![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
177 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
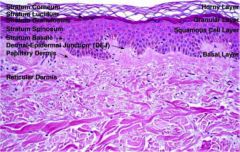
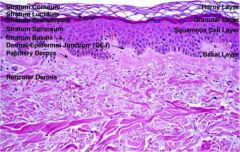
layers of the skin from superficial to basement membrane
|
|
|
|
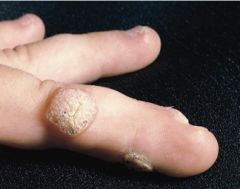
what virus causes this?
|
Human papillomavirus
- Verruca vulgaris - areas of skin trauma, periungal area, plantar surface of foot - confined to epidermis and do not penetrate dermis |
|
|
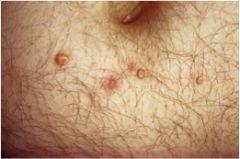
Molluscum contagiosum
Virus that causes this? Who is it seen in? |
Poxvirus (DNA virus)
central area of umbilication filled with keratin Where are the viral particles located? |
viral particles in keratin debri
can be sexually transmitted in AIDS self inoculating by scratching the infective viral particles |
|
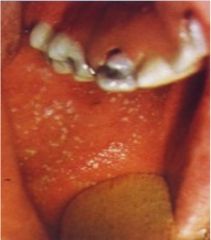
How would your patient present?
What type of virus is this? |
RNA paramyxovirus
Rubeola (first disease) Prodrome: Fever, cough, caryza, conjuctivitis Kaplik spots develop on the buccal mucosa What do the Kaplik spots show up before? |
Macupapular rash
|
|
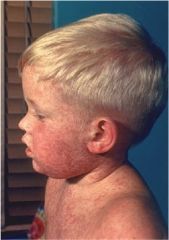
When does this maculopapular rash appear in this disease? Describe the pathogenesis.
|
Rubeola
- maculopapular rash appears after the Kaplik spots Pathogenesis: Cytotoxic T cell damage of endothelial cells containing the virus Typically begins on the head and then to the trunk and extremities -tends to become confluent on face and trunk but discrete on extremities |
|
|
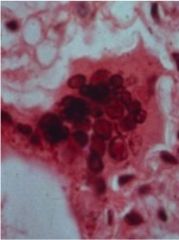
what are some potential complications of this disease?
|
Rubeola
- Giant cell pneumonia - Acute appendicitis in children - encephalitis - prevent through vaccination |
|
|
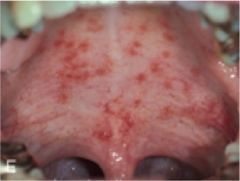
Patient presents with Farchheimer's spots. What is the suspected cause?
|
Rubella (German measles)
RNA togavirus: produces three day measles |
|
|
|
What does an infection of Rubella in the first trimester of pregnancy cause?
|
congenital abnormalities
prevent through vaccination |
|
|
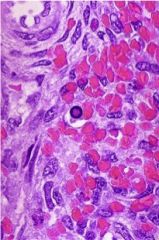
What is a common presentation of this virus in adults?
|
Parvovirus B19
Polyarthritis is common in adults |
|
|
|
What could happen to a pregnant woman if she is exposed to a child with parvovirus B19?
|
may cause abortion of fetus
|
|
|
|
Common disorders caused by parvovirus B19?
|
pure red blood cell aplasia
aplastic anemia chronic arthritis |
|
|
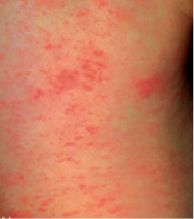
describe Roseola infantum
|
most common viral exanthem in children < 2 years old
Erythematous macules develop on soft palate 48 hours before rash |
|
|
|
A 2 year old child has had a high fever for 5 days and then develops a maculopapular rash. What is your diagnosis?
|
Rosela infantum
|
|
|
|
Can a high fever in a child under the age of 2 with Roseola infantum precipitate a febrile convulsions?
|
YES
|
|
|
|
Your patient has varicella. How long before the rash appears are they contagious?
|
patient is infectious one week before the rash appears
infectious an additional 4-5 days until vesicles become crusted |
|
|
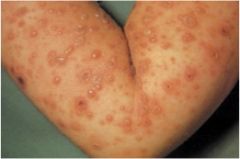
progression of disease.
