![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How will an increase in interest rates impact the 6 macroeconomic objectives? (Inflation,Economic Growth, Unemployment, Current Account, Inequality, Pollution) |
Less spending, harder to borrow, earn more on savings, less imports so: Inflation will go down Economic Growth will go down Unemployment will go up Current Account will go up Inequality will go up (Rich people save, poorer people borrow. Pollution will go down |
|
|
How will an increase in the money supply impact the 6 macroeconomic objectives? (Inflation,Economic Growth, Unemployment, Current Account, Inequality, Pollution) |
More spending/consumption so: Inflation will go up Economic Growth will go up Unemployment will go down Current Account will go down (more imports) Inequality go down (erodes the value of rich people’s savings) Pollution will go up |
|
|
How will an increase in government spending impact the 6 macroeconomic objectives? (Inflation,Economic Growth, Unemployment, Current Account, Inequality, Pollution) |
Higher level of disposable income, more jobs available so: Inflation will go up Economic Growth will go up Unemployment will go down Current Account will go down (Inflation is bad for exports as they become more expensive. Less people will want to buy them) Inequality will go down (spending is usually on public sectors like NHS and school which the rich will not use as much) Pollution may go up depending on type of spending. Could go down if government invest into environmentally friendly products e.g. solar panels |
|
|
How will an increase in direct taxation rates impact the 6 macroeconomic objectives? (Inflation,Economic Growth, Unemployment, Current Account, Inequality, Pollution) upppp |
Less disposable income, less spending so: Inflation will go down Economic Growth will go down Unemployment go up Current Account goes up (people importing less) Inequality depends on whether tax is progressive or regressive Pollution will go down
|
|
|
Define Fiscal Policy |
Government spending and Taxation. It is a demand side policy that is generally set out in the Budget |
|
|
What are the 11 areas of government spending? (Try and order them with their values) |
1. Social Protection (£252bn) 2. Health (£155bn) 3. Education (£102bn) 4. EU Transactions and Other (£53bn) 5. Defence (£49bn) 6. Net Debt Interest (£23bn) 7. Transport (£35bn) 7. Public Order and Safety (£35bn) 8. Personal Social Services (£32bn) 9. Housing and Environment (£31bn) 10. Industry/Agriculture/Employment (£23bn) |
|
|
Define direct tax |
A tax levied on an Individual or organisation (affects income+wealth) |
|
|
Define an indirect tax |
A tax levied on purchasing goods and services. |
|
|
Define Progressive Taxation |
The marginal rate of tax increases as income rises. Requires the rich to pay a higher % of their income - leads to a fall in inequality |
|
|
Define Regressive Taxation |
Marginal rate of tax falls as income rises. Taxes which are a fixed amount will always be regressive as they’re a higher % of poorer persons income. Leads to a rise in inequality |
|
|
Define proportional taxation |
A constant marginal rate of taxation. (Set percentage) won’t affect inequality |
|
|
Income Tax: -Progressive or regressive? -Direct or indirect? - How much revenue is raised from it? - What percentage of the government’s tax revenue is it? |
Progressive Direct £185bn Roughly 30% |
|
|
Corporation Tax: -Progressive or regressive? -Direct or indirect? - How much revenue is raised from it? - What percentage of the government’s tax revenue is it?
|
Progressive Direct £55bn Roughly 8% |
|
|
National Insurance -Progressive or regressive? -Direct or indirect? - How much revenue is raised from it? - What percentage of the government’s tax revenue is it? |
Regressive (hits the poor hardest, ones who are more likely to need state benefits) Direct £134bn Roughly 20% |
|
|
What would expansionary fiscal policy do for the seven economic objectives in the short run? |
Economic Growth: go up Unemployment: go down Inflation: go up (depending on type of tax?) Current Account Go down(importing more) Inequality: Go down Pollution: likely to go up spending onn type of spending Fiscal Balance: go down |
|
|
What would expansionary fiscal policy do for the seven economic objectives in the long run Classical view/ Keynesian view at full employment? |
Economic Growth: No change Unemployment: No change Inflation: Go up by large amount Current Account: Go down (exports more expensive, less attractive) Inequality: no change Environment: depends on spending Fiscal Balance: go down. |
|
|
What would expansionary fiscal policy do for the seven economic objectives in the long run Keynesian view at spare capacity? |
