![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The 1994 __ earthquake killed 33/57 people, injured 7,000, left 20,000 homeless, & caused $20-40 billion in damage. 3 weeks of 3,000 aftershocks. What was unusual about the earthquake? |
Northridge; happened at 4:30 a.m. |
|
|
|
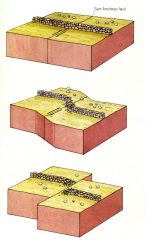
As plate motion progresses, blocks of rock are strained and accumulate __. This builds up until the strength of the rock is overcome, and the rocks break at their weakest points along the fault. The rocks give away, then spring back into a new position. Like a bow and arrow. The distance the arrow flies is proportional to the amount of strain stored in the bow, just as the size of an earthquake reflects the amount of strain energy accumulated in the rocks. |
strain energy; |
|
|
|
Some of the stored strain energy is released in the form of frictional heat as the rocks grind against each other, and some is released as vibrations or ___. |
seismic waves |
|
|
|
This explanation for earthquakes was first developed by ___ who studied the patterns of displacements along the San Andreas fault before and after 1906 earthquake. |
H.F. Reid |
|
|
|
An earthquake is initiated when fault rupture begins, & the point of original rupture is known as the earthquake's __. Earthquakes do not originate at the Earth's surface, but __% originate at depths less than 100 km. Shallow earthquakes 70 km or less are where the largest most historic earthquakes occur. Most earthquakes along the San Andreas originate in the upper __ km of the crust. |
focus; 90%; 10 km |
1989 Loma Preita earthquake 18 km and 1994 Northridge earthquake 19 km unusual for being on San Andreas fault |
|
|
Deep earthquakes happen 70-300km below where rocks are plastic not brittle anymore. Happen in subduction zones. 1964 ___ earthquake is the strongest recorded in U.S. with 30 km depth. |
Alaska |
|
|
|
A __ is an abrupt line or zone breaking through the rocks or sediments. The rocks or sediments on either side do not match up. ___ were created by forces no longer operating and unlikely to be a source of earthquakes. __ are capable of earthquakes. |
fault; inactive fault; active fault; |
|
|
|
How can you recognize an active fault? |
1. Earthquake occur on them today. 2. Earthquakes have occurred on them in historic time. 3. They displace young features or materials (think cross cutting relationships). |
|
|
|
During a single earthquake, only a part of a fault might slip, This slipped surface is known as the __ for that earthquake. Large magnitudes with ruptures along a great area of a fault. |
ruptured surface; |
|
|
|
___ are active faults lie concealed beneath the surface. Hazard for urban areas. |
blind faults; |
|
|
|
Seismic waves travel outward from the point of original rupture. They arrive at the Earth's surface first at the __, the point closest to the earthquake's focus. |
epicenter |
|
|
|
Name the two types of body waves that propagate through solid rock and the two types of surface waves that travel at or near the ground surface. Place them in order of speed. |
P wave (primary wave) S wave (secondary wave) Love waves Rayleigh waves |
|
|
|
- fastest - alternating push and pull (compression/dilation) - May be transmitted as sound wave when it hits surface. - Rumbling/sonic boom. |
P wave (primary wave) |

|
|
|
- slower body wave - propagates through rock by a sideways motion at right angles to the direction of travel. (Similar to shaking jump rope.) - At surface, shakes ground surface with both vertical & side-to-side motion. - responsible for most of the damage from shaking. |
S waves (secondary waves) |

|
|
|
-Surface wave - moves similar to S waves except motion is ONLY side-to-side. - Damaging to structures. |
Love waves |

|
|
|
- Surface wave - Slowest type of wave. - Moves across surface like ocean waves producing both horizontal & vertical motion. |
Rayleigh waves |