|
pruritic rash progresses from macules, to vesicles, to pustules
all stages of development are simultaneously present |
|
|
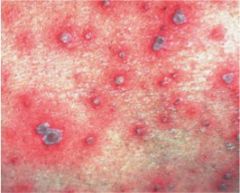
what would be the laboratory findings?
|
Positive Tzanck test similar to HSV
|
|
|
|
What are possible complications of Varicella?
|
associated with Reye syndrome
pneumonia self limited cerebelitis in adults: hepatitis, pneumonia, encephalitis |
|
|
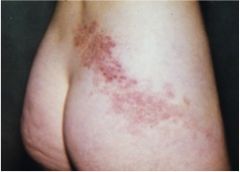
Diagnosis. What were possible signs of this occurring before rash eruption?
|
Herpes zoster (shingles)
prodrome of radicular pain and itching before rash occurs |
|
|
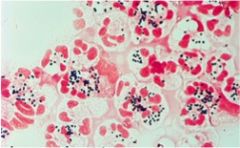
Patient has been diagnosed with Toxic Shock Syndrome. What physical findings may be present?
|
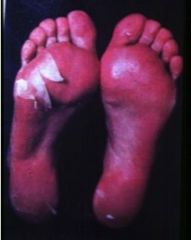
superantigen stimulates release of cytokines
Fever HYPOtension Desquamating, sunburn like rash |
|
|
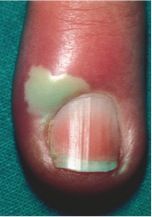
Diagnosis.
|
Hidradenitis suppurativa
- chronic condition characterized by swollen, painful, inflamed apocrine glands usually in the axilla or groin |
|
|
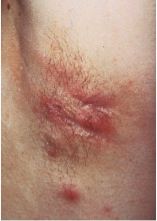
what is the hallmark of this disorder?
|
Hidradenitis suppurativa
- presence of sinus tracts - must aspirate and culture pus |
|
|
|
what is the most common cause of post surgical wound infection?
|
Staphlycoccus aerus
- Gram positive coccus in clumps |
|
|
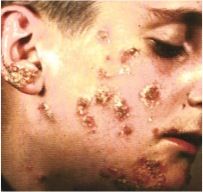
most common cause?
|
Staphylococcus aureus
- vesicles and pustules rupture to form honey-crusted lesions - presence of bullae commonly occurs |
|
|
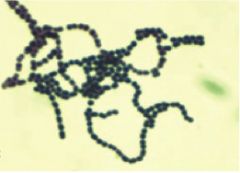
what disease could this bacteria cause?
|
Scarlet fever
|
|
|
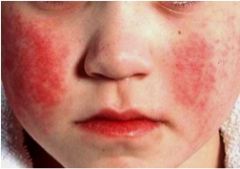
what could be the cause of this infection?
|
Patient has scarlet fever
- streptococcus pyogenes - Erythematous rash develops that involves the skin and tongue - initially on the face and neck |
|
|
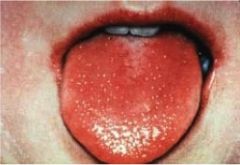
what is this a characteristic finding of?
|
Scarlet fever
- white exudate on the tongue disappears - tongue is beefy read "strawberry tongue" |
|
|
|
Your patient had scarlet fever. What are they at risk for developing?
|
poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever
|
|
|
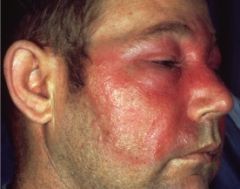
What causes this cellulitis?
|
Streptococcus pyogens skin infection
- Erysipelas - type of cellulitis: border is raised and surface appears like an orange peel - skin surface is hot and bright red - patient is ill and febrile |
|
|
|
what is the bacterial cause of leprosy?
|
Mycobacterium leprae
|
|
|
|
what is the reservoir for Mycobacterium leprae?
|
Armadillos
|
|
|
|
what does a positive lepromin skin test indicate?
|
intact cellular immunity
|
|
|
|
your patient has autoamputation of their digits and a positive lepromin skin test. Diagnosis?
