![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the hallmarks of stem cells? (2)
|
(1) Self-renewal: generating more stem cells indefinitely
(2) Differentiation: non-specific stem cell developing into particular cell types with specific characteristics and functions |
|
|
Pluripotent, multipotent, unipotent
|
(1) pluripotent- embryonic stem cells & induced pluripotent cells; can differentiate into any cell type
(2) Multipotent stem cells- neural stem cells and intestinal stem cells; can differentiate into some different cell types (3) Unipotent stem cells- esophageal basal cells; only one cell type |
|
|
Where are embryonic stem cells from?
|
Inner cell mass of a blastocyst. The inner cell mass has the potential to develop into an embryo.
|
|
|
How are induced pluripotent stem cells generated?
|
By reprogramming somatic cells using stem-cell transcription factors. You can do this by virus mediated overexpression strategy (Yamanaka was the first person to do this) or use of small compounds, chemicals, or proteins
|
|
|
Neural stem cells can generate more than one mature cell type (3)
|
Multipotent;
(1) Map2+ve- process and transmit information (2) Olig2+ve- provide support and nutrition to nerve cells (3) Gfap+ve- provide structural support |
|
|
Epithelial cell organization
|
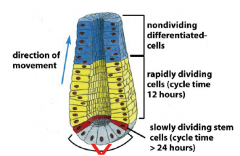
Stem cells in the crypt (which are multipotent), rapidly dividing cells are in the middle, nondividing differentiated cells at the villus at the top. The stem cells give rise to the cells above them. This was found by tracing Lgr5-positive stem cells
|
|
|
Cre-Loxp system
|
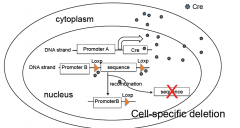
Cre is an enzyme that cuts out specific DNA sequence, Lox-p. Promoter A transcribes Cre. Cre goes into the nucleus and cuts out Loxp. If there are two Loxps, the sequence in between them is removed. This allows you to do a cell specific deletion. This is irreversible
|
|
|
CreER-Loxp system
|
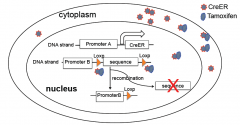
ER (estrogen receptor) is fused to Cre to keep the CreER fusion protein in the cytoplasm. Tamoxifen (estrogen homolog) binds to ER and brings CreER into the nucleus. Cre-mediated (Cyclization recombination) DNA recombination occurs at the Loxp site. Allows temporal (because you can add tamoxifen whenever you want) and cell specific lineage tracing or gene deletion.
|
|
|
Lineage tracing of Lgr5-positive crypt cells
|
Example of using the CreER-loxp system to trace the cells that came from a stem cell in the crypt. In normal cells, lacZ is not expressed. Lgr5 is only expressed in stem cells, so Lgr5-CreEr mouse line was made. When tamoxifen is injected, lacZ is expressed, activates Lgr5 which is labeled. Showed that cells above the stem cell come from that stem cell. Rosa26 is the promoter that drives transcription of downstream gene.
|
|
|
Multicolored Lineage tracing
|
Replace LacZ with four different fluorescent proteins, can see the multiple types of intestinal cells that the intestinal stem cells become
|
|
|
Multicolored lineage tracing & CreER with lung epithelial cells
|
Showed that clara cells are the stem cells for the lung. They can give rise to ciliated cells & proliferate
|
|
|
Tetracycline transgenics
|
Spatial and temporal control of expression. Target gene expression is induced by deoxycycline rapidly, and the level of expression can vary with the dose of deoxycycline. Different promoters can be used to activate transgene expression in various tissues.
|
|
|
Tet-Cre system
|
Need three mouse lines. Also achieves spatial and temporal control of expression. Without dox, doesn't promote cre, with dox expresses cre which cuts out the sequence you want to delete. The advantage of it is that it's reversible.
|
|
|
What controls proliferation of intestinal stem cells?
|
Signaling molecules and transcription factors. Wnt signaling.
|
|
|
Wnt signaling
|
At the crypt, Wnt pathway is active so the cells proliferate. Above the crypt, Wnt pathway is inactive. Hyperactivation of Wnt leads to overproliferaction of crypt cells. Activation of Beta-catenin with Cre-loxp system induces expansion of crypt cells. Without Wnt, Beta-catenin is degraded
|
|
|
Stem cell niche
|
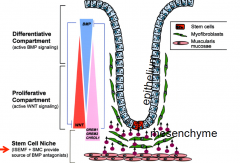
A cellular environment that allows stem cell to maintain "stemness". Grem1/Grem2 signals from the mesenchyme blocks BMP. BMP signaling induces differentiation of stem cells. WNT promotes proliferation of cells.
