![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Phacomatosis |
heredofamilial group of congenital disseminated hamartomas |
|
|
features of Von Hippel Lindau |
retinal haemangiomas cerebellar and spinal haemangiomas bilateral pheochromocytoma renal cysts and carcinoma |
|
|
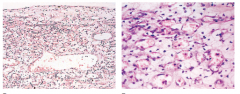
Capillary haemangioma |
|
|
Sturge Weber Syndrome |
Unilateral (rarely bilateral) meningeal calcification, facial nevus flammeus(port-wine stain, phakomatosis pigmentovascularis),frequently along the distribution of the trigeminalnerve, and congenital glaucoma.
Cavernous haemangioma |
|
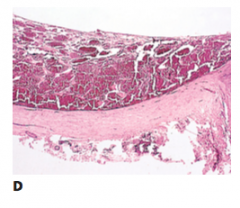
|
Cavernous haemangioma associated with SWS |
|
|
NF1 |
Two or more:
six or more café-au-lait spots>5 mm in greatest diameter in prepubertal personsand 15 mm in postpubertal persons, Two or moreneurofibromas of any type or one plexiform neuro-fibroma; freckling in the axillary, inguinal, or otherintertriginous region; optic nerve glioma; two ormore Lisch nodules; a distinctive osseous lesion(e.g., sphenoid bone dysplasia); a first-degreerelative who has NF-1. |
|
|
Chromosome and inheritance pattern of NF 1 |
AD Chromosome 17 |
|
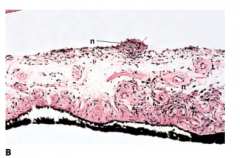
|
Lisch Nodule |
|
|
ocular features of MENII |
prominent corneal nerves |
|
|
Tuberous Sclerosis clinical triad |
Mental retardation + Seizures + adanoma sebaceum (angiofibroma) |
|
|
Ocular findings |
Lid angiofibroma Retinal glial hamartoma ON Glial hamartoma Iris and Ciliary body neuroectodermal hamartoma |
|
|
what is the meaning for the genetic short hand terms p, q, +, -, r, t |
p = short arm, q = long arm, + = increase in length, − = decrease in length, r = ring form, and t = translocation.
|
|
|
what does 47, 21+ mean |
trisomy 21 |
|
|
aniridia and Wilms’ tumor syndrome
|
Deletion of chromosome 11p (aniridia–genitourinary–mental retardation syndrome—AGR triad) shows aniridia as its main ocular finding. The chromosome band 11p13 has been associated with it
|
|
|
Ocular features of congenital rubella |
Cataract (30%) Glaucoma (9%) Salt and pepper retinopathy, Iris anomalies (poorly developed dilator muscle) |
|
|
Name and describe the 3 types of anopthalmia |
Primary anophthalmos: caused by suppression of theoptic anlage during the mosaic differentiation of theoptic plate after formation of the rudiment of the fore-brain
Secondary anophthalmos: caused by the complete suppression or grossly anomalous development of the entire anterior portion of the neural tube. Consecutive or degenerative anophthalmos: caused byatrophy or degeneration of the optic vesicle after it has been formed initially. |
|
|
Microphthalmos
|
a congenital condition in which the affected eye is smaller than normal at birth (<15 mm in greatest diameter; normal eye at birth varies between 16 and 19 mm).
|
|
|
oculocerebrorenal syndrome of miller |
Wilms’ tumor, congenitalnonfamilial aniridia, and genitourinaryanomalies.
Deletion of chromosome 11 |
|
|
Why is Aniridia is a misnomer?
|
The iris is not absent but is hypoplastic andrudimentary
|
|
|
nanophthalmos vs mircophthalmos |
microphthalmos, is a developmental disorder of the eye in which one (unilateral microphthalmia) or both (bilateral microphthalmia) eyes are abnormally small and have anatomic malformations. Different from nanophthalmos in which the eye is small in size but has no anatomical alterations.
|