|
Leprosy tubercuoloid
- localized skin lesions with nerve involvement |
|
|
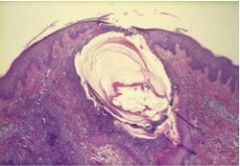
This is a clinical lesion of Acne vulgaris. Is it opened or closed comedone?
|
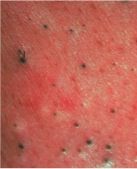
Open comedone "blackhead"
- plugging of the outlet of a hair follicle by keratin debri |
|
|
lesion of acne vulgaris. what is the noninflamed comedone?
|
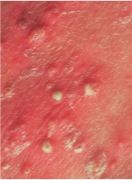
Whitehead
- closed comedone: plugging of the outlet of a hair follicle by keratin debris |
|
|
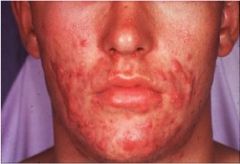
What is the cause?
|
Propionibacterium acnes
- produces irritating fatty acids - produces inflammatory reactions - increased sebum production - abnormal keratinization of the follicular epithelium |
|
|
|
what is the most common cause of infectious skin disease?
|
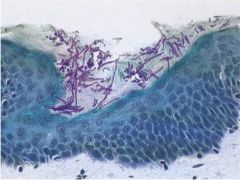
superfiical mycoses (dermatophytoses)
group of fungi confined to the stratum corneum or appendages |
|
|
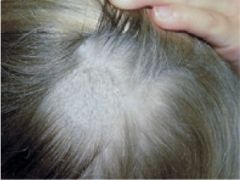
Most common cause?
|
Trichophytan tansurans
- MC in children - NEGATIVE Wood's lamp - fungus infects the inner shaft |
|
|
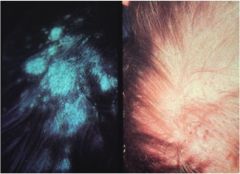
What would your Wood's lamp finding be?
|
Positive Wood's lamp
Tinea capitis Microsporum canis |
|
|
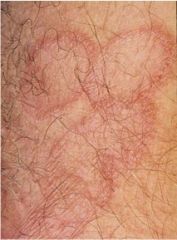
what are most of these infections caused by?
|
Trichophyton rubrum
(tinea corporis) |
|
|
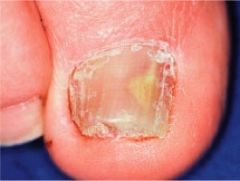
This is the second most common superficial dermatophyte infection. What is the most common cause?
|
T. rubrum (MC)
T. mentagraphytese most common dermatophytes |
|
|
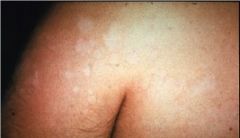
Tinea versicolor.
What is the cause of hyperpigmented type of this disorder? |
an enlargement of melanosomes
|
|
|
|
What is the fungal cause of tinea versicolor?
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
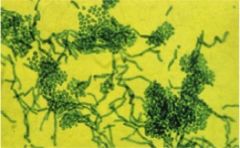
You are using this KOH scrapping to confirm your diagnosis of what you suspect your patient has. Diagnosis?
|
Tinea versicolor
- KOH findings of the Fungi appearing as "spaghetti and meatballs" |
|
|
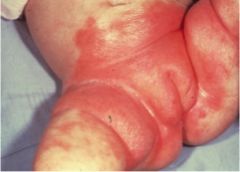
What is responsible for this infection?
|
Candida albicans
|
|
|
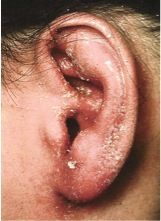
describe.
|
Seborrheic dermatitis
- caused by M. furfur - common locations: scalp, eyebrows, and nasal creases - called craddle cap in newborns |
|
|
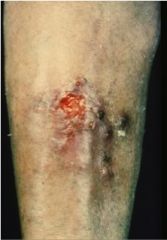
This patient is a lobster fisherman. What is causing this?
|
Sporothrix schenckii
- subcutaneous mycotic infection - dimorphic fungus - traumatic implantation of fungus |
|
|
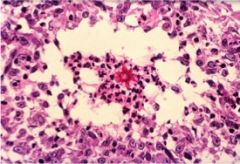
what would your expected microscopic findings be?
