![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Function of the kidneys |
Hydrostatic homeostasis: filter blood and produce urine. |
|
|
Where are the kidneys located |
Retroperitonealy |
|
|
Organs of the urinary system |
Two kidneys, two uteres and one urinary bladder. |
|
|
Ways the kidneys contribute to homeostasis |
1. Regulate volume of water 2. Regulate chemical composition of blood 3. Remove waste and uneeded substances from blood 4. Regulate pH of blood 5. Regulate blood pressure (secretes renin) Stimulate erythrocyte production ( secrets eyrthropoetin) |
|
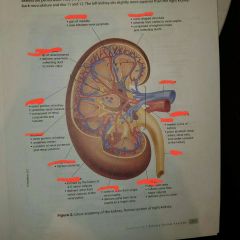
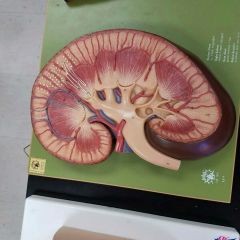
Gross anatomy of kidneys |
|
|
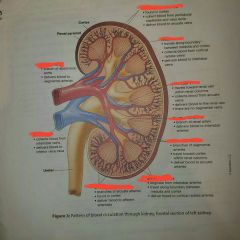
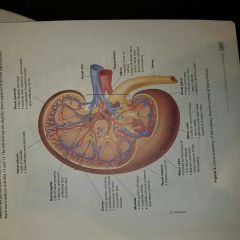
Arteries and Veins of the kidneys |
|
|
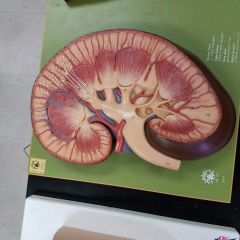
Renal blood flow from Renal artery to cortical radiate arteries |
Renal arteries➡segmental artery ➡interlobar artery➡arcuate artery➡cortical radiate artery➡afferent arterioles |
|
Renal blood flow from cortical radiate Veins to renal Vein |
Cortical radiate vein➡arcuate vein➡interlobar vein➡renal vein➡inferior vena cava. |
|
|
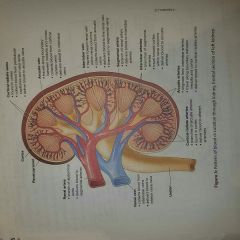
Function of a nephron |
It is the structural unit of the kidneys and performs filtering blood and producing urine. |
|
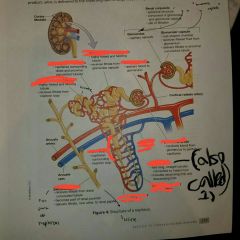
Structures of a renal tubule |
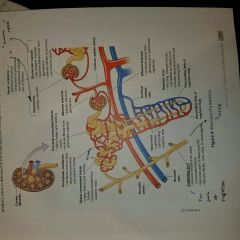
1. Loop of Henle |
|
|
True/false Filtrate is protein free |
True |
|
|
Renal corpuscle= 1.) + 2.) |
1.) Glomerulus 2.) Glomerular capsule |
|
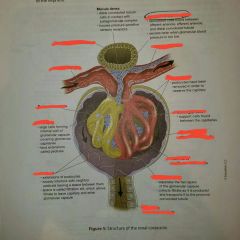
Structures of renal corpuscle |
|
|
|
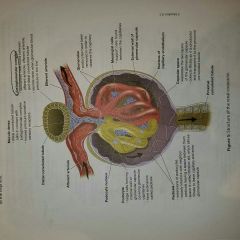
Difference between peritubular capillary beds and Vasa recta? |
Peritubular capillary beds: capillaries surrounding distal and proximal convoluted tubes Vasa recta: capillaries surrounding nephron loop |
|
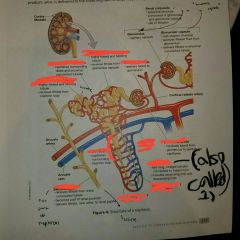
Identify afferent arteriole and vessel that delivered blood to it |
Blood vessel: cortical radiate artery |
|
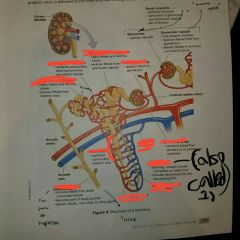
Identify the efferent arteriole and the blood vessel network that the blood vessel with be delivered to afterwards. |
Blood vessel network: Veins or the cortical radiate vein |
|
|
Flow of urine from the distal convoluted tubule to the ureters of the kidneys |
Distal convoluted tubule➡collecting duct➡renal papilla ➡ minor calyx➡ major calyx➡renal pelvis➡ureter |
|
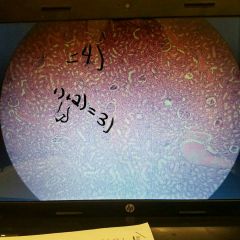
Kidney histology structures (What ET is used?) |
1.) Glomerulus 2.) Glomerular Capsule 3.) Renal Corpuscle 4.) Renal tubule Simple cuboidal epithelium |
|
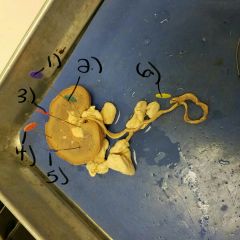
Kidney dissection (structures) |
1.) Renal pyramids 2.) Fibrous capsule (encloses kidney) 3.) Renal pelvis 4.) Renal Cortex (outer part) and Renal medulla (inner part) 5.)Renal columns 6.) Ureter |
|
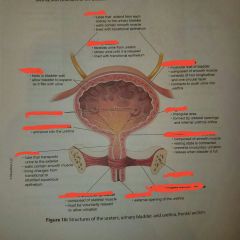
Structures of the bladder |
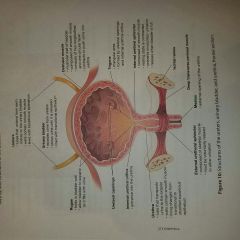
|
|
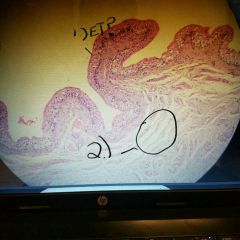
Bladder histology (structures) 1.) ET type 2.) Smooth muscle (T/F) |
1.) Transitional epithelium 2.) True |