Economic Growth: increase Unemployment: go down Inflation: increase but not massively Current Account: go down Inequality: go down Environment: depends on spending Fiscal Balance go down. |
|
|
Define Supply Side Policy |
Actions taken by the government designed to increase the productive potential of the economy I.e. increase LRAS |
|
|
What are the two types of supply side policy? |
Market Based: where the governor allow the market to work more freely Interventionist: government intervening and producing something to stimulate aggregate supply |
|
|
What will a decrease in direct tax look like on a graph in the short run? |
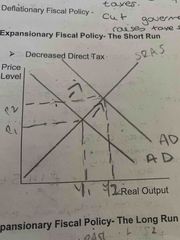
AD would shift outwards. Expansion along SRAS. Inflation from P1 to P2, increase in output Y1 to Y2 |
|
|
What would a decrease in indirect tax look like on a graph in the short run? |
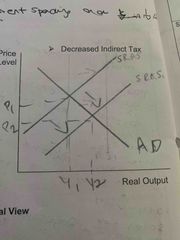
Outwards shift of SRAS. expansion on AD curve. Deflation from P1 to P2, increase in output from Y1 to Y2 |
|
|
In the long run, what do expansionary fiscal policy look like from a Classical View? |
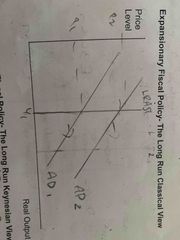
Outwards shift in AD. No increase in output. Just inflation. |
|
|
In the long run, what do expansionary fiscal policy look like from a Keynesian View? |
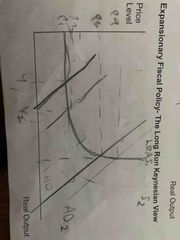
Increase in output and little inflation if there’s spare capacity. If no spare capacity, just inflation no change in output. |
|
|
List 5 advantaged of interventionist based policies |
More producers in the market leads to more people working and lower prices (competition policies) More skilled worked force (education and training) Easier to commute into London (HS2) Workforce moved out of London/ could lead to crowding in (Regional Policies) Higher productivity (immigration)
|
|
|
VAT -Progressive or regressive? -Direct or indirect? - How much revenue is raised from it? - What percentage of the government’s tax revenue is it? |
Regressive Indirect £145bn Roughly 20% |
|
|
List 5 disadvantages of interventionist policies |
Can be hard to prove (fining predatory pricing) Time Lag (education and training) Can lead to congestion. Possibly a bottleneck? (HS2) Other Regions aren’t as easy to get to. Could lead to crowding out. (Northern Powerhouse) Could be skills mismatch. Also lead to congestion(immigration |
|
|
Where do fiscal and supply side policies cross over? |
Where the government is spending money e.g. infrastructure/education or cutting taxes. |
|
|
What would implementation of supply side policies look like in the long run from a classical view? |
Outwards shift in LRAS. Expansion along AD curve. Deflation. |
|
|
What would implementation of supply side policies look like in the long run from a Keynsian view? |
No affect while there’s spare capacity. Once full unemployment is reached, deflation and increase in output. |
|
|
What would supply side policies do for the seven economic objectives in the long run Classical view/ Keynesian view at full employment? |
Economic Growth: Go up Unemployment: Go down Inflation: go down Current Account: go up (exports are cheaper so much attractive) Inequality: go down Environment: depends on policy Fiscal Balance: depends on policy |
|
|
Excise Duties -Progressive or regressive? -Direct or indirect? - How much revenue is raised from it? - What percentage of the government’s tax revenue is it? |
Regressive Indirect Tax £49bn 10% |
|
|
Council Tax -Progressive or regressive? -Direct or indirect? - How much revenue is raised from it? - What percentage of the government’s tax revenue is it? |
Regressive Direct £34bn Paid to local government not main |
|
|
Business Rates -Progressive or regressive? -Direct or indirect? - How much revenue is raised from it? - What percentage of the government’s tax revenue is it? |
Regressive Direct £30bn Paid to local government not main |
|
|
What are the two types of fiscal policy? |
Expansionary: government spending is raised/taxes cut to increase AD Deflationary/Tight : government spending cut/taxes increases to reduce AD |
|
|
What will a decrease in direct tax look like on a graph in the short run? |
AD would shift outwards. Expansion along SRAS. Inflation from P1 to P2, increase in output Y1 to Y2 |
|
|
What would implementation of supply side policies look like in the long run from a classical view? |
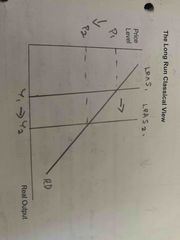
Outwards shift in LRAS. Expansion along AD curve. Deflation. |
|
|
What would implementation of supply side policies look like in the long run from a Keynsian view? |
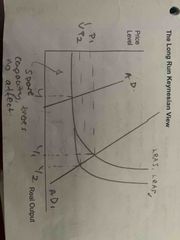
No affect while there’s spare capacity. Once full unemployment is reached, deflation and increase in output. |
|
|
In the long run, what do expansionary fiscal policy look like from a Keynesian View? |
Increase in output and little inflation if there’s spare capacity. If no spare capacity, just inflation no change in output. |

