
When does translation take place? |
G2 in interphase |
|
|
From what organisms did you extract DNA? |
Strawberries. |
|
|
Why did you use soap for the strawberries in DNA extraction? |
Helps dissolve or break apart cell membranes. |
|
|
What did the meat tenderizer do in the DNA extraction? |
Acts as an enzyme to cut proteins away from DNA. |
|
|
Why did you need DNA extraction cold? |
To protect DNA and slow down enzyme activity. So that it can't break apart. |
|
|
Interphase |
Collectively G1, S, and G2. Typical cell spends most of its time. Requires approximately 23 hr. DNA IN preparation for mitosis. |
|
|
S phase |
Cell duplicates all genetic material in the cell. |
|
|
G1 |
Period of cell growth before the DNA is duplicated. (Interphase begins in daughter cells) |
|
|
G2 |
Period after DNA is duplicated. Cell prepares for division. |
|
|
Amoeba cell |

Eukaryotic Viewed: pseudopods, nucleus. |
|
|
Elodea cell |

Eukaryotic. Viewed: cell wall, cytoplasm, cell membranes, chloroplast, nucleus, central vacuole. |
|
|
Cheek cells |
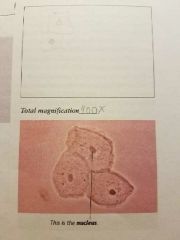
Eukaryotic Viewed: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membranes. |
|
|
Why are dyes needed to see cells? |
To enhance visualisation . |
|
|
Organelles seen in samples with light microscope. |
Elodea: Chloroplast, cell wall, nucleus, central vacuole Amoeba: pseudopods, contractile. Cheek cells: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membranes, bacteria. |
|
|
Biological molecule |
Carbohydrates Lipids Protein Nucleic acids |
|
|
Functional Group |

