![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Name examples of congenital and acquired causes of infertility
|
Developmental (congenital) defects:
Segmental aplasia, agenesis (absence of parts), hypoplasia, freemartinis |
Acquired defects:
Adhesions, vaginal lacerations, cervical incompetence, urine pooling, conformational defects Abscesses Neoplasia |
|
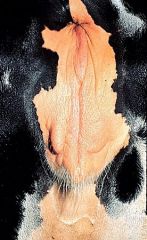
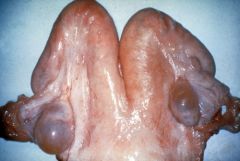
What is the structure in this picture called and what is its significance?
|
Congenital vulvar wattle. May be attached to the external skin of the
vulva but more frequently are attached to the vestibular mucosa. They resemble a rudimentary penis. They are of no clinical significance. Owners frequently think that the cow is a hermaphrodite and may be infertile. |
|
|
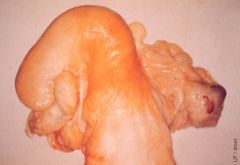
What developmental anomaly is pictures here and what is its significnace?
|
Uterus unicornis (segmental aplasia of the paramesonephric (Müllerian) ducts)
|
Can be fertile or infertile. Can have prolonged periods of
dioestrus due to deficiency of PG from the missing uterine horn ipsilateral to the persistent CL |
|
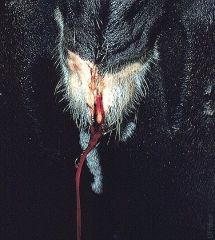
|
Normal vaginal discharge of blood tinged mucus, typically observed 48
hours after the onset of oestrus in some cycling cows & heifers. The amount of blood is usually only slight. The colour varies from that of fresh red blood, to dark, black and subsequently chocolate brown as the interval from the onset of oestrus to its observance increases. Note any bloody vulval discharge from a cow that might be pregnant should be investigated |
|
|
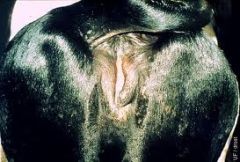
|
Labial insufficiency
•Incomplete labial closure is the result of an old injury of the labia, generally associated with a dystocia |
|
|
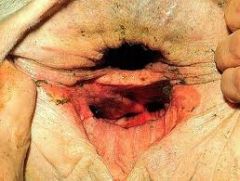
|
Third Degree Perineal Laceration.
In a third degree perineal laceration the dorsal commissure of the vulva, the perineal body and the anal sphincter have all three been disrupted during an excessively forceful delivery usually involving indiscriminate use of a mechanical fetal extractor (calf puller). |
|
|
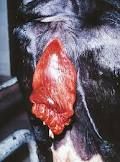
|
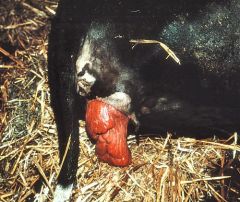
Cervical Prolapse
The enlarged hyperemic cervix can prolapse due to poor vestibular tone and abdominal pressure, when the cow lies down |
|
|
|
What is the aetiology of freemartinism?
|
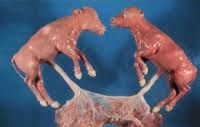
Co-twinning of male and female foetus results in placental fusion (vascular
anastomosis) and exposure of the female foetus to testosterone, mullerian inhibiting substance &/ or expression of the SRy gene in the male at the time when sexual differentiation is occurring (Day 40 of pregnancy) Masculinisation of the female foetus occurs Incidence: >90% of female foetuses cotwinned with a male will be affected |
|
|
|
Follicular Cyst.
Follicular cysts are anovulatory structures. Notice the absence of a corpus luteum. Follicular cysts occur most commonly during the postpartum period (Days 15 to 45) |
|
|

|
Sterility hump
• Seen occasionally in cows with chronic cystic ovarian disease. Elevation of the tailhead can occur as a result of chronic relaxation of the pelvic ligaments due to chronic exposure to elevated concentrations of oestrogen. These cows show frequent behavioral estrus. In the vernacular they are called buller cows. They can be of help in a heat detection program, however their behavior is not consistent. The elevated tailhead is sometimes referred to as the sterility hump. |
|
|
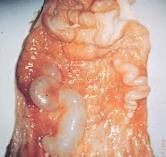
Tubular structures were visualised on the floor of the vagina of a
cow. What is the name of these structures and what is their origin? |
Cysts or Gartner’s ducts
• A linear series of cysts located on the floor of the vagina, remnant of Wolffian or mesonephric ducts in the embryo. • Wolffian duct becomes the vas deferens in males and degenerates in the female. • Potentially 2 • See them on the floor of the vagina as a individual cysts or tubular structure • Do not normally interfere with fertility |
|