|
|
|
Seismologist use the time difference between the first arrival of P waves and the first arrival of S waves to determine the distance between an earthquake's focus & a seismograph station. Knowing this distance for 3 or more stations, it is possible to locate the point of origin. Can take days sometimes. |
An important characteristic of both types of body waves is they reflect/refract or bed when they encounter boundaries between different rock layers. The reflected waves amplify ground shaking. |
|
|
|
U.S. Geological Survey & California Institute of Technology in Pasadena responsible for seismograph network in southern CA. U.S. Geological Survey in Menlo Park & UC Berkeley for North. |
More than 1,000 strong-motion sensors placed throughout state. |
|
|
|
__ record earthquakes by capturing relative motion between a suspended pendulum and the vibrating earth. Incoming seismic waves are recorded as electrical signals on tape or as lines on a paper drum. |
Seismographs |
|
|
|
Charles Richter of CIT developed first system for measuring earthquake SIZE using wiggly lines of seismograph records. ___ of an earthquake uses the amplitude of waves recorded by a seismograph as an indicator of the energy released during a quake. |
Richter magnitude |
|
|
|
Richter scale made specifically for CA, but used worldwide. In CA, magnitudes are generally equivalent to the reported local magnitude. |
The Richter scale is weak after magnitudes above 7.5. |
|
|
|
Since 1990s, CA seismologists used ___ (Mw) as a measure of earthquake size. 1972, based on seismic moment of an earthquake. Takes into account both area of ruptured surface & amount of displacement. |
moment magnitude (better for larger earthquakes). |
|
|
|
Earthquake magnitudes are logarithmic meaning each whole number increase on the scale is a __fold increase in amplitude & a __fold increase in the amount of energy released. |
tenfold; thirtyfold; |
|
|
|
A great earthquake strikes Earth about once every __ years. |
5 years |
27 quakes 5.7-7.0 have hit CA since 1979. |
|
|
The ___ is used to categorize earthquake intensity. Focuses on intensity of shaking perceived by observer or structural damage. Two additional factors are the __and ___. |
modified Mercalli scale; bedrock/soil (unconsolidated sediments are worse farther away than bedrock near earthquake); Type/density of structures (poorly build houses, etc.); |
|
|
|
__ generally causes the greatest damage during an earthquake. Worse where unconsolidated sediments saturated with water and artificially filled lands. Pipes and water mains ruptured easily so many fires. 80-90% of destruction in SF 1906 from fire. |
Ground shaking |
|
|
|
The process by which ground shaking transforms wet/saturated, sandy sediment into an unstable, dense fluid during an earthquake. |
liquefaction |
|
|
|
Gravity driven movement or rock and soil down a slope due to weak rocks. Earthquakes can cause this. |
landslides |
|
|
|
CA coast is vulnerable to __. They are created when an earthquake ruptures the ocean floor, or as a result of huge submarine landslides or volcanic eruptions. Earthquakes with vertical displacement (often subduction zone types) cause the water above the sea floor to be displaced. A series of long waves radiates outward from the point of rupture. They pile up along the shoreline to create a wall of water more than 30 m high. Can originate anywhere in Pacific Ocean. Safer in San Andreas because horizontal motion. |
Tsunamis. |
Crescent City tsunami after Alaska earthquake (went as far down to SF, SC, & LA). Cascadia subduction too near Eureka. Some active faults off CA coast in south. Santa Barbara & Ventura areas. |
|
|
The most comprehensive of earthquake programs is the ___ 1977 to reduce risk to life & property from earthquakes in the U.S. Identify active faults, look at patterns from past especially those quiet sections of active faults which pose the greatest danger. Excavate trenches to measure displacement & look at young materials. Date old materials from past earthquakes is paleoseismology. Based on these studies there is 62% chance of 6.7 in SF in next 30 years & __% for south CA. |
National Earthquake Hazards Reduction Program (NEHRP); 85% |
foreshocks not very helpful. |
|
|
Other predictors are foreshocks, electrical resistivity, changes in dissolved radon gas in groundwater, water well levels, bulging of ground surface, radio wave signals. |
1989 U.S. Geological Survey map of San Andreas showed possiblity 1988-2018. Earlier map of this type showed Loma Prieta earthquake possibility. |
|
|
|
Several things determine how much damage will result from ground shaking. |
1. amplitude 2. Duration 3. frequency of vibrations 4. Peak acceleration |
|
|
|
15 seconds of shaking during Loma Prieta earthquake had lasted a few additional seconds, the Embarcadero Freeway in SF would have entirely collapsed. |
k |
|
|
|
Some materials & structures respond to vibrations by amplifying the motions at particular frequencies. If frequency of some of the earthquake vibrations matches the natural ___ of the soil beneath the structure of the structure itself, then the stress on the structure is increased.
|
resonant frequency. |
Unconsolidated sediments or artificial fill w/ high water can greatly amplify ground shaking. |
|
|
Peak acceleration. A structure exposed to vertical accelerations greater than _g or 100% of the force of Earth's gravity would be airborne unless fastened to the ground. Before 1971 measured acclerations 0.35-0.5 but then San Fernando earthquake had 1.25 g & Northridge 1.8g. |
1g |
|
|
|
Impossible to build structures that remain motionless during earthquake, but can build structures that can withstand strong ground shaking. Unified motion of building is a good sign rather than different motions. |
Bad: Multistory, split-level houses, on stilts. |
|
|
|
__ buildings are relatively resistant because light & flexible, but still can be damaged. Most dangerous structures in CA are unreinforced __ buildings built before 1940. Masonry is heavy, strength depends on mortar holding it together. Buildings need to be anchored. |
Wood-frame; brick; |
|
|
|
Long Beach 1933 moderate earthquake killed 120 mostly because poor construction. Led to ___ which requires state approval & inspection of both plans & construction of school buildings. Amended twice in 1967 adding inspection of older school buildings, with replacement or strengthening by 1975 & proposed all school sites to be inspected to avoid sitting within a fault zone or in a landslide area. |
Field Act; |
|
|
|
1971 __ moderate earthquake 15 seconds killed 65 worse if 5 more seconds. 2 hospitals, freeway destroyed. Van Norman Dam surface broke away, but half full so spared disastrous flood. This earthquake is responsible for CA's current legislation for seismic safety & activity because more studied than any other. |
San Fernando earthquake |
|
|
|
1927 International Conference of Building Officials established the __ in an attempt to bring standardization to all aspects of building construction. Updated every 3 years. Extensively modified after 1971 San Fernando quake. More surprising amount of damage to the welds in __-frame buildings has been of particular concern. |
Uniform Building Code; steel; |
|
|
|
___ 1972 prohibits the construction of most human-occupied structures within 50 feet of an active fault based on CA Geo Survey maps of past 11,000 faults. People with property in area before this unable to remodel their home. Also requires property owners to disclose existence of any active faults in property being sold. Enforcement/exemptions are the responsibility of local planning agencies. |
Alquist-Priolo Earthquake Fault Zoning Act; |
|
|
|
__ Act to strengthen hospitals. ___ 1973 strengthen dams & prepare evacuation plan. Seismic Safety Element part of general plan. |
Hospital Safety Act; Dam Safety Act; |
|
|
|
___ 1986 required CA local governments to make an inventory of URM buildings & to develop earthquake hazard mitigation programs for those buildings by 1990. URM buildings pose one of the greatest hazards. |
Unreinforced Masonry (Brick) Building Law |
|
|
|
Since 1976, __ earthquakes with magnitudes estimated or measured at 6.0 or great occurred in CA, western Nevada, & the northern part of Baja CA. ___ on San Andreas Fault. |
206; 117; |
|