|
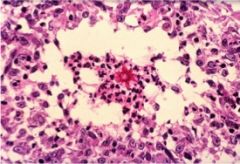
Sporotrichosis
- lymphocutaneous disease - chain of suppurating lymphocutaneous nodules - small yeast surrounded by intensely eosinophilic Splendore Hoeppli substances - probable antigen-antibody complexes |
|
|
|
what causes cutaneous larva migrans?
|
Ancyclostroma braziliensis (dog and cat hookworm;nematode)
|
|
|
|
how are cutaneous larva migrans transmitted to humans?
|
1. dogs and cats are definitive host
2. sexually mature host that can mate and lay eggs 3. Larvae evolve in sand/soil from eggs passed in the feces 3. Larvae penetrate the skin in children/adults (intermediate host) |
|
|
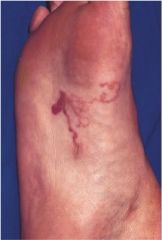
What is causing this in your pediatric patient?
|
Cutaneous larva migrans
- Larvae penetrated skin - serpiginous tunnels in the skin which cause intense pruritis and scratching and eosinophilia |
|
|
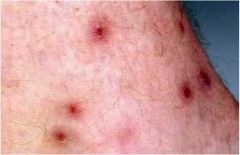
What are your expected findings if a patient where to come into your office and tell you " I itch all over, I spent the weekend cutting tall grass on my property."
|
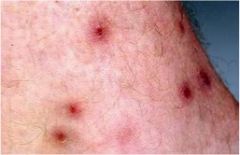
Chiggers: small red to organge colored mite caused pruritic dermatitis
- bright red papular, urticarial or vesicular rash - favors the legs and areas of tight fitting clothing |
|
|
|
a 36 year old mother of two children has a 4 day history of swollen painful hands. Her wrists and MCP joints are boggy and inflamed bilaterally. Her 5 year old son was sent home from school approximately 3 weeks ago with red cheeks and a blotchy rash on his torso. What did he have? What is the matter with the mother?
|
Fifth disease: slapped face appearance and arthritis
Parvovirus: smallest DNA virus associated with RBC aplasia in the setting of chronic hemolytic anemias, patients with thymomas, and recurrent spontaneous abortions. |
|
|
|
parvovirus B19
|
DNA virus
Erythema infectiosum |
|
|
|
color differences between blacks and whites
|
same number of melanocytes and more dendritic processes to transfer melanin to keratinocyte in blacks vs whites
|
|
|
|
Hyperkeratotic, dry skin on palms and soles, extensor areas throughout life
|
Icthyosis vulgaris
it is the MC inherited AD disorder of keratinocytes |
|
|
|
Liver spots in sun exposed areas
|
UVB light related changes in elderly
- liver spots represent solar lentigo (increased number of melanocytes) |
|
|
|
Acute eczema
|
type IV HSR
|
|
|
|
itch that rashes
rash on the cheeks in a child |
Atopic dermatitis
Type I HSR |
|
|
|
Xerosis
|
dry skin
|
|
|
|
Woman with eczematous rash on both ear lobes
|
this reaction is to nickel and is a Type IV HSR
- allergic contact dermatitis |
|
|
|
Man develops pruritic eczematous rash after a picnic in a wooded area
|
reaction is to Rhus an is a Type IV HSR
- allergic contact dermatitis |
|
|
|
Hyperkeratosis
|
Lichen planus
chronic eczema both conditions have excessive scratching leading to thick scales on the skin surface from hyperkeratosis (increase in stratum corneum) |
|
|
|
Patient on tetracycline develops a rash in sun-exposed areas
|
contact photodermatitis
|
|
|
|
Polymorphus light eruption
|
sun exposure reaction
common in native americans |
|
|
|
infant with acute eczema on cheeks and extensor and flexor surfaces
|
Atopy
Type I HSR |
|
|
|
what is the difference between eczema in children and adults.
