![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The primary benign tumor that is found primarily in the LA is _____. This is the most common BENIGN tumor found in adults. |
Myxoma |
|
|
____ % of myxomas found in adults are benign. |
30% myxoma |
|
|
A myxoma is usually attached to the ______by a stalk on the____ atrial side. |
IAS Left atrial side |
|
|
Pedunculated means it is attached by a ____. |
Stalk |
|
|
The texture of the myxoma is usually different than the _____. It is smooth, rounder or oval. |
Myocardium |
|
|
A myxoma often hinders proper closure of the valve during ______ causing _____ to happen. |
Systole Regurgitation |
|
|
If the myxoma is mobile and it drops through the valve during diastole, it will mimic mitral or tricuspid ______. |
Stenosis |
|
|
The size of the myxoma can be estimated by direct measurements with the calipers |
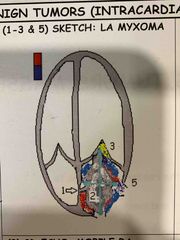
The cross in blue is direct measurement |
|
|
Size of myxoma measured with planimetry |
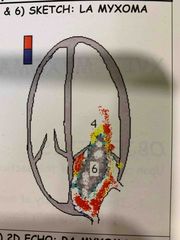
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Complications of myxoma are |
Embolization, infection, fever, weight loss,hemolytic anemia, arthralgia (joint pain), rash, clubbing of fingertips, sudden death, regurg and stenotic complications |
|
|
Treatment of myxoma is |
Surgery Follow up study to check for recurrences. With benign recurrence is rare |
|
|
Another benign tumor that affects the valves(most common) is the ______. |
Papillary fibroelastoma |
|
|
With Papillary fibroelastoma, the valve most commonly affected in adults is/are ______. In children the valve most commonly affected is____. |
Aortic and mitral (mv more typical) Tricuspid |
|
|
With Papillary fibroelastoma the tumor is on the ______ stream side of the valve. |
Down |
|
|
The Papillary fibroelastoma tumor rarely exceeds ___ cm in diameter. It is a dense, Mobil mass with a consistency that closely resembles the _____ ____. |
1cm Chordae tendineae |
|
|
With Papillary tumor, the treatment is _____ and____. |
Anti coagulation Surgery depending on location |
|
|
Another BENIGN tumor is FIBROMA. It's a _____ tumor that is frequently embedded in the myocardial wall of the _____ or the ______. |
Bulky Ventricles IVS |
|
|
FIBROMA typically presents during ______. It is associated with other complications such as dysrhythmias, ______, heart failure and sudden death. |
Childhood LVOTO |
|
|
Treatment for Fibroma is ____,or ____ with children who have a very large LV FIBROMA. |
Surgical removal Heart transplant |
|
|
Benign tumors and their locations. 1-5 |
1. Myxoma = usually LA can be in RA, usually attached to I AS 2. Papillary fibroelastoma = valvular, adults aortic and MV, kids TV 3. FIBROMA = LV, myocardial wall or IVS 4. Lipoma= IAS and looks like a dumbbell. 5.Rhabdomyoma= LV |
|
|
_______ is a well encapsulated tumor that is composed of mature fat cells. Very large in size and may have an associated ________. This is the second most common BENIGN tumor. Most commonly located in the ____. Looks like a_____ in appearance. Treatment can be ____. |
Lipoma Pericardial effusion IAS dumbbell Surgery |
|
|
______ is a yellowish gray tumor(s) found in the _____ walls or intracavity. Multiple tumors might be present. This is the most common cardiac tumor found in _____. ____ Is the most common sight. Many present within the first year of life and greater than 90% by the age of 15. |
Rhabdomyoma Ventricle Children LV |
|
|
With Rhabdomyoma, it is associated with _____ ______ |
Tuberous sclerosis, rare diseases that causes tumors to grow in skin, organs etc.Also associated with obstruction of conduction pathways, and ventricular tachycardia. |
|
|
With Rhabdomyoma, ____ may result due to an obstruction of the conduction pathways and ventricular tachycardia. Treatment is _____ but can be impossible to remove. |
Heart failure Surgical excision |
|
|
Two types of primary malignant tumors are _____ and_____. |
Angiosarcoma and sarcoma |
|
|
_______ is the most common primary malignant tumor. It is seen most often in the_____. These tumors often have an association with____ and_____. |
Angiosarcoma Right atrium Pericardial effusion and tamponade |
|
|
_____ is a malignant tumor with a wide variety of types to include rhabdomyosaroma, fibrosarcoma, and osteosarcoma. It is most commonly seen in the____. May need surgery to obtain an accurate diagnosis. Prognosis is poor. |
Sarcoma Right atrium |
|
|
Secondary tumors (metatastic) are more common than primary malignant tumors. Most secondary metastasize from lymphoma, melanoma, lung cancer and breast cancer. They freq travel to the ____, then the____, and then the _____. The tumors that metastasize from the IVC into the RA and RV are _____ and_______ cancer. The tumors that metastasize from the pulmonary veins into the LA are _____ cancer. Patients presents with PEff, tamponade,HF and dysrhythmias. Prognosis depends on primary treatment. |
Pericardium, myocardium, endocardium Renal and liver Lung cancer |
|
|
Extracardiac tumors is a tumor anywhere in the vicinity of the heart. ____ involvement is common. |
Pericardial |
|
|
_____ heart disease is the result of a metastisizing carcinoid tumor (usually from the____ or ____ ) that secretes serotonin. If tumor metastasize to the liver, the serotonin is deposited on the _____ linings of the right heart. Serotonin does not travel to the left heart because the serotonin is inactivated in the _____. |
Carcinoid Appendix or ileum Endocardial Lungs |
|
|
The echo findings with carcinoid heart disease are: TV appears______ and____, they do not open and close. TR is often_____ along with____. TS and PS is rare Leads to right heart ____ |
Fixed and rigid Severe, PI Failure |
|
|
A _____ usually forms in areas of akinesis, or dyskinesis. Always document ______ abnormalities, ventricular ______ and chamber ____. |
Thrombus Wall motion Function Size |
|
|
There are different types of thrombus.1-4 |
1. Layered 2. Single 3. Peduculated 4. multilobulated |
|

