![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The innermost layer of the root cortex, which is a selectively permeable barrier that helps control the movement of water and dissolved minerals, is called the |
endodermis |
|
|
Plant cells called _____ are a type of ground tissue that often develop thick secondary walls that become heavily lignified and are dead when mature. |
sclerenchyma *Secondary Sclerenchyma |
|
|
Girdling a tree is eventually lethal because it prevents |
sugar transport to roots |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT typically found in primary plant cell walls? |
lignin |
|
|
Sieve tube members are part of the |
phloem |
|
|
Which of the following can waterproof cell walls, allowing for structures such as watertight conduction channels? |
lignin |
|
|
Among other functions, the ______ of a vascular plant performs most of the photosynthesis that is conducted by the plant. |
ground tissue |
|
|
Cells called ______ are a type of vascular tissue that join end to end in tubelike columns. They develop thick, lignified cell walls and die at maturity, leaving a water-conducting tube. At maturity the ends of the cells are open or have large openings, allowing for enhanced water flow compared to other types of vascular tissue. |
vessel members |
|
|
Which of the following is true of typical plant development? |
Growing tips and zones are present throughout a plant's life, and plant bodies do not have a fixed final size |
|
|
Specialized outgrowths of the plant epidermis called ______ are hairlike projections, such as root hairs. |
trichomes |
|
|
Plant cells called _____ make up the bulk of the soft primary growth of roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits. |
parenchyma |
|
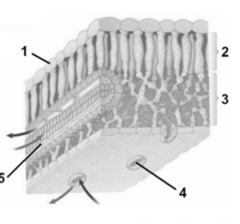
In the internal leaf structure shown, the item labeled "2" is |
palisade mesophyll |
|
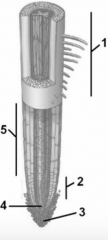
In the diagram of a root tip shown, the item labeled "2" is the |
zone of cell division |
|
|
Which of the following most directly gives rise to primary vascular tissues? |
procambium |
|
|
Companion cells are connected via plasmodesmata to |
sieve tube members |
|
|
Which of the following represents the correct order of structures from outside to inside for a stem that has a vascular cylinder? |
epidermis, cortex, stele, pith *Excuse Carla, She's Picky |
|
|
Starting from the outside and moving in toward the center, which gives the correct order of tissues in the stem of a young tree? |
primary phloem, secondary phloem, secondary xylem, primary xylem |
|
|
Cork cambium produces |
secondary epidermis |
|
|
Growth from apical meristems, generally resulting in an increase in length of a plant, is referred to as |
primary growth |
|
|
Plant cells called ______ form flexible support strands such as the "strings" in celery |
collenchyma |
|
|
Cells called ______ are a type of vascular tissue with long, tapered, overlapping ends. They develop thick, lignified cell walls and die at maturity, leaving a water conducting tube with pits at the tapered ends that allow for lateral water transport between cells. |
tracheids *think trenches |
|
|
The upper angle between a stem and attached leaf is called a(n) |
axil |
|
|
When an apical meristem cell divides, one daughter cell is called the initial and the other is called the derivative. What are the fates of these cells? |
the initial remains part of the apical meristem, and the derivative is used to form primary meristems |
|
|
In response to increased carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, stomata in leaves of some species have _______. |
declined in number |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT typically a main function of stems? |
energy capture |

