![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Binomial Coefficient (Formula)
|

|
The number of ways of arranging k successes among n observations
|
|
|
Binomial Probability (Formula)
|
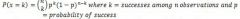
|
|
|
|
Binomial Mean (Formula)
|
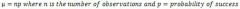
|
|
|
|
Binomial Standard Deviation (Formula)
|
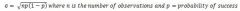
|
|
|
|
Geometric Probability (Formula)
|

|
|
|
|
Geometric Mean (Formula)
|

|
|
|
|
Geometric Standard Deviation (Formula)
|
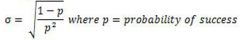
|
|
|
|
Geometric Probability of the Success greater than a number of Trials (Formula)
|
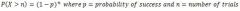
|
|
|
|
Geometric Setting
|
1. Each observation falls into one of just 2 categories: success or failure.
2. The observations are all independent. 3. The probability of a success, p, is the same for each observation. 4. The variable of interest is the number of trials required to obtain the first success. |
Ex.
Flip a coin until you observe a tail. |
|
|
Binomial Setting
|
1. Each observation falls into one of just 2 categories: success or failure.
2. There is a fixed number n of observations. 3. The n observations are all independent. That is, knowing the result of one observation tells you nothing about the other observations. 4. The probability of a success, p, is the same for each observation. |
Ex.
When an opinion poll calls residential telephone numbers at random, only 20% of the calls reach a live person. You watch the random dialing machine makes 15 calls. X is the number that reach a live person. |
|
|
Binomial Random Variable
|
The random variable X = (number of successes) in a binomial setting.
|
To do so, one must calculate the probability that P(x=k) for all values n through k. These probabilities should sum to a value close to one, in order to encompass the entire sample space.
|
|
|
Binomial Distribution
|
The distribution of the count X of successes in a binomial setting. n = the number of observations, p = the probability of success on any one observation, X = the whole numbers from 0 to "n".
|
B(n,p)
|
|
|
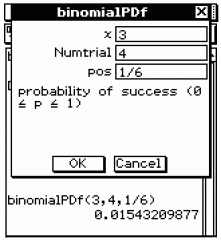
Probability Distribution Function (PDF)
|
Function that assigns a probability to each value of X when given a discrete random variable X.
|
|
|
|
Cumulative Binomial Function (CDF)
|
Function that calculates the sum of the probabilities for 0, 1, 2, . . . , up to the value X when given a random variable X. It finds the probability of obtaining at most X successes in "n" trials.
|
|
|
|
Binomial pdf
|
Given a discrete random variable X, the probability distribution function (pdf) assigns a probability to each value of X.
Use: 2nd VARS, A |
|
|
|
Binomial cdf
|
Given a random variable X, the cumulative distribution function (cdf) of X calculates the sum of the probabilities for 0,1,2..., up to the value X. That is, it calculates the probability of obtaining at most X successes in n trials.
Use: 2nd VARS, B |
|
|
|
P(X>n)
|
P(X>n) = (1-p)^n
|
|
|
|
Normal Approximation
|
Use when np ≥ 10 and n(1-p)≥10
|
2 conditions
|
|
|
Factorial n! = ?
|
n!= n*(n-1)*(n-2)*........*3*2*1
|
|
|
|
Probability Distribution Function (pdf)
|
Given a discrete random variable X, pdf assigned a probability of each value of X.
|
|