|
|
|
Monomers |
Carbohydrates: monosaccharide Lipids: glycerol and fatty acids. Nucleic acids: nucleotide Protein: amino acids |
|
|
Polymers |
Carbohydrates: polysaccharide Lipidsl: fats Amino acids: polypeptides Nucleic acids: DNA & RNA |
|
|
Polymers are synthesized? |
By dehydration reaction. Monomers are linked into polymers using a type of reaction called dehydration while polymers are split into monomers using a type of reaction called hydrolysis. |
|
|
Isomers |
One of two or more molecules that have the same chemical formula but different arrangement in the atom space. |
|
|
Structural formula |
Gives orientation of atoms in eachothers others space. |
|
|
Molecular formula |
Type of atoms found in the molecule and the number of each atom. |
|
|
How was glucose tested? |
Benedict's solution(yellow-orange) |
|
|
How we tested for starch? |
Lugol' s solution(iodine). Dark blue/black |
|
|
Testing for protein? |
With combistix strip. |
|
|
Enzyme |
Protein that catalyzed (speeds up) chemical reaction in biological cells without itself being changed into different molecule. Catalase is the enzyme we studied in lab. Heat affects enzymes by breaking them up and denaturizing enzymes. Equation for enzyme reaction: Enzyme + substrate ➡ product + Enzyme Source of enzyme: potatoes Gas that was produced: O2 |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Made up of Nucleotides, which are important building blocks of nucleic acids. |
|
|
4 nitrogenous bases in DNA |
Adenine, Guanine, Cytocine, Thymine. |
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement of particles from a high concentration to a less concentration. (Passive transport) |
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane. (Special case of passive transport) |
|
|
Dialysis |
Diffusion of solute through a semi-permeable membrane. |
|
|
Brownian movement |
Constant molecular motion due to kinetic energy of molecules. |
|
|
How does temperature affect dialysis, diffusion, and osmosis? |
The process will either increase with heat, due to pressure or decrease with cold. |
|
|
Temperature on diffusion directly proportional or inversely proportional? |
Directly proportional to temp. |
|
|
The effect of mass on diffusion directly proportional or inversely proportional? |
Inversely proportional to mass of molecule. |
|
|
Selectively permeable membrane |
Membranes allow some material to pass through and excludes other material based on size and charge. Dialysis experiment: used dialysis tubing as semi-permeable membrane. |
|
|
Hypertonic solution |
Solution with high concentration on solutes. |
|
|
Hypotonic solution |
A solution with lower concentration of solutes. |
|
|
Isotonic soultion |
Solution of equal solute concentration. |
|
|
Dialysis experiment set up |
1. Soaked dialysis tubing with each side cut. 2. Tie off one end of tubing and pour in glucose and starch and ties off other end. 3. Wash bag with tap water and dry, and weigh bag. 4. Placed bag in 250ml beaker of water. Mixed every 15-20 min. 5. 4 test tubes set up. For inside glucose and starch and for outside glucose and starch. 6. Take out bag, dry, and weigh. 7. Untie bag and fill test tubes. Benedict's solution: test glucose(yellow-orange) Lugols iodine solution: starch(Dark blue) |
|
|
Plasmolysis |
Plant cell is placed in hypersonic solution, water from the cell including central vacuole exit the cell via osmosis. Cell membrane shrinks away from cell wall. |
|
|
Do plant cells lyse? |
No, because of rigid walls. Lysis: rupture of cell wall or membrane. |
|
|
Cellular respiration equation |
C6H12O6+6O2➡6CO2+6H2O+ATP Aerobic respiration Takes place in the mitochondria. |
|
|
Photosynthesis equation |
6CO2+6H2O➡ C6H12O6+6O2 ⬇ LIGHT ENERGY Occurs in plants, some bacteria, and protestants. Energy from sunlight to produce sugar. Takes place in chloroplast. 2 stages: light reaction and carbon reaction(or calvin fixation). |
|
|
Yeast experiment |
Measuring production of CO2. Sucrose(table sugar) was the sugar that produce the greatest amount if product(CO2). |
|
|
Measuring Goldfish Metabolism |
Changing the temperature in water changed the rate in oxygen use by decreasing metabolic rate in cold water. |
|
|
Oxygen productionin Elodea |
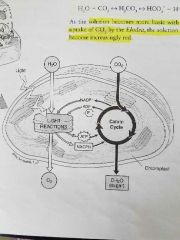
Phenol red solution changed yellow to red due to solution becoming more basic with the increase in CO2. During Calvin cycle plants use CO2 from atmosphere and energy molecules produced during light reactions to produce glucose. |
|
|
Oxygen production in Elodea |
Product of photosynthesis that was produced and measured by collecting bubbles was oxygen. Sodium bicarbonate was used in photosynthesis experiment because it is a good source of CO2, which is used in Calvin cycle. |
|
|
Histone |
A group if basic protein found in chromatin. |
|
|
Mitosis |
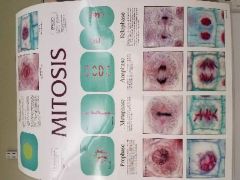
Prophase: chromatin fibers are more tightly coiled, condensing into discrete chromosomes, arranged randomly in nucleus. Metaphase: centromeres of the double chromosomes occupy the equator of the biotic apparatus . Anaphase: separation of the sister chromatids and their passages as "daughter chromosomes" to spindle poles. Telophase: new nuclear membrane are constructed from material that may be remnants of original membrane. Cytokinesis(division of cell) takes place during prophase. |
|
|
Meiosis |
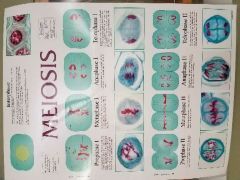
Consist of Meiosis I and meiosis II. Occurs with reproductive cells (gametes). |
|
|
Chromosome |
Threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in nucleus of most living cells, carry genetic info in firm of genes. |
|
|
Chromatin |
Material of which chromosomes of organisms other than bacteria are composed of.(protein, RNA,DNA) |
|
|
Centromere |
Region on chromosome where microtubules of spindles attach. |
|
|
Chromatid |
One-half of two identical copies of replicated chromosome. |
|
|
Haploid (n) |
An individual cell having a single complete set of chromosomes. |
|
|
Diploid |
An individual or cell having two complete sets of chromosomes. |
|
|
Mitotic spindles |
Structure composed of microtubules that segregate chromosomes onto daughter cells during mitosis. |
|
|
Difference between plants and animal cells during mitosis? |
The difference is in Cytokinesis. |
|
|
Meiosis differ in male and femal |
Spermatogenesis: process that produces sperm in males. Oogenesis: process that produces eggs in females. |
|
|
Nondisjuction |
In meiosis occurs when a chromosome pair fails to separate in anaphase I or II. Results in a sperm or oocyte with either 2 copies of the same chromosome or no copies of a particular chromosome. Can cause Down Sydrome(trisomy 21) |
|
|
Karyotype |
Complete set of all chromosomes of a cell of a living organism. Female: X Male: XY |
|
|
Prokaryotic cell |
Lack a nuclear membrane. ex. Bacteria. |
|
|
Eukaryotic cell |
Has a membrane enclosed nucleus and is more complex. |

