![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
213 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Token ring |
Ring topology where a token is passed between devices to dictate who can transmit. |
|
|
Token ring hub |
Token ring with hub device that controls passing the token. Improves the topology reliability as the hub is less likely to fail as one of the devices attached to the network. |
|
|
Bus topology |
Also known as thinnet. Easy to set up but has numerous issues including being bandwidth inefficient. |
|
|
Star topology |
Most common. With a switch as the hub transmissions only go between the necessary devices and devices can be hot swapped on and off the network. |
|
|
Mesh topology |
Full redundancy. Increased cost to setup and hardware requirements make it unsuitable for general networking applications. |
|
|
Open system interconnect OSI model |
Development in 1984 to describe network functions from the physical interface to the software application. Ensuring compatibility in network hardware and software. |
|
|
Physical layer |
Provides electrical and mechanical connection to the network. Fiber and NICs are examples. |
|
|
Data link layer |
Handles error recovery, flow control, and sequencing. Defines MAC addresses to identify terminals involved in the transmission. Ethernet 802.3 is an example |
|
|
Network layer |
Accepts outgoing messages and combines messages into packets. Adds the header to allow routing. IP is an example. |
|
|
Transport layer |
Concerned with message integrity between source and destination. It also segments and reassembles packets for flow control. TCP and UDP are examples. |
|
|
Session layer |
Provides control functions necessary to establish, manage, terminate connections as required to satisfy the request. Examples are SQL. |
|
|
Presentation layer |
Accepts and structures the messages for the application. Translates the message from one code to another if required. Performs data compression and encryption as well. JPEG is an example. |
|
|
Application layer |
Interacts with programs that incorporates a comm component like email. Logs your message, interprets the request, determines what is needed to support the request. SMTP and HTTP are examples. |
|
|
OSI layer path |
Layer 1: physical: transmit bitstream Layer 2: data link: messages and bits Layer 3: network: route messages Layer 4: transport: messages Layer 5: session: high level protocol Layer 6: presentation:convert/format Layer 7:application:request/response |
|
|
Ethernet |
Originated in 1972, usually uses CSMA/CD collision detection. Devices first listen and when no devices are transmitting it will transmit. Data is transmitted in packet format. Minimum frame size is 64 bytes max is 1518 bytes |
|
|
Packet format. |
Preamble Start frame delimiter Destination MAC address Source MAC address Length type Data Pad Frame check sequence |
|
|
Preamble |
Alternating binary used for synchronization |
|
|
Start frame delimiter |
Eight bit sequence that indicates the start of the frame. |
|
|
Destination MAC address |
MAC address packet is being sent to |
|
|
Source MAC address |
Sender's MAC address |
|
|
Length type |
Indication of the number of bytes in data field If less than 1500. It more than 1500 indicates the data format like IP. |
|
|
Data |
The variable length of data being transmitted |
|
|
Pad |
Used to bring total bytes to 46 if data field isn't big enough. |
|
|
Frame sequence check |
4 byte CRC value used for error detection. |
|
|
MAC address |
6 byte identifier of a network device. |
|
|
IP address |
32bit address divided into four eight bit parts. |
|
|
IP class A |
Governments and large networks. 0.0.0.0 - 127.255.255.255 |
|
|
IP class B |
Mid size companies, universities, etc. 128.0.0.0 - 191.255.255.255 |
|
|
IP class C |
Small networks. 192.0.0.0 - 233.255.255.255 |
|
|
IP class D |
Reserved for multicast groups. 224.0.0.0 - 239.255.255.255 |
|
|
Private IP address blocks |
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 |
|
|
802.11a wireless a |
54mbps 75 feet 5ghz |
|
|
802.11b |
11mbps 100-150ft 2.4ghz |
|
|
802.11g |
54mbps 150ft 2.4ghz |
|
|
802.11n |
Four times faster than G, 200+Mbps, 2.4ghz |
|
|
Network address translation NAT |
Router is assigned one public IP. Devices connected to the router are assigned private IP addresses. Router tracks requests by assigning device's port numbers when using the public IP. |
|
|
Port address translation PAT |
Method a router uses to track local devices when using a single public IP. |
|
|
Ping |