|
|
|
What is important for maintaining intestinal homeostasis?
|
Crosstalk between the epithelium and mesenchyme. It's mediated through the activities of many signaling pathways
|
|
|
Uses for iPS cells (4)
|
(1) Disease modeling (2) Drug toxicity screening and drug discovery (3) supply genetically matched cells for transplantation (Autologous transplantation) (4) Supply cells that have disease-causing mutations repaired by gene targeting and correction technologies
|
|
|
What are the Yamanaka factors that lead to iPCs? (6)
|
Oct4, Klf4, Sox2, c-Myc, Nanog, and Lin28
|
|
|
Why is protein-based reprogramming efficiency low?
|
virus has additional functions- can activate toll like receptor. It activates p65 and IRF3 which leads to epigenetic modification which primes cells for reprogramming.
|
|
|
How can you facilitate efficient nuclear reprogramming?
|
You can put the peptide with an irrelevant retrovirus which accelerates Cell permeant proteins-induced pluripotent gene expression
|
|
|
TLR3 & TRIF
|
Knocking down TLR3 or TRIF causes fibroblasts to exhibit impaired nuclear reprogramming mediated by virus vectors. TLR3 activation enhances reprogramming.
|
|
|
SImilarities between cancer cells and stem cells (2)
|
(1) They can proliferate indefinitely
(2) The transcription factors and signaling proteins that are important for maintaining stem cells are also important to cancer cells. |
|
|
Leukemia stem cells
|
If a mutation happens to a stem cell, can lead to a leukemia stem cell which can self renew. This explains tumor heterogeneity and relapse of leukemia
|
|
|
Extrinsic influences on cancer cells
|
May be an explanation for tumor heterogenity. Tumor environment is different than normal cell environment, and this can make cells react differently.
|
|
|
Context of stem cell properties as a function of leukemia disease stage
|
From normal stem cells to refractory period, the hierarchical structure, defined stem cell phenotype, and the frequency of LSC's decreases. Self renewal mechanisms, and drug resistant mechanisms increases
|
|
|
Where have cancer stem cells been found? (3)
|
Breast cancer, brain tumors, and colon cancer
|
|
|
Characteristics of cancer stem cells (7)
|
(1) Self-renewal (2) Resistance to noxious stimuli (3) increased activity of survival cascades (4) differentiation (5) Symmetric division/asymmetric division (5) invasion and metastasis (6) reduced rate of proliferation (7) Higher number of drug resistant pumps
|
|
|
How can you detect CSC's?
|
Cancer stem cells can pump out dye while regular ones can't so they won't be labeled with dye.
|
|
|
What is the cell origin for CSC? Two hypotheses
|
From normal stem cells or from differentiated cells that were dedifferentiated?
|
|
|
What happened when Apc in crypt stem cells was deleted?
|
Caused transformation of intestinal stem cells. So intestinal stem cells may be the origin of intestinal cancer. Used Cre-ER lineage tracing system to find this. Deleting Apc in differentiated intestinal cells did not lead to tumor formation.
|
|
|
Sox2 overexpression
|
Showed transformation in CreER system in esophagus
|
|
|
How do stem cell principles effect development of cancer therapy?
|
Can use them to target cancer stem cells with drugs
|
|
|
Why would breast cancer originate in primitive cells? (2)
|
(1) Stem cells are long-lived so they could accumulate more genetic lesions
(2) Stem cells have similar properties to cancer cells |
|
|
Why can't we ablate cancer stem cells with chemotherapy? (3)
|
(1) ATP binding casset (ABC) drug transporters can protect CSCs from chemotherapeutic agents
(2) Having an active DNA-repair capacity (3) Resistance to apoptosis |
|
|
BikDD
|
A mutation of components in Bcl-2 family which are proapoptotic. It can eliminate CSCs in breast cancer because it leads to increased apoptosis. It's also been shown to kill regular tumor cells.
|
|
|
Stochastic vs Hierarchical model
|
The stochastic hypothesis says that every cancer cell has an equal opportunity to repopulate cancer. Hierarchical hypothesis says there are cancer stem cells which explains the relapse and refractory of cancer.
|
|
|
Evidence of stochastic model
|
One paper found that cancer cell populations can convert phenotypic states randomly from cancer stem cell to regular cancer cells and vice versa. This is described with a Markov model which predicts equilibrium of phenotypes.
|