|
Children: dry skin and eczema on cheeks and extensor surfaces. Usually mouth breathers due to allergic rhinitis
Adults: dry skin and eczema on hands, eyelids, elbows, and knees |
|
|
|
Fungi that locate in the stratum corneum
|
Trichophyton rubrum
Malassezia furfur - superficial dermatophytes |
|
|
|
MCC of tinea capitis
|
Trichophyton tonsurans is the MCC
Woods lamp test is negative because the infection is of the inner shaft |
|
|
|
Cause of tinea capitis with a Positive Woods lamp test.
|
Microsporum canis
infections of the outer hair shaft |
|
|
|
Pruritic circular rash with scaly red margins and clear centers
|
Scrape material from outer margin for KOH prep
- rule out superificial dermatophyte infection |
|
|
|
Trichophyton rubrum
|
MCC of tinea coporis, pedis
|
|
|
|
Tinea versicolor
|
Malassezia furfur
|
|
|
|
Associated with a herald patch
|
feature of pityriasis rosacea
|
|
|
|
Intertrigo
Onychomycosis |
due to Candidia albicans
|
|
|
|
Dandruff, scaly rash on eyebrows and nasal creases
|
Seborrheic dermatitis
due to M. furfur |
|
|
|
Common warts
condyloma accuminata |
HPV
|
|
|
|
Child with multiple crateriform lesions with sandy material in the center
|
Molluscum contagiosum
due to poxvirus (DNA) |
|
|
|
Child with fever, runny nose, white lesions in the mouth on an erythematous base followed by a maculopapular rash
|
Rubeola
- Regular measles - note the description of the Koplik's spots in the mouth which proceed the rash |
|
|
|
Child develops high fevers and febrile seizures which is followed by a maculopapular rash
|
Roseola infantum
- HHV-6 - common cause of febrile convulsions |
|
|
|
Young woman develops fever, mental status abnormalities, desquamating erythematous rash during menses
|
Due to toxin producing Staphylococcus aureus
- Toxic shock syndrome |
|
|
|
Young child with fever, sandpapaer rash, circumoral pallor, and a tongue coated by white material
|
Due to toxin producing streptococcus A
- this is scarlet fever - tongue is initially white and then becomes red when desquamation occurs |
|
|
|
A patient on penicillin develops a maculopapular rash
|
Type I HSR
-b-lactam group of drugs are not only famous for Type I skin reactions but also anaphylactoid reactions |
|
|
|
Child with rash, arthralgia, and painful postauricular lymphadenopathy
|
Rubella (3 day measles)
the presence of arthralgia with rubella infections |
|
|
|
Patient with erythematous plaque like lesions with silvery scales on the elbows and lower back
|
Psoriasis
|
|
|
|
Lichen planus
|
violaceous appearance on the wrist
Lacy white areas on bucosal muscosa |
|
|
|
Patient with an erythemaous plaque like lesion with silvery scales on the elbows develops pin point hemorrhage when a scale is picked off
|
Auspitz sign
|
|
|
|
Koebner's phenomenon
|
psoriatic lesions develop in areas of skin trauma
|
|
|
|
Farmer has pearly white lesion on the dorsum of his hands
|
precursor lesion for squamous cancer
- actinic (solar) keratosis which has squamous dysplasia - recurs when scrapped off |
|
|
|
Patient with erythematous plaque like lesion on his elbow has a scaly lesion on his scalp
|
this is psoriasis
when only located in the scalp it is easily confused with dandruff |
|
|
|
Patient develops an oval shaped patch on his back which is shortly followed by a papular eruption on his trunk that follows cleavage lines
|
pityriasis rosea with a herald patch and christmas tree like rash
|
|
|
|
Tzank prep
|
multinucleated cells with intranuclear inclusions in patients with Herpes simplex and varicella
|
|
|
|
Patient with a lchenified rash on his wrist has a white, net-like rash on the buccal mucosa
|
Lichen planus
the wrist lesion and findings of Wickham's stria in the mouth is diagnostic Wickham's stria may develops into squamous cancer |
|
|
|
Febrile child with painful vesicles at different stages of development
|
Varicella
this describe chickenpox |
|
|
|
If a child has Varicella and takes aspirin (salicylic acid) what are they at risk for developing?
|
Reye's syndrome
|
|
|
|
Adult with bullous lesion in the mouth and on the skin. Vesicles are suprabasal.