Tech to use to interrogate thrombus. |
👌 |
|
|
Left atrial thrombus is usually associated with mitral ____, and left atrial _____ and _____. |
Stenosis Enlargement Afib |
|

LA thrombus |
👌 |
|
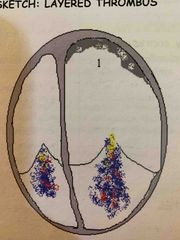
Layered thrombus |
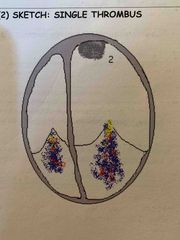
Single thrombus |
|
|
A ____ is a foreign body, such as a bullet, knife, or nail etc. |
Missile |
|
|
With echo, a missile appears as an ______ structure with strong ______. Rule out all of these p. 272 |
Echogenic Reverberations |
|
|
Things that are mistaken for masses or thrombus. Aberrant trabeculation in 4C,3C |
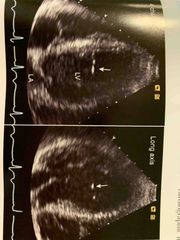
Abberrant trabeculation |
|
|
Christa terminalis in RA |
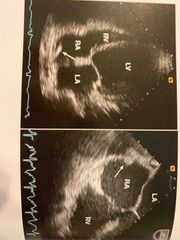
Christa terminalis |
|
|
Eustachian valve, by IVC in RA. |
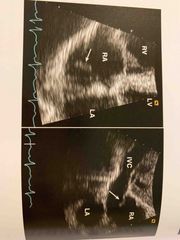
Eustation valve |
|
|
Eustachian valve, by IVC in RA. |
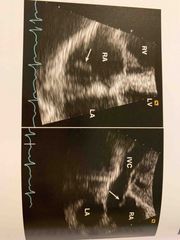
Eustachian valve |
|
|
Normal LAA |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Dilated coronary sinus |
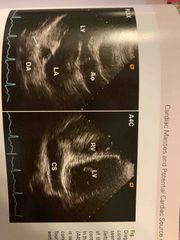
Dilated coronary sinus |
|
|
Aortic valve veg secondary |
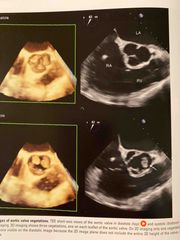
You see the on TEE One one TTE |
|

Secondary |

Primary |
|
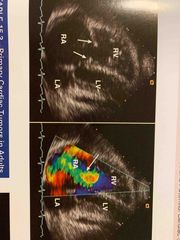
Carcinoid heart disease is caused from a build up of____ in the endocardial lining. |
Serotonin |
|
|
Carcinoid heart disease is caused from a build up of____ in the endocardial lining. |
Serotonin |

