![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Sulfate |
SO4 2- |
|
|
|
Sulfite |
SO3 2- |
|
|
|
Carbonate |
CO3 2- |
|
|
|
Phosphate |
PO4 3- |
|
|
|
Ammonium |
NH4+ |
|
|
|
Ammonia |
NH3 |
Not an ion! |
|
|
Nitrate |
NO3- |
|
|
|
Nitrite |
NO2- |
|
|
|
Molecule |
2+ chemicals connected by a chemical bond |
|
|
|
Compound |
Different atoms bonded together |
|
|
|
Mega |
10E6 |
M |
|
|
Kilo |
10E3 |
K |
|
|
Deci |
10E-1 |
d |
|
|
Centi |
10E-2 |
c |
|
|
Milli |
10E-3 |
m |
|
|
Micro |
10E-6 |
U |
|
|
Nano |
10E-9 |
n |
|
|
Pico |
10E-12 |
p |
|
|
Overlap of e- cloud? |
In molecular compounds in covalent bonds |
|
|
|
Group 1 |
Alkali metals |
Very reactive |
|
|
Group VIII |
Noble gases |
Very unreactive |
|
|
Group VII |
Halogens |
Non-reactive metals |
|
|
Methane |
CH4 |
|
|
|
Oxidizing agent |
Gets reduced (loses e-) |
|
|
|
Reducing agent |
Being oxidized (gaining e-) |
|
|
|
Soluble |
Li, Na, K, NH4, NO3-, C2H3O2- |
|
|
|
Strong Base |
OH-and Group I and II Metals |
|
|
|
Strong Acid |
H+, HClO4, HCLO3, H2SO4, HI, HBr, HCl, HNO3 |
|
|
|
Metal activity (most) |
Group I and II Metals, displace H2 from H2O and acids |
|
|
|
Metal Activity (least) |
Cu, Ag, Au, Hg. Displace H2 from acids, but not water |
|
|
|
Metal Activity (moderate) |
All other metals. Cannot displace H2 |
|
|
|
Giga |
10E9 |
|
|
|
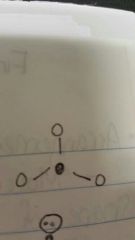
Trigonal planar |
|
|
|
|
Bent |

|
|
|
|
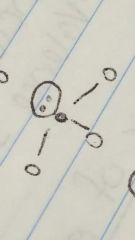
Trigonal pyramidal |
|
|
|
|
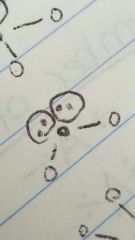
Bent (tetrahedral) |
|
|
|
|
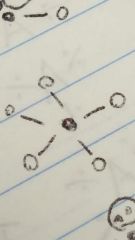
Trigonal bipyramidal |
|
|
|
|
Seesaw |
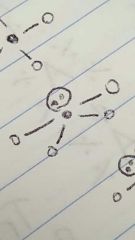
|
|
|
|
T-shaped |
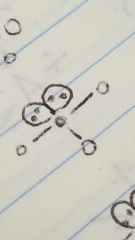
|
|
|
|
Linear |
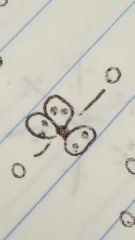
|
|
|
|
Square pyramidal |
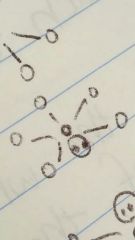
|
|
|
|
Square planar |
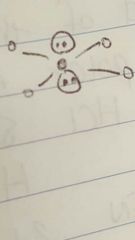
|
|
|
|
Cis |
Same side |

|
|
|
Trans |
Opposite sides |
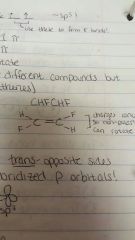
|
|
|
Move right phases |
Endo |

|
|
|
Move left phases |
Exo |

|
|
|
Strong IMF |
Small vapor pressure, high Tm and Tb |
|
|
|
Weak IMF |
Large vapor pressure, low Tm and Tb |
|
|
|
Endothermic reactions are? |
Decomposition, vaporization and melting. All others are exo! |
|
|
|
Finding delta H from q |
Whatever q is in one mole of the substance |
|
|
|
n |
1 to infinity. Describes energy and size of orbital |
|
|
|
L |
0 to n-1. Describes shape of orbital |
|
|
|
ML |
-l to +l. Orientation of orbital |
|
|
|
Pauli principle |
No 2 e-s in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers |
|
|
|
Hunds rule |
Electrons will occupy different orbitals with the same spin |
|
|
|
Paramagnetic |
One or more unpaired electrons. Attracted to magnet |
|
|
|
Unusual e- configurations |
Cr, Cu, Ag and Au |
|
|
|
Ionization energy |
Lowest energy needed to remove an electron from an atom |
400-2400 kj |
|
|
Electron affinity |
Energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom |

|
|
|
Pressure |
The amount of collisions on a wall |
|
|
|
How do you get a salt? |
Acid plus base yields acid plus water |
|
|
|
Redox reaction |
The more reactive element displaces the less reactive element |
|
|
|
Transition metals (naming) |
Cation followed by anion. Roman numerals |
|
|
|
Molecular compound naming |
Preceeded with Greek prefix |
|
|
|
Hess's law |
DH1 + DH2 = DH3 |
|