Uses internet control message protocol ICMP to verify if devices are connected to the network. |
|
|
Cat6 |
Twisted pair cables 1gbps up to a 100 meters. |
|
|
Crossover |
Transmit and receive signals are crossed to align two communicating devices ports properly. |
|
|
CSMA/CD |
Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection. Used in Ethernet LAN. |
|
|
Host number |
Post of IP that defines the location of the device connecting to the network. |
|
|
IANA |
Internet assigned numbers authority, agency that assigned IP addresses to networks. |
|
|
ICMP |
Internet control message protocol |
|
|
IEEE |
Institute of electrical and electronics engineers. Standards setting body |
|
|
Link integrity test |
Protocol used to verify that a communication link is established |
|
|
Network number |
Portion of IP address that defines which network the IP packet is from or going to. |
|
|
Organizational unique identifier OUI |
First three bytes of a MAC that IDs the manufacturer of the network hardware. |
|
|
Overloading |
Process the NAT uses to translate private IP addresses to a single public one. |
|
|
Stateful packet inspection SPI |
Type of firewall that inspects incoming data packets to make sure they where requested |
|
|
MAC |
Media access control |
|
|
Building entrance, entrance facilities |
Point where external services interconnect to the interval building cabling. ISP hardware for example |
|
|
Equipment room |
A room where complex equipment like network servers and telephony equipment is stored. |
|
|
Telecommunication closet or enclosure |
Location where cabling from the backbone terminates into the horizontal cabling. |
|
|
Backbone cabling |
Cabling that connects telecommunication closets, equipment rooms, and building entrance. |
|
|
Horizontal cabling |
Cabling that extends from telecommunication closet to the LAN work area, telecommunication outlets in each work space. |
|
|
Work area |
The location where network connected devices like computers are located. |
|
|
EIA/TIA 568B standards |
568B.1 commercial cabling standard 568B.2 twisted pair media 568B.3 Optics fiber standard |
|
|
ACR |
Attention to crosstalk. Compares signal level from transmitter at far end to near end. Determines the cables bandwidth. |
|
|
AXT alien crosstalk |
Unwanted signal coupling from one permanent link to another. |
|
|
Attenuation, insertion loss |
The amount of loss in signal strength as it propagates down a cable. |
|
|
Balanced mode |
Neither wire in a pair connects to ground |
|
|
Delay skew |
Measure of difference in arrival time between the fastest and slowest signal in a utp wire pair |
|
|
EIA |
Electronics industries alliance |
|
|
ELTCTL |
Equal level transverse conversion transfer loss |
|
|
ELFEXT |
Equal level next test but from the far end and does not depend on cable length. |
|
|
Fast Ethernet |
100mbps system |
|
|
Hybrid echo cancellation circuit |
Removes transmit signal from the receive signal |
|
|
LCL |
Longitudinal conversion loss |
|
|
Near end crosstalk NEXT |
Measure of crosstalk within the cable. Higher level being desirable. |
|
|
Nominal velocity of propagation NVP |
Percentage of the velocity of light. |
|
|
Power sum NEXT |
Measures total crosstalk of all four cable pairs. |
|
|
Propagation delay |
Measure of time it takes a signal to propagate down a cable. |
|
|
PSAACRF |
Power sum alien attenuation crosstalk ratio far end. |
|
|
PSACR |
Power sum ACR uses all for cable pairs. |
|
|
PSANEXT |
Power sum alien near end crosstalk |
|
|
PSELFEXT |
Power sum ELFEXT all four pairs to measure signal level against crosstalk. |
|
|
Return loss |
Measures ratio of power put into a cable compared to what comes out. |
|
|
TCL |
Transverse conversion loss |
|
|
TCTL |
Transverse conversion transfer loss |
|
|
TIA |
Telecommunications industry association |
|
|
Macro bending |
Loss of light due to light breaking up and escaping into the cladding. |
|
|
Scattering |
Responsible for 96% of attenuation loss. Caused by refraction of fiber. |
|
|
Dispersion |
Refers to broadening of a light pulse as it propagates down the fiber. |
|
|
Cladding |
Material surrounding the core of an optical wave guide. |
|
|
Attenuator |
Reduces the recieve signal level. |
|
|
Xenpack |
10gb optical to fiber interface. |
|
|
Physical fiber map. |
Shows terrain and routing of fiber. |
|
|
Logical fiber map |
Shows how data is distributed and how fiber is interconnected. |
|
|
Absorption |
Light interaction with fiber. Conversion of optical power into heat |
|
|
Chromatic dispersion |
Broadening of a pulse due to different propagation velocities of spectral components of light pulses. |
