![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of the enzyme is inhibited by both acarbose and miglitol?
|
Alpha-glucosidase |
|
|
Which of the following is a new anti-diabetic drug that is a pancreatic peptide analog? |
Pramlintide |
|
|
What are the recombinant human insulin and analogs used for diabetes?
What are the two modified crystal size insulins? |

|
|
|
What are the sulfonylurease? Meglinitides? Biguanides? Thiazolidindiones? |

|
|
|
What are the alpha-glucosidase inhibitors?
Incretins? (GLP-1 receptor agonists)
Incretins (dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors)
Amylin analogues
Bile acid sequestrants
|

|
|
|
What is another name for short-acting insulin?
What are the two intermediate acting insulins? How was this extension made? |

By adding zinc => formation of hexamers |
|
|
Where does regular insulin and NPH or LENTE act with respect to meals (graph)? |
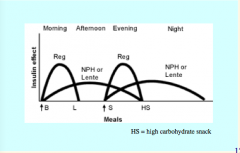
Gives broader coverage (patient needs to measure glucose before each meal) |
|
|
Based on patient measurement of blood glucose" – Measurements made _______ times a day, BEFORE each meal. Two insulin injections each day (see arrows on previous slide). " – Blood glucose before lunch reflects __________ dose" – Blood glucose before supper reflects the ___________ dose"– Blood glucose before bedtime reflects the __________ dose" – Blood glucose before breakfast reflects the __________ dose" |
Based on patient measurement of blood glucose" – Measurements made 4 times a day, BEFORE each meal. Two insulin injections each day (see arrows on previous slide). " – Blood glucose before lunch reflects morning regular insulin dose" – Blood glucose before supper reflects the morning NPH insulin dose" – Blood glucose before bedtime reflects the evening regular insulin dose" – Blood glucose before breakfast reflects the evening NPH insulin dose" |
|
|
– If before lunch is too high,________morning dose of _______ insulin." – If before supper is too high, increase ________ dose of ________ insulin." |
– If before lunch is too high, increase morning dose of regular insulin." – If before supper is too high, increase morning dose of NPH insulin." |
|
|
What are two other insulin therapeutic strategies? What is the drug for the inhaled version? |

|
|
|
In what age group the insulin group useful? |
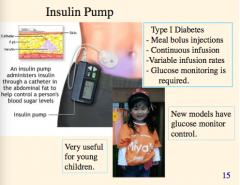
|
|
|
What are the two ways to produce human insulin? What produced with each method? Are animal insulins allowed by the FDA? |

|
|
|
What is the analogue of humulin in which the normal proline B28 and Lysine B29 are switched? How is switching done?
Which insulin drug doesn't form hexamers?
Which insulin drug has a faster onset of action and shorter half-life than regular insulin
What does insulin in circulation form hexamers with? Do the hexamers bind the insulin receptor? |

|
|
|
Which drug is rapid acting insulin analog substitution Asp for Pro? Does it exist as a monomer?
What is another rapid-acting insulin that has AA asparagine at positive B3 replaced by lysine and the lysine in position B20 replaced by glutamic acid? Does it form hexamers?
|

|
|
|
What is common among insulin lispro, insulin aspart, and insulin glulisine? |

|
|
|
What is a recombinant human insulin analog for subcutaneous injection. It is a clear solution as supplied (pH 4)."
Amino acid aspargine 21 replaced by glycine and two arginines are added to the C-terminus f the B-chain
Which drug is similar? |
Insulin glargine
Insulin determir |
|
|
What are the two drugs?
Long-acting (up to 24-hour duration of action)"
When injected, the acidic solution is neutralized, causing crystals to precipitate = slow absorption= long-acting. "
Can be injected once a day."
Low peak insulin concentration decreases chances of nocturnal hypoglycemia." |
Insulin glargine
Insulin detemir |
|
|
What is the problem with this drug? What is the drug? Is there peak concentration? Absorption? Can it be mixed with other insulins?
One aa deleted and conjugated to hexadecanediooic acid via gamma-glutamyl spacer at the aa lysine at position B29. |
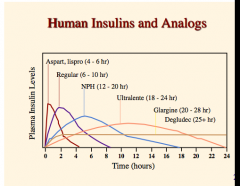
Insulin degludec (used to be every other day= > hard to follow) |
|
|
What is ketoacidosis caused by?
What four things (all elevated in diabetes) exaggerate metabolic effects of low insulin?
What causes increased ketone bodies and decreased pH?
Why is there hyperglycemia? |

|
|
|
What is hypoglycemic coma caused by?
Treatment? |

|
|
|
What is a test for long term control of glucose?
How long do RBCs live?
What is the target A1C level? |
|
|
|
When is glucagon elevated? Is it used for treatment? |

