![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pathway of air |
1. Mouth 2. Larynx 3. Trachea 4. Bronchus 5. Bronchi 6. Bronchioles 7. Alveoli |
|
|
Pulmonary Edema |
Left ventricle failure, hypertension, lung fluid |
|
|
Atelectasis |
Lung collapse, surfactant bubbles |
|
|
Pneumothorax |
Lung collapse-inverted glass of water |
|
|
Bronchiolitis |
Inflamed. mucus |
|
|
Bronchiectasis |
Dilated bronchi, poor mucus movement, bad breath (bacteria) |
|
|
Respiratory S&S |
1. Dyspnea
2. Cyanosis- hypoxia 3. Pain 4. Cough -productive |
|
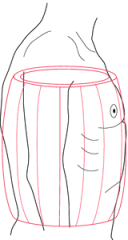
Barrel Chest |
Chest shape in emphysema patients |
|
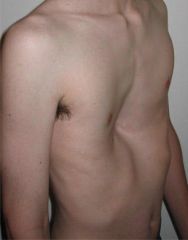
Pigeon Chest |
Chest shape seen in children with asthma due to constant intercostal breathing and thoracic recruitment to breathing |
|
|
Spinal conditions that may provoke secondary pulmonary complications |
Scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis |
|
|
Tracheal Sounds |
Over lung sounds may indicate consolidation or pneumonia |
|
|
No sound |
may indicate collapsed lung, pneumothorax, or pleural ephusion |
|
|
Wheezing and Ronchi |
Obstructive sounds due to partial blocking of the bronchi and bronchioles |
|
|
Crepitations and Crackles |
Short duration sounds due to opening and closing of airways |
|
|
Plural Rub |
Squeak on inhalation and exhalation indicates pleuritis or pleurisy |
|
|
Enhanced Vocal Sounds
|
Indicates solid areas- Consolidation or pneumonia |
|
|
"Solid" Percussion |
Indicates possible consolidation. Hollow sound is good |
|
|
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
Chronic Bronchitis or Emphysema |
|
|
COPD Type A "Pink Puffer" |
Typically emphysema: loss of alveoli elasticity, barrel chest |
|
|
COPD Type B "Blue Bloater" |
Typically chronic Bronchitis: Productive cough at least 3 months >2 years |
|
|
Asthma |
Acute, reversible, inflammatory, obstructive pulmonary condition secondary to bronchial sensitivity |
|
|
Intrinsic Asthma |
Exercise induced, infection |
|
|
Extrinsic Asthma |
Allergen-induced (mold, smoke, perfume) |
|
|
Conditions with dyspnoea |
Chronic bronchitis Asthma Pneumonia ARDS |
|
|
Conditions with cyanosis: hypoxia |
Pulmonary infarction ARDS |
|
|
Pain |
Pleura fracture Tumor |
|
|
Cough |
Asthma Cystic fibrosis |
|
|
Productive Cough |
Chronic Bronchitis Pneumonia TB |
|
|
Neuropraxia |
-Relatively short term -Block of motor or sensory function without nerve injury |
|
|
Axonotmesis |
-Nerve sheath remains intact -Axon may grow back (1mm/day) |
|
|
Neurotmesis |
-Axon and nerve sheath are damaged -No path to grow back |
|
|
Sensation Testing |
Two point discrimination |
|
|
Tinel's Sign |
Tapping along nerve to find the problem |
|
|
Neural Tension Test |
Straight leg raise and slump test |
|
|
Upper Limb Neural Tension |
Medial, Radial and Ulna Nerve test |
|
|
Neuroma |
Clump of nerve cells growing without direction |
|
|
Wallerian Degeneration |
Myelin sheath deteriorates back to the previous Node of Ranvier |
|
|
Radiculopathy |
Nerve root compression (dermatome, myotome, sclerotome) |
|
|
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome |
Compression of medial nerve -Phalen's wrist flexion test |
|
|
Guyon's Canal |
Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome |
Compression of nerves from neck go into axilla |
|
|
Bell's Palsy |
Facial Palsy |
|
|
Radial Nerve Conditions |
Crutch Palsy Post-Humeral Fracture |
|
|
Bumper Injury |
-Fibula head fracture -Below knee cast -Common peroneal injury -Foot drop |
|
|
Lateral Cutaneous Nerve of thigh entrapment |
compression between the upper front hip bone and the inguinal ligament near the attachment at the ASIS |
|
|
Peripheral Neuropathy |
30% associated with diabetes |
|
|
Degenerative Arthritis |
Osteoarthritis |
|
|
Inflammatory Arthritis |
Rheumatoid Arthritis |
|
|
OA Primary |
Unknown etiology Age Related Some genetic links in the hands |
|
|
OA Secondary to |
Joint injury, obesity, repetitive joint stress, joint infections, hemophilia |
|
|
Loose bodies may be irritants to joint |
Crepitus or locking |
|
|
Fibrillation |
Cracking of cartilage surface |
|
|
Eburnation |
Joint becomes bone on bone and becomes polished |
|
|
Osteophytes |
Boney spurs that may develop at joint margins |
|
|
Genu Valgus |
atrophied quad, hamstring spasm |
|
|
Genu Varus |
Knees out |
|
|
Genu Recurvatum |
knees curved back |
|
|
OA Hip |
Pain in the groin not the hip |
|
|
Trendelengerg gait |
hip abductor weakness |