|
|
Dense wavelength division multiplex DWDM |
Incorporates the propagation of several 1550nm wavelengths in a single fiber. |
|
|
Dispersion compensating fiber |
Cancels dispersion effects to yield close to zero dispersion in the 1550nm region. |
|
|
Distributed feedback laser DFB |
Ideal for use in a DWDM system |
|
|
Fiber Bragg grating |
Short strand of modified fiber that changes the index of refraction and minimizes intersymbol interference. |
|
|
FTTB |
Fiber to the business |
|
|
FTTC |
Fiber to the curb |
|
|
FTTD |
Fiber to the desktop |
|
|
FTTH |
Fiber to the house |
|
|
Graded index fiber |
Index of refraction is gradually varied parabolically |
|
|
Isolator |
Inline passive device that allows optical power to flow only in one direction |
|
|
Logical fiber map |
Shows how fiber is interconnected and data is distributed. |
|
|
Modal dispersion |
Broadening of pulse due to different path lengths. |
|
|
Mode field diameter |
Actual guided optical power distribution. |
|
|
Numerical aperture |
Fibers ability to accept light. |
|
|
Physical Map |
Shows routing of fiber with details of terrain, underground conduit, and entries into building. |
|
|
Polarization more dispersion |
Broadening of a pulse due to the different propagation velocities of light waves. |
|
|
Pulse dispersion |
Stretching of recieved pulse width because of multiple paths taken by light. |
|
|
Recieved signal level |
Input signal to optical receiver |
|
|
Refractive index |
Ratio of the speed of light in free space to its speed in a given minute. |
|
|
Single mode fiber |
Core diameter 7-10 light follows a single path. |
|
|
SONET/SDH |
Synchronous optical network protocol standard for transmissions in long haul communication |
|
|
STS |
Synchronous transport signals |
|
|
FTTH wavelength |
1600 nm |
|
|
Multimode fiber max length |
2km |
|
|
Single mode wavelength |
1550 and 1310 |
|
|
Multimode cable core size |
62.5 |
|
|
Numerical aperture |
Measure is how well fiber passes light |
|
|
Multimode wavelength |
850 and 1310 |
|
|
OC-3 |
155.52mbps |
|
|
Single mode max length |
80km |
|
|
Parts of a fiber system |
Source. Cable, connectors, photodiode. |
|
|
802.11 WLAN layers |
Physical layer, medium access control layer, media access control management protocols and services. |
|
|
Basic service set |
Fundamental topology of WLAN |
|
|
Direct sequence spread spectrum DSSS |
Used in 802.11b,g,n. |
|
|
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing OFDM |
Used in 802.11a,g,n |
|
|
Multiple input multiple output MIMO |
Splits data into multiple streams, requires multiple antennas. Increased data speed multiplicative of the number is data streams. |
|
|
Backscatter |
Reflection of radio waves striking an RFID tag and reflecting back to the transmission source. |
|
|
Beacon |
Used to verify the integrity of a wireless link |
|
|
Extended service set ESS |
The use of multiple access points to extend user mobility. |
|
|
Hopping sequence |
The order of frequency changes |
|
|
Inquiry procedure |
Used by Bluetooth devices to discover and be discovered by other Bluetooth devices. |
|
|
Paging procedure |
Establishes and syncs a connection between Bluetooth devices. |
|
|
Piconet |
Ad-hoc network of up to eight Bluetooth devices. |
|
|
RADIUS |
Remote authentication dial in user service |
|
|
Slotted aloha |
A wireless network protocol similar to the Ethernet protocol |
|
|
U-NII |
Unlicensed national information infrastructure. |
|
|
Wimax |
30 mile max range. 5.8 and 2.5ghz unlicensed frequencies. |
|
|
Wireless security guidelines |
Turn on security features, use firewall, use encrypted services. |
|
|
Association |
Term used to describe that a wireless connection has been obtained. Provides client MAC address |
|
|
Site surveys |
Supported bandwidth, connection points to network, RF coverage, electrical power |
|
|
SSID |
Used by access points to determine if a data packet is meant for its network. |
|
|
802.1x |
Standard designed to improve the security of wireless networks |
|
|
Data rates of wireless standards |
B 11, a 54, g 54, n 600. Mbps. |
|
|
Cisco leap |
Doesn't require users provide SSID |
|
|
Store and forward |
Entire data frame must be recieved by the switch before it is sent to the final destination. Data packet is checked for errors but takes longer to transmit data. |
|
|
Cut through |
Send data to destination as soon as location is read. |
|
|
Cut through fragment free |
Filters out fragment collisions. |
|
|
Address resolution protocol ARP |
Used to map an IP address to its MAC address. |
|
|
Advertise |