Emergency only |
|

What drug can block these symptoms? |
Non-specific beta blockers |
|

Again, what drugs can block these symptoms? |
Non-specific beta blockers |
|
|
Are sulfonylureas good for the long term? Why?
What is the effect?
Administration?
Bound? Metabolism? Excretion?
|

|
|
|
What are the oral hypoglycemic (sulfonylurea) drugs? |
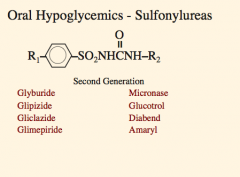
|
|
|
What are the oral hypoglycemic meglitinides?
Derivatives of what?
Increase what?
Rapidly absorbed where? Long or short half life?
Taken when?
Metabolized by what organ?
Major side effec?
|

|
|
|
What are the oral hypoglycemic biguanide drugs?
Do they affect insulin secretion? Adverse effects? Effect on glucose production? Absorbed where? Metabolism? |

|
|
|
Where does metformin act? |
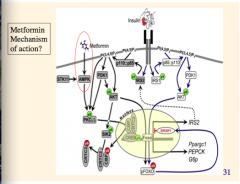
AMPK |
|
|
What are the oral hypoglycemics (thiazolidinediones)? Mechanism of action (specific difference from others)?
Increase what two things?
Absorbed where, metabolism? |

|
|
|
What are the oral hypoglycemics (alpha-glucosidase inhibitors)? What is the effect (two major things)? Usually used with what? |

|
|
|
What does somatostatin inhibit the release of? What does this further inhibit the release of (two things in pancreas)? |
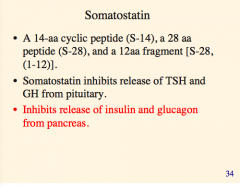
|
|
|
What are the two therapeutic uses of somatostatin?
Long or short half-life?
What is the long-acting analogue? What does this also control excess secretion of? Useful in what disease? |

|
|
|
What is an antihypertensives antidiuretic that has potent hyperglycemic actions?
What does it inhibit secretion of? (but not SYNTHESIS of)?
What does this cause a buildup of?
Useful to treat what? |

|
|
|
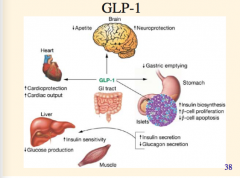
What are the effects of GLP-1? Increases what?
Inhibits what?
Effect on gastric emptying, appetite, glucagon secretion?
All these actions decrease what? |

|
|
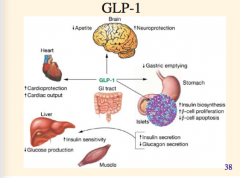
|
|
|
|
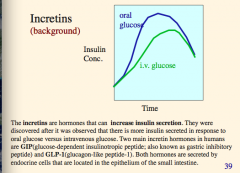
What are the two main incretin hormones in humans? Both hormones secreted where? Located where? Effect on insulin concentration in response to glucose? |
|
|
|
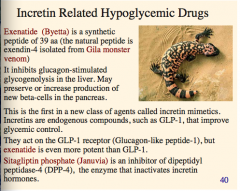
What is a synthetic peptide (incretin related) isolated from the Gila monster venom?
What does it inhibit? What does it preserve or increase production of?
What do the incretin mimetics act on (what receptor)?
What is an inhibitor of DPP-4, the enzyme that in actives incretin hormones? |
|
|
|
What are the three GLP-1 receptor agonists (incretins)?
What are the three DPP-3 inhibitors (incretins)? |

|
|
|
Which drug is an analogue of amylin?
Is amylin deficient in T1 DM?
What is the effect of pramlintide (same as amylin)? Which receptors? Effect on glucagon?
|

|
|
|
What other amylin analogue has been approved for use in T1 and T2 DM?
What are the effects on weight, insulin, blood glucose, and postprandial glucose rise? |

|
|
|
What can human amylin form in B-cells? |

|
|
|
Where are SLGT2 cells located? What about G1?
What is each responsible for?
Why is glucose excreted in the urine in T1 DM?
What is the SGLT2 inhibitor drug? What is the effect? |

|
|
|
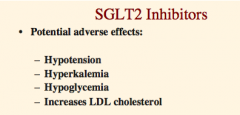
What are the four side effects of SGLT2 inhibitors? |
|
|
|
What three groups of patients should you never give SGLT2 inhibitors to? |
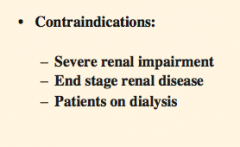
|
|
|
What bile acid sequestrant is used in the treatment of T2 diabetes?
What does it lower (two things)?
What does it interrupt and lower?
What is the general class of side effects? |
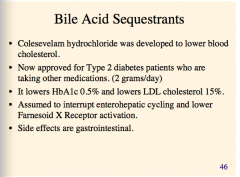
|