|
Pemphigus Vulgaris
- produces intraepidermal vesicles above the basal layer - basal cells look like a row of tombstones - Positive Nikolsky sign |
|
|
|
Nikolsky sign
|
skin sloughs off with pressure
|
|
|
|
Child with honey colored crusted lesions around his mouth and cheeks
|
Due to S. aureus, causing impetigo
- S. pyogenes is second MCC |
|
|
|
Munro microabscesses
elongation rete pegs microcirculatory changes hyperplasia of squamous epithelium |
Psoriasis
the microscopic changes are characteristic It is a disease characterized by unregulated proliferation of Squamous cells light therapy with psoralen is key treatment along with topical steroids in localized cases |
|
|
|
Adult with bullous lesions on the skin
Subepidermal locations |
Bullous pemphigoid
There is no acantholysis present of Nikolsky sign |
|
|
|
Adult with steatorrhea and vesicular rash
|
dermatitis herpatiformis
associated with celiac disease It is an autoimmune subepidermal vesicular disease anti-reticulin and endomysial antibodies are present |
|
|
|
Adult with targetoid lesions on the palms, soles, and extensor surfaces.
Later develops lesions of the mouth |
Erythema multiforme with Stevens Johnson Syndrome
|
|
|
|
Disease associated with Proprionibacterium species
|
Acne vulgaris
it produces lipases which convert lipids in sebum into fatty acids leading to an inflammatory reaction |
|
|
|
Androgen generated skin disorder with papules, pustules, nodules, cysts, and scars
|
Acne vulgaris
the androgen receptors are on the sebaceous glands around the hair follicle Spironolactone blocks these receptors |
|
|
|
Patient develops itchy, raised papular lesions shortly after being bitten by gnats
|
Urticarial reaction to an insect bite
Type I HSR with histamine release |
|
|
|
Family history of recurrent episodes of diffuse swelling of the face and laryngeal stridor
|
Patient most likely has C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency owing to the recurrent nature of the angioedema
|
|
|
|
Sudden onset of painful, pruritic, vesicular lesions with necrosis after crawling under the house
|
Type I HSR
patient has been bitten by fire ants |
|
|
|
Adult with a flushed face, telangiectasias, pustules, and an enlarging nose
|
Acne rosacea
- this often confused with malar rash of SLE except it is pustular |
|
|
|
What are the rhinophyma (nose changes) due to in Acne rosace?
|
sebaceous gland hyperplasia
|
|
|
|
Malar rash with positive band test in uninvolved skin
|
SLE
band test detects IC (DNA-anti-DNA) in the basement membrane of skin - in SLE involved and uninvolved skin are positive |
|
|
|
In discouid lupus where is the positive band test found?
|
only in involved skin
|
|
|
|
Lobster fisherman develops subcutaneous nodules up the extensor surface of his forearm
|
Sporotrichosis
the spines of the lobster pick up spores of Sporothrix from sphagnum moss and pricking of the skin introduces the orangisms Traumatic implantation from skin pricks related to rose gardening is another common scenario |
|
|
|
Crateriform lesion develops on the index finger in 3 months. It regreses with scar formation.
|
Rapid development of the lesion and its regression indicates that it was keratoacanthoma
|
|
|
|
Painful SC nodules on the anterior aspect of the lower legs in a patient with coccidioidomycosis
|
Erythema nodusum
- MC inflammatory lesion of SC fat It commonly accompanies systemic fungal infections, TB, and occurs with certain drugs |
|
|
|
Black male has nodular masses on the face and trunk associated with dyspnea, hilar adenopathy, and uveitis
|
Sarcoidosis
history of dyspnea, hilar adenopathy, and uveitis is clearly sarcoidosis and the nodules represent involvement of the skin. biopsies show NONcaseating granulomas |
|
|
|
patient with crateriform lesion on the inner canthus of the eye. the walls are read and have vessel telangiectasias
|
Basal cell carcinoma
this is classic location and description |
|
|
|
Pregnant woman has hyperpigmented lesions on her forehead and cheeks
|
Chloasma
pregnancy mask |
|
|
|
Solar lentigo
|
liver spots
- that develop in sun-exposed areas in the elderly |
|
|
|
Child has flat, brown lesion on his cheek
|
junctional nevus since it is flat
|
|
|
|
Compound nevi
|
raised and cerrucoid and develop around puberty
eventually junctional nevus develop into intradermal nevi |
|
|
|
Patient with epigastric distress and weight loss suddenly develops multiple raised pigmented lesions
|
Leser-Trelat sign in a patient with stomach adenocarcinoma
- the pigmented lesions are seborrheic keratosis |
|
|
|
adult with more than 100 pigmented lesions on his body has one 6 mm lesion that is irregular and has na irregular distribution of pigment
|
Dysplastic nevus in dysplastic nevi syndrome
|
|
|
|
Acral lentiginous melanomas
|
under the nails or on the palms, soles of feet
they are the only type of melanoma in blacks |
|
|
|
Elderly man has 1.5 cm irregular pigmented lesion on his face with irregular borders, focal areas of depigmentation
|
Lentigo malignant melanoma: develops n the face
-recall the early exposure to excessive sunlight is the most important risk factor for melanomas they are the most rapidly increasing cancer in the US |
|
|
|
patient with epigastric distress and weight loss has a verrucoid, pigmented lesion in the axilla.
