![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Enamel is the specialized epithelium covering the teeth that are produced by__. These are removed during tooth eruption and therefore acellular
It's the most mineralized tissue in the body (96% mineral) - It's hard and brittle and needs __ as base or else it can fracture |
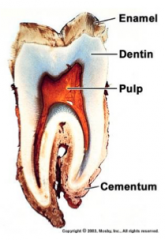
Ameloblasts Dentin |
|
|
The inorganic material of enamel is? Organic material is tyrosine-rich amelogenin polypeptide (TRAP) and nonamelogenin protein |
Hydroxyapatite (crystaline calcium phosphate) |
|
|
The basic unit of enamel is? Enamel also includes? |
The enamel rod Interrod enamel -this is made first |
|
|
As enamel matures, the crystals of enamel become __ and more pushed together -Ions can also be incorporated (fluoride, magnesium, strontium, lead) Region between the interrod region and the rod is the? |
Hexagonal Rod sheath with more organic material |
|
|
Enamel formation is a 2 step process: In the presecretory+secretory phase, inner epithelium becomes preameloblast then emeloblast and secretes enamel. Here __% is mineralized enamel In the maturation phase, there is the removal of __ and __ and addition of mineral Amelogenesis occurs during? |
30% mineralized enamel (5% water, 66% protein) removal of water (now 1%) and protein (now 4%) The appositional stage |
|
|
Enamel formation requires dentin and there is a reciprocal induction: Internal enamel epithelium induces the __ to become odontoblasts which secretes dentin Dentin induces the internal enamel epithelium (presecretory ameloblasts to become? Therefore __ is present before __ |
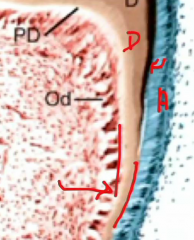
Underlying dental papilla secretory ameloblasts dentin is present before enamel |
|
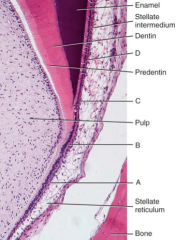
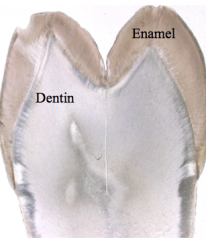
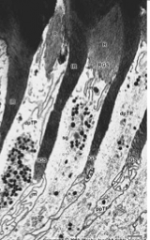
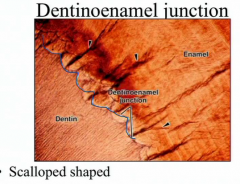
What is A, B, C, and D? |
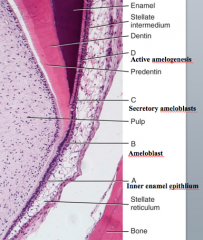
|
|
|
In amelogenesis there are 7 stages: The first stage is the __ with inner enamel epithelium What stage is when cell becomes polarized, the nucleus is at the base and secretory vesicles near the apex, and getting ready to secret? Then there is the initial secretory stage and secretory stage After that is the maturation stage (ruffle ended and smooth ended) to get the __ form of enamel Finally, before the tooth erupts is the? |
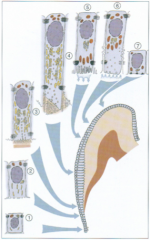
Morphogenetic stage Histodifferentiation stage crystaline protective stage |
|
|
After the early secretory stage is the secretory stage where __ is present During amelogenesis, the outer enamel epithelium, stellate reticulum, and the stratum intermedium fuse to form? The above has __ while the ameloblast layer does not |
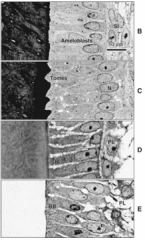
Tome's processes The papillary layer Papillary has blood vessels and supply blood to the ameloblast layer |
|
|
In morphogenetic phase the cells of Inner enamel epithelium (dental lamina) have?
In the histodifferentiation phase, the cells become more differentiated toward the? - Nuclei shifts toward? -Stratum intermediumGolgi, RER, junctional complexes, and terminal web is also seen |
Centrally place nuclei Crown of the tooth |
|
At the differentiation stage ameloblast secretes Initially there is a basal lamina which breaks down and enamel appear as patches. This is seen with dentin -Terminal web holds cells together as enamel is made |
- |
|
|
After dentin is made by odontoblasts (which are induced by presecretory ameloblasts), there is the initial secretory stage where __ and __ is produced but rods are not formed -has extensive golgi surrounded by RER |
Enamel protein and mineralization |
|
|
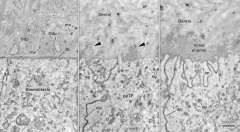
Initially when enamel is laid down, there is only the proximal portion of? Inter rod enamel is made by? -This occurs where? Rod enamel is made by? This occurs where? |
Tome's process Proximal process -By the cell junctions distal Tome's process -The tip of Tome's process |
|
|
The region where the interrod enamel forms are areas that have? Initially when the enamel first forms its structureless because? When they are present, what forms? |
highly folded membranes so nothing gets through the cells there are no tome's processes proximal enamel |
|
|
Secretion of enamel at the proximal sites that are close to junctional processes form pits into which tome's processes fit The pit is then filled with matrix that becomes the? The wall enamel becomes? |
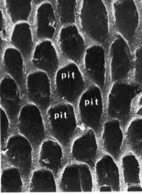
enamel rod Interrod enamel |
|
|
Enamel in the outer third has different orientation due to changes in the morphology of Tome's processes In the maturation stage ameloblasts get shorters and have what 2 morpholgies? -What happens in each? When it transitions to ruffled ameloblasts, they get smaller but what else occurs? |
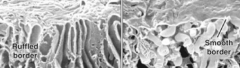
Ruffled cell border: adding inorganic material Smooth ended border: removal of water and organic material Apoptosis (50% of ameloblasts will die) |
|
|
Ruffled ameloblasts produce bicarbonate ions, alkalizes enamel fluid to prevent reverse demineralization, and maintains pH for degrading matrix When they undergo modulation to the smooth ameloblasts, molecules withdrawn from enamel pass between ameloblasts and through the? Note tight junctions move from the enamel area to the border area from ruffled to smooth In the maturation phase there is also a basement membrane |
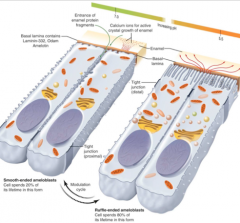
lateral borders of the cell |
|
|
In the protective stage, what is secreted and what is formed? Enamel protein include amelogenins and nonamelogenins. Nonamelogenins promote mineral formation |
basal lamina is secreted hemidesmosomes are formed |
|
|
In amelogenesis: Stage 1 is the formation of? In stage 2, there is increase in mineralization from __ to __ layers In stage 3, mineralization continues from __ to the __ and mineralizes more slowly In stage 4, there is heavy mineralization in the? |
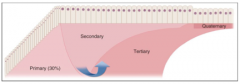
partially mineralized enamel (30%) surface to deeper inner to surface outer layer |
|
|
Rods run __ to the surface of dentin They run circumferentially around the? Not formed in a straight line, and inner part of enamel have intertwining rods |
perpendicular long axis of the tooth |
|

