![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Benign Tumor
|
Tumor has no effect
|
|
|
|
Malignant tumor
|
Invades surrounding cells
|
|
|
|
Metastasis
|
Cells break away
|
|
|
|
Genes
|
Section of DNA that has instructions for making protein
|
|
|
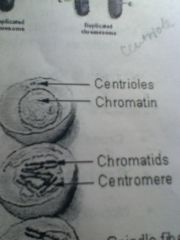
|
-time in between division
-DNA is copied here |
Interphase
|
|
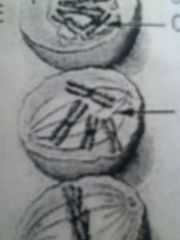
|
Chromosomes condense
Sister chromatids pair up Nuclear membrane disappears |
Prophase
|
|
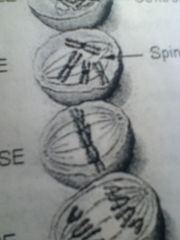
|
Paired chromatids line up in the middle of the cell
|
Metaphase
|
|
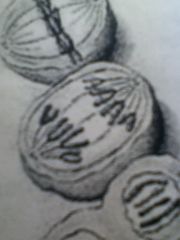
|
Chromatids are pulled into the two daughter cells (v shaped)
|
Anaphase
|
|

|
Cells start to separate and nuclear membrane reforms
|
Telophase
|
|
|
Mutation
|
A change in the sequence of DNA
|
|
|
|
Phenotype
|
Physical traits if an individual
|
|
|
|
Genotype
|
Description of the alleles for a particular gene
|
|
|
|
Homozygous
|
Both alleles are identical
|
Purebred
|
|
|
Heterozygous
|
The gene ha two different alleles
|
|
|
|
Recessive
|
The phenotype of an allele is seen only when recessive
|
|
|
|
Dominant
|
The phenotype is seen when homozygous or heterozygous
|
|
|
|
Sex linked disorders
|
- colorblind
- muscular dystrophy - hemophilia - baldness ( sex linked disorders are recessive!) |
Four types
|
|
|
Osteoblasts
|
Deposit mineral salts an collagenous fibers. Build up bones.
|
|
|
|
Osteocytes
|
Maintains bone tissue and bone cells
|
|
|
|
Osteoclasts
|
Break down bone tissue
|
|
|
|
Diaphysis
|
Shaft of a long bone
|
|
|
|
Epiphysis
|
Ends of long bones
|
|
|
|
Metaphysis
|
Area between the diaphysis and the epiphysis. Contains the epiphyseal plate
|
|
|
|
Articular cartilage
|
Hyaline cartilage that covers the ends of movable joints
|
|
|
|
Periostem
|
Outer covering of long bone
|
|
|
|
Medullary cavity
|
Houses marrow
|
|
|
|
Endusteum
|
Inner lining of medullary cavity
|
|
|
|
Process
|
Any projection from the surface of the bone
|
Bone marking
|
|
|
Condyle
|
"Knuckle" a large rounded prominence on a bone
|
Bone marking
|
|
|
Trochantor
|
A large blur process found only on the lateral side of the femur
|
|
|
|
Tuberosity
|
An elevated, rounded, usually roughened area of a bone
|
Bone marking
|
|
|
Tupercule
|
A small rounded process
|
|
|
|
Foramen
|
An opening or hole in a bone
|
Bone marking
|
|
|
Fossa
|
A depression or groove on a bone
|
Bone marking
|
|
|
Meatus
|
A tube like passageway running within a bone
|
|
|
|
Sinus
|
A space within a bone lined with a mucus membrane that reduces the weight of a bone
|
Bone marking
|
|
|
Type of bones
|
1. Long bones
2. Short bones 3. Irregular bones 4. Sesamoid bones 5. Flat bones |
Five types
|
|
|
Long bones
|
Have a distinct diaphysis
Longer than wide Humerus, ulna... |
|
|
|
Short bones
|
Somewhat cube shaped bones
Wider than long Carpal and tarsal bones |
|
|
|
Flat bones
|
Protect organs
Cranial bones, sternum, scapula, ribs... |
|
|
|
Irregular bones
|
" other" category
Facial, vertebrae... |
|
|
|
Sesamoid bones
|
Small bones situated in tendons where considerable pressure develops
Patella, hyoid... |
|
|
|
Cervical vertebrae
|
Neck
|
7
|
|
|
Thoracic vertebrae
|
Attach to ribs
|
12
|
|
|
Lumbar vertebrae
|
Lower back
|
5
|
|
|
Sacrum
|
Pelvic bones
|
5
|
|
|
Coccyx vertebrae
|
Tail bone
|
4
|
|
|
Scoliosis
|
Lateral curving of the spine usually in the thoracic an lumbar region
|
|
|
|
Kyphosis
|
Hunchback exaggeration of the thoracic region
|
Abnormal curvature
|
|
|
Lordosis
|
Swayback exaggeration if the lumbar curvature
|
Abnormal curvatures if the spine
|
|
|
Tendons
|
band of dense fibrous connective tissue extending from muscle to bone
|
|
|
|
Ligaments
|
A band or cord of dense fibrous connective tissue that is extended from bone to bone
|
|
|
|
Sprains
|
Forcible wrenching or twisting of a joint with partial or complete rupture or injury to joint attachments without dislocation
|
|
|
|
Strains
|
Pulling or over stretching a muscle
|
|
|

|
1. Frontal
2. Parietal 3. Occipital 4. Temporal 5. Nasal 6. Zygomatic 7. Superior maxillary 8. Ethmoid 9. Mandible |
|