|
Patient has acanthosis nigricans and stomach adenocarcinoma
- this is a phenotypic marker for stomach cancer as well as insulin receptor deficiency and MEN IIb |
|
|
|
Black man has widespread metastases of malignant melanoma
|
the MC melanoma in blacks is acral lentiginous malignant melanoma which has no associattion with UV light. Lesions are on the palms, soles, or subungual
|
|
|
|
Rapid growth phase of melanoma
|
it is a phase where malignant cells proliferate laterally either within the epidermis or papillary dermis without danger of metastasis. Once they enter the vertical growth phase there is risk of metastasis
|
|
|
|
Nodular melanoma
|
lack of radial growth phase
they directly grow into a vertical growth phase Acral lentiginous melanomas have the same property. Depth of invasion is the key prognostic factor in melanoma |
|
|
|
Staging of system of melanomas
|
Depth of invasion the most important prognostic factor in melanoma
depth of invasion < 0.76 mm invasion offers no change of metastasis depth of invasion > 1.7 mm increases risk for metastasis |
|
|
|
patient with hypertrichosis and bullous lesions in areas of sun exposure
|
deficiency of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase
- this is Porphyria Cutanea Tarda - Uroporphyrin I and Coproporphyrin I are increased - photosensitive porphyrin deposition skin and produces bullous lesions in sun-exposed areas. - HCV and alcohol excess may be associated with PCT |
|
|
|
Prevention of melanomas
|
best prevetion is sunscreen > 15
|
|
|
|
Woman loses all her hair after delivery of her child
|
the hair loss is due to excess estrogen during pregnancy, which causes hair growth to become synchronous
|
|
|
|
Alopecia areata
|
produces hairless areas on the scalp with under-developed hairs noted in the areas of baldness
|
|
|
|
massive hairloss in radiation/chemotherapy
|
radiation and chemotherapy inhibit anagen phase of hair growth which involves cell division within the hair bulb
|
|
|
|
Nail pitting
|
Psoriasis
|
|
|
|
Spoon nails
Koilonychia |
iron deficiency
|
|
|
|
Mee's lines
|
transverse white lines in the nail plate that are seen in arsenic poisoning and systemic illness
|
|
|
|
granuloma annulare
|
associated with DM
|
|
|
|
Vitiligo
|
autoimmune destruction of melanocytes
|
|
|
|
Albinism
|
absence of tyrosine leading to absent melanin in melanocytes
|
|
|
|
epidermal inclusion cysts
|
derived from the epidermis of the hair follicle
located on the face, base of ears, and trunk spontaneous inflammation and rupture may occur |
|
|
|
Pilar cysts
|
derived from hair root sheaths
located on scalp and face spontaneous inflammation and rupture may occur |
|
|
|
Fibroepithelial tag
|
pedunculated lesion with fibrovascular core
no clinical significance |
|
|
|
Pyoderma gangrenosum
|
associated with ulcerative colitis
Neutrophil destruction |
|
|
|
Hereditary telangiectasia
|
associated with chronic iron deficiency
AD disorder with dilated small vessels on skin and mucosa lining GI tract bleeding in the GI tract produces chronic iron deficiency anemia |
|
|
|
Spider telangiectasia
|
sign of hyperestrogenism
central macule with radiating vessels seen in hyperestrinism related to normal pregnancy, cirrhosis, where estrogen cannot be metabolized |
|
|
|
Capillary (strawberry hemangioma)
|
usually spontaneously resolve
|
|
|
|
Cherry angioma
|
common in elderly
