![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the 4 characteristics that allow muscle tissue to perform? |
Excitability Contractibility Extensibility Elasticity |
|
|
|
Name the 3 types of muscle tissue: |
Cardiac Smooth Skeletal |
|
|
|
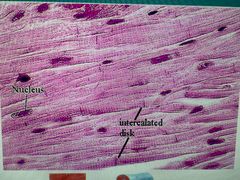
Found only in heart Short, branching (striated) Involuntary Contains intercalated discs |
Cardiac muscle |
|
|
|
Short fibers Spindle/kayak shaped Found in hollow organs Non-striated Involuntary |
Smooth muscle |
|
|
|
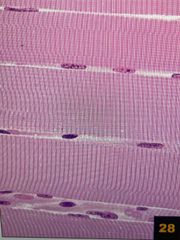
Long, straight fibers Mostly attached to bones Voluntary Striated |
Skeletal |
|
|
|
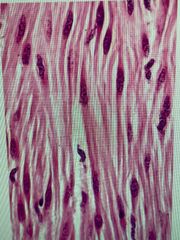
Short fibers Spindle/kayak shaped Found in hollow organs Non-striated Involuntary |
Smooth muscle |
|
|
|
4 functions of SKELETAL muscle |
Movement Maintain posture/position Stabilize joints Generate heat |
|
|
|
What is a single skeletal muscle cell called? |
Muscle FIBER |
Multiple nuclei |
|
|
Cytoplasm of a muscle cell |
Sarcoplasm |
Contains large amount of myoglobin- A pigment that holds reserve supply of oxygen in muscle |
|
|
Cell membrane of a muscle cell |
Sarcolemma |
Contain T-Tubules - invaginations that extend into middle of muscle fiber |
|
|
Elaborate NETWORK of membranes Whos function is to store calcium |
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum |
|
|
|
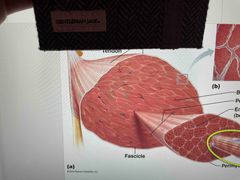
Individual muscle fiber surrounded by dense connective tissue |
Endomysium |
|
|
|
Smallest component of a muscle fiber |
Filament |
|
|
|
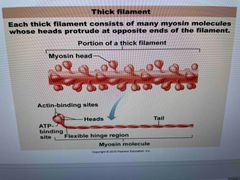
What filament is composed of the protein myosin? |
Thick filament |
|
|
|
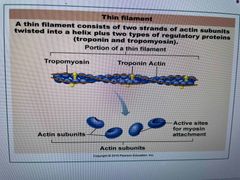
What 3 proteins create a thin filament? |
Actin Tropomyosin Troponin |
|
|
|
Binds to myosin during contractions |
Actin |
|
|
|
Covers myosin binding sites on action |
Tropomyosin |
|
|
|
Attached to tropomyosin at rest Binds Ca2+ (calcium ion) during contractions |
Troponin |
|
|
|
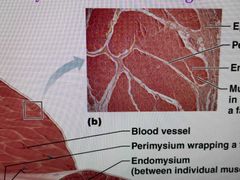
Bundle of many muscle filaments together |
Myofibril |
|
|
|
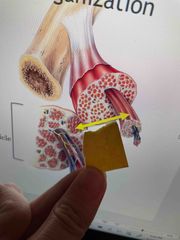
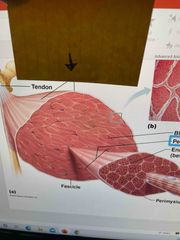
Bundle of muscle fibers together |
Fascicle |
|
|
|
Dense, irregular connective tissue that surrounds each individual fascicles |
Perimysium |
|
|
|
A bundle of fascicles with similar functions |
Whole muscle |
|
|
|
A bundle of fascicles with similar functions |
Whole muscle |
|
|
|
Dense, irregular connective tissue that surrounds the ENTIRE muscle |
Epimysium |
|
|
|
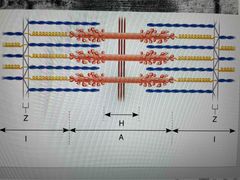
Functional unit of skeletal muscle contraction Due to myofibril not being long enough |
Sarcomere |
|
|
|
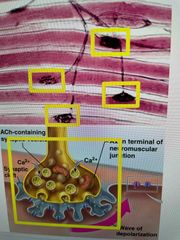
Site where a motor neuron meets a muscle fiber |
Neuromuscular Junction |
AKA: motor end plate |