The sharing of route information |
|
|
Aging time |
The length of time a MAC address remains assigned to a port |
|
|
ARP table |
Also called the cache stores MAC addresses for faster routing. |
|
|
Attachment unit interface AUI port |
10mbps Ethernet port. |
|
|
Auxillary input |
Allows logging into the router without a network connection |
|
|
Cisco Network assistant CNA |
Tool that simplifies switch configuration |
|
|
Content addressable memory CAM |
MAC address table used by a switch to identify connected network devices |
|
|
CSU/DSU |
Channel service unit data service unit |
|
|
DTE |
Data terminal equipment, connects a CSU/dsu to outside com services |
|
|
Fast link pulse FLP |
Carries the config information between each end of a data link. Used in auto negotiation. |
|
|
Flooding |
When a switch doesn't have the destination MAC address stored in cam. |
|
|
Gateway |
Network device that enables hosts in a LAN to connect to networks outside the LAN |
|
|
Multilayer switch MLS |
Operates at layer two but functions at higher layers |
|
|
Auto negotiation |
Simplifies LAN config, can max data link through put. Useful in LAN with multiple users with multiple connection capabilities. Link only goes as fast as slowest connection |
|
|
ARP -a |
Shows contents of ARP cache |
|
|
Logical address |
Network address, IP. |
|
|
Association |
That the destination address for a networking device is connected to one of its ports. |
|
|
Bridge advantages. |
Inexpensive, easy to install, avg reduces collision domains. |
|
|
Network bridge |
Isolates traffic, uses MAC address to forward, only forwards data to specific ports. |
|
|
T1 interface |
Serial interface |
|
|
Bridge |
Layer two device that connects two LANs |
|
|
Router console input type |
Rs-232 and rj-45 |
|
|
Router interface to the network |
Auxillary, Ethernet, serial |
|
|
Decimal hex binary table |
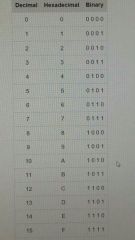
|
|
|
Binary values |
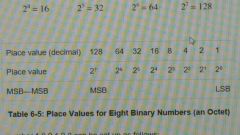
|
|
|
CIDR blocks |
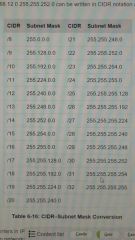
|
|
|
ARP |
Address resolution protocol used to map an IP address to its MAC address. |
|
|
CIDR |
Classless interdomain routing |
|
|
Internet layer |
Defines the protocols used for addressing and routing data packets |
|
|
Network interface layer |
Defines how the hosts connect to the network. |
|
|
Application layer |
Process requests from hosts to ensure a connection is made to the appropriate port. |
|
|
Ipv6 SLA id |
Site level aggregation ID and is used by individual networks to ID the subnets in their site |
|
|
TCP/IP layers |
Application, transport, internet, network interface |
|
|
Subnet mask bit size |
32bit |
|
|
Ipv6 features |
Double colon, 128bits, 32 hex characters. |
|
|
IGMP features |
Data streaming to multiple hosts, no error checking, data is handed to the application it arrives. |
|
|
Brute force attack |
Attacker uses every possible combination of characters for the password. |
|
|
CHAP |
Challenge handshake authentication protocol |
|
|
DES, 3DES |
data encryption standard, triple data encryption standard |
|
|
Dictionary attack |
Uses known passwords and many variations to try and gain access. |
|
|
Diffie-hellman |
Key generation algorithm |
|
|
Directed broadcast |
The broadcast is sent to a specific subnet |
|
|
EAP |
Extensible authentication protocol |
|
|
ESP |
Encapsulating security protocol |
|
|
GRE |
Generic routing encapsulation |
|
|
IKE |
Internet key exchange |
|
|
ISAKMP |
Internet security association and key management protocol |
|
|
MD5 |
Message digest 5 |
|
|
Netstat -a -b |
-a lists all ports currently open. -b displays executable involved in creating the the connection or listening to a port. |
|
|
Packet filtering |
Limits the information that can enter a network |
|
|
Packet sniffing |
A technique in which the contents of data packets are watched. |
|
|
PAP |
Password authentication protocol |
|
|
UDP |
User datagram protocol |
|
|
IPsec protocols |
DES, ESP, AES |
|
|
Cisco command to block broadcasts |
No IP directed-broadcast |
|
|
IP tunnel |
Secure VPN connection between two endpoints |
|
|
Encryption |
Guarantees data confidentiality |
|
|
DDoS defense |
Prevent intrusions |
|
|
Ethernet DIX frame order |
Preamble, destination address, source address, type/length, data, pad, FCS. |
|
|
Data link |
Controls which terminals are sending and receiving |
|
|
Session layer technologies |
SQL and NFS |
|
|
Transport layer technologies |
TCP and UDP |
|
|
VPN |
Concept of extending a private or trusted network over public infrastructure. |
|
|
PPP |
Dial up protocol |