regress leaving area of pigmentation |
|
|
|
Cavernous hemangioma
|
larger than capillary hemangioma and commonly leaves residual scar
|
|
|
|
Kaposi's sarcoma
|
most common cancer in AIDS
due to HHV-8 malignancy of vessels |
|
|
|
Bacillary angiomatosis
|
vascular infection due to Bartonella henselae
occurs in AIDS and simulates the nodular phase of Kaposi's sarcoma - biopsy to differentiate the two |
|
|
|
Hair growth pattern
|
usually asynchronus
- if synchronous causes massive loss of hair 1. Anagen phase: hair growth/development of new shaft of hair from hair bulb, hair length, determined in this stage 2. Catagen phase: regression growth site of hair shaft, resting phase 3. Telogen phase: regression/hair producing elements of hair follicle. Hair growth is usually asynchronous only a small percentage of hair is lost at any point in time |
|
|
|
EStrogen effects on hair
|
causes synchronous hair growth by causing all hair to enter resting phase at once
- massive hair lost: postpartum MCC, OCP, stress |
|
|
|
radiation/chemotherapy effect on hair growth
|
inhibition of anagen phase when cells in hair bulbs are dividing
|
|
|
|
Xeroderma pigmentosum
|
AR disorder with a DNA repair enzyme deficiency
there is increased risk of UVA/UVB skin cancers |
|
|
|
Koilonychia
|
sign of iron deficiency
|
|
|
|
Subungual hematoma
|
usually associated with a history of trauma
- blood clot under nail - do not confuse with acral lentiginous malignant melanoma |
|
|
|
Ingrown toenail
|
nail pierces lateral nail fold causing S. aureus infection
PAINFUL |
|
|
|
Onycholysis
|
loosening and lifting of nail seen in some fungal infections and Graves disease
|
|
|
|
Beau's lines
|
transverse grooves or depression parallel to lunula
due to conditions that slow nail growth: infections/nutritional disorders/drugs/MI |
|
|
|
Lindsay's nails
|
half and half nails
proximal portion of nail is white and distal part is pink or red sign of chronic renal disease |
|
|
|
Terry's nails
|
white nail beds more than half way up the nail
sing of HYPOalbuminemia |
|
|
|
Splinter hemorrhages in nails
|
most commonly signs of subacute endocarditis
aslo seen in RA, SLE, trichinosis, and leukemia |
|
|
|
Clubbing of the nails
|
normal angle between the nail base and finger is about 1600
angle increases to > 1800 in clubbing due to swelling of tissue from periosteal reaction in bone called hypertrophic osteoarthropathy Associated with cyanotic congenital heart disease, CF, bronchogenic carcinoma |
|
|
|
Chiggers
|
red mite
pruritic red papular/urticaria/vesicular rash |
|
|
|
Human itch mite
|
adult females bore into skin between fingers
lay eggs at end of tunnel |
|
|
|
Cutaneous larva migrans
|
dog/cat hookworm
associated with beaches, sandoboxes, red serpiginous tunnels |
|
|
|
head louse
|
nits on hair shaft
|
|
|
|
body louse
|
treat clothing not the patient
|
|
|
|
pubic louse
|
live in pubic hair
look like crabs |
|
|
|
bed bug
|
feed on human blood
pruritic rash |
|
|
|
erythema toxicum
|
self limited erythematous rash in newborn infants
|
|
|
|
sebaceous hyperplasia
|
yellow white papules due to hyperplastic sebaceous glands
|
|
|
|
Milia
|
superifical epidermal inclusion cysts
epstein pearl in mouth |
|
|
|
Miliaria crystallina
|
clear vesicles due to blocked sweat glands
|
|
|
|
miliaria rubrum
|
prickly heat
|
|
|
|
mongolian spot
|
occurs in dark skinned babies
not premalignant |
|