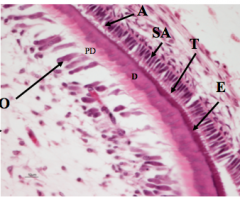
In enamel what are the incremental lines of growth? In horizontal section they appear as? |

Stria of Retzius concentric rings |
|
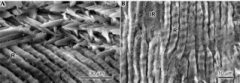
**Stria represent __ in enamel formation What is the most prominent stria in enamel? What represents the daily formation of enamel? |

Weekly formation (growth of enamel) Neonatal line because its the most significant change that occurs during birth cross striations |
|
|
What are optical patterns resulting from changes in rod direction? |
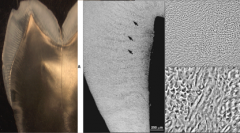
Hunter-Schrager Bands (light gray and dark gray patterns) |
|
|
The cuspal region of the crown where the enamel rod twist and become irregular is called? What does it allow for? |
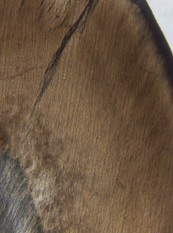
Gnarled enamel Occlusal stress |
|

|
|
|
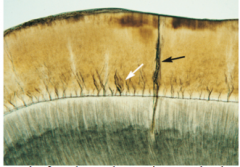
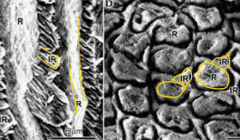
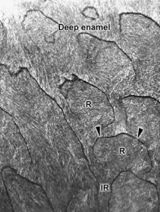
White Arrow: What are abrupt changes at the DEJ? -have less mineralization -have a different ratio of rod to interrod enamel Black arrow: What runs from the enamel surface and is filled with enamel protein or organic debris? |
Enamel tufts Enamel lamellae |
|

What are newly formed odontoblast processes caught between enamel formed by adjacent ameloblasts? |
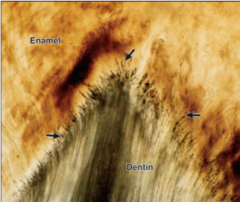
Enamel spindles (very short) |
|
|
Stria of Retzius end at the surface as? |
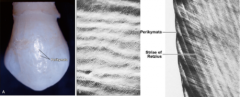
Perikymata |
|
|
Enamel wears during?
Conditions like tetracyclin in utero/infant and excess fluoride treatment are conditions that can affect enamel |
Aging or Illness |

