![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
McLuhan's prediction |
Emergence of "global village" from spread and development of information tech |
|
|
|
Medium is the Message |
Content of things is the least important aspect of our exp w/ culture |
A story could stay the same but it could be told from a movie instead of a book |
|
|
Hot Media |
Rich in one sensory (little for imagination) Little audience participation Brief & intense exp
|
Music, movies |
|
|
Cold Media |
Engages multiple senses Needs audience's involvement Longer, sustained exp |
Comics |
|
|
McLuhan and Media Trend |
Transitioning from hotter to colder mediums for communicating things |
Tv over film, Internet over TV |
|
|
Technological Determinism |
Tech shapes and determines social and cultural developments |
|
|
|
Tech Determinism changes |
New or changing mediums cause us to act and think differently |
Wording for googling and texting Or attention span when reading any form of text |
|
|
Tribal Era |
Oral comm of storytelling Pre-literate societies Interdependent societies |
|
|
|
Print Era |
Written comm Intro of alphabet led to linear and rational thinking (systematic thought) Preserving information |
|
|
|
Electronic Era |
Both written and oral comm Extending visual and aural senses Global awareness |
|
|
|
Global Village |
Interconnection through internet creates tribal-esque connection |
|
|
|
Intentional Theory of Representation |
Repre refers to meaning intended by ppl who produce them Meaning however is not something the author can completely control |
Painting means what painter intended |
|
|
Reflective Theory of Representation |
Repre either reflects or distorts the meaning Meaning of some repre is not always about true or false |
News reports |
|
|
Constructionist Theory on Representation |
Meaning is constructed by the way it's repre (things don't have meaning before repre) |
|
|
|
Semiotics |
Study of signs and language Everything is text and Everyone is a reader |
|
|
|
Signifier, Signified, Sign, Referent |
Symbol, interpretation (denotative/connotative), both, thing being referred to by sign |
|
|
|
Naturalization |
Ideas widely shared and common to appear universal |
|
|
|
Encoding |
Power tries to fix meaning and close interpretation Signs and other repre are encoded to encourage preferred meaning |
|
|
|
Decoding |
Meanings have to be decoded, but audience may not always read things as expected |
|
|
|
Dominant Hegemonic |
Type of reading that reflects interests of existing social order |
|
|
|
Oppositional |
Reading that challenges official meanings |
|
|
|
Negotiated |
Reading that incorporates dominant and oppositional codes in contradictory ways |
|
|
|
Capitalism |
Market economy which property and wealth are owned privately |
|
|
|
Socialism |
Planned economy which property and wealth are owned collectively |
|
|
|
Tribal societies |
Hunter-gatherer society No social class or labour division |
|
|
|
Ancient Civilization |
Slave society Slave-noble |
|
|
|
Feudalism |
Agricultural society Peasant-aristocrasy |
|
|
|
Critique of Capitalism |
1. Capitalist-worker 2. Caps own production line, works sell labour 3. Works exploit by caps 4. Works alienated under caps 5. Capitalism plagued by economic crisis (unemployment) 6. Works lead revolution against caps |
|
|
|
Alienation |
Feeling of powerlessness and separation They view human institutions as alien (beyond their control) |
|
|
|
Types of Alienation |
1. From the product (not entitled to product of work) 2. From the process (less control over work circumstances) 3. From others (exp as hostile) 4. From nature (perform uncreatively) |
|
|
|
Ideology |
Ideas that are reflective of a social group Dominant ideas that shape the thinking of groups |
Seeing the world through certain lenses
Or common sense that preserves existing social order |
|
|
Marx on Ideology |
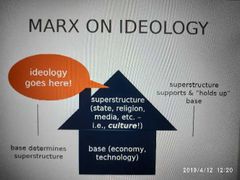
|
|
|
|
Frankfurt School |
Jews who fled Nazi Germany to California; left 1 form of fascism for another; totalitarianism isn't different from liberal democracy |
|
|
|
Explaining Nazism |
Nazis came into power through parliamentary road; fascism was voted into office; liberal democracy led to totalitarianism |
|
|
|
Cultural industry |
Mass culture makes us blindly accept things in culture without critical thing of it; popular culture isn't popular |
|
|
|
High vs. Low Culture |
High embodies sophosticated aesthetic Low is for the oppresses toiled masses and reflects their values and struggles |
|
|
|
Frankfurt School on Culture |
It's suppose to represent intellect but celebrates mediocrity; it's now produced industrially |
|
|
|
Popular Culture |
Not popular at all; isn't shaped by masses but is imposed upon them |
|
|
|
Neurosis |
Unconscious impulse to satisfy desires; gains upper hand on indiv |
|
|
|
Cure for neurosis |
Understsnding psychoanalysis and using the "talking cure", self-thinking of impulses leads to overcoming it |
|
|
|
Psychoanalysis in reverse |
As it was studied to give people rational control, mass cultures studied it to manipulate masses |
|
|
|
Incorporation |
Process which the ways of subcultures are appropriated by dominant cultural order; from opposition against society, to society norm outrage, to mainstreaming |
|
|
|
The gaze |
Cinematic exp produced spectatorship, unseen voyeurs, voyeuristic pleasure |
|
|
|
Male gaze |
Voyuerism in cinema is from a straight male perspective through representations of women being body objectification and eroticism |
|
|
|
The navel |
Women now depicted as active, independent, sexually poweful |
|
|
|
Problem with navel |
Images of empowered women can lead to seeking empowerment through purchasing and in service of own desires (not men or society) |
|
|
|
Stereotypes |
Representation and "knowledge" of the other; not just for hate, but also desire |
|
|
|
Post modern culture |
Through tech, perception of reality and signs are changing; perceiving articifial as natural |
|
|
|
Simulcra |
Signs preceding referents; repre not referring, but constructing reality |
|
|
|
Hyperreality |
Simulations feel more real than the genuine article |
|
|
|
Placebo Effect and its reverse |
Idea that actions have no effect but feelings of participation allow us to fall into it; reverse when ppl don't believe in feeling of participation |
|
|
|
Public sphere |
Forum where issues affecting all of society can be raitionally debated |
|
|
|
Retreating from the public |
Capitalism is believed to be causing people to spend as much away from the public sphere |
|
|
|
Economic Globalization |
Liberalization of trade between nations |
|
|
|
Political Globalization |
Undermined power of nations to dictate their own affairs |
|
|
|
Tech & Media Globalization |
Proliferation of mass media and info comm tech (circulation of images and info) |
|
|
|
Oreintalism |
Fetishism of East vs. West |
|
|
|
Holocaust etiquette |
Was a singular, unique event Must be treated seriously Historical records can't be altered |
|
|
|
Race as social construction |
To notice skin colour and consider them as signs of racial identity |
|
|
|
Cause of race differences |
As modern scientific culture got obsessed with classifying differences (plants, animals, places), racial diff were biologized and naturalized |
|
|
|
From classifying to stereotyping |
As race has become unreliable as a way for classification, stereotyping became the strategy to make boundaries |
|
|
|
Stereotypes |
A way to reduce ppl to simple features taken as fixed by nature (sometimes establishes binaries) |
|
|
|
Challenging stereotypes |
1. Reversing (embracing negatives and making the desirable) 2. Positive image (creating positive view on stereotyped groups) 3. Opening practice (satire) |
|
|
|
Panopticon |
18 century Brit prison design to min violence with max security |
|
|
|
Private Sphere |
The idea of chosen isolation, however it is disappearing through self security |
|
|
|
Industrial vs. Surveillance capitalism |
Labour to nothing between product or service; from wealth from sellings goods to data extraction |
|

