![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Doxazosin, terazosin and alfuzosin
|
For symptomatic BPH relief.
MOA: Antagonists of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors. - Relax prostate smooth muscle at bladder neck to allow urination - Don’t shrink prostate size/don’t correct underlying problem - Antagonize vascular a1 adrenergic receptors - Must titrate dose to reduce side effects - Adverse: CV: syncope, orthostatic hypotension common Nasal: congestion Penis: impairs ejaculation * Contraindicated in patients with angina or heart failure |
|
|
What would you predict to be an effect of activating a1 adrenergic receptors?
|
Vasoconstriction
|
|
|
TAMSULOSIN and silodosin
|
Uroselective andrenergic antagonists.
- MAO: selective α1A antagonists – α1A is concentrated in prostate & penis - Less α1B adrenergic affinity (in blood vessels) = Less hypotension, less vascular - Less α1D affinity = less nasal congestion - Ejaculation still possible problem Silodosin - requires dose adjustment (renal or hepatic failure) |
|
|
An elderly man with BPH needs relief; which best explains why tamulosin wouldn’t promote dizziness or syncope?
|
Doesn’t block a1b vascular receptors.
|
|
|
FINASTERIDE and dutasteride
|
MAO: Competitive enzyme inhibitors of 5α-reductase reduce dihydrotesterone (DHT) production
- DHT major androgen promoting prostate hyperplasia – for BPH treatment only - Prototypical: finasteride, dutasteride - Finasteride – selective inhibitor 5α-reductase II - Dutasteride –non-selective inhibitor 5α-reductase used more severe BPH - Adverse Decrease serum PSA ; can mask cancer detection Impotence/libido decreases in some patients Rare– slight increase risk male breast cancer |
|
|
Aminoglutethimide and Ketoconazole for Prostate Cancer:
|

|
|
|
FLUTAMIDE; androgen receptor antagonists:
|

|
|
|
Leuprolide and Goserelin
|
GnRH agonists:
- For prostate cancer - Decreases LH/FSH release from pituitary - Continuous administration decreases sex steroid production via negative feedback –takes weeks to shut down - Given with androgen receptor antagonist - Adverse: Impotence, hot flushes & bone loss can occur - Patients often need biphosphate therapy to guard against osteoporosis. |
|
|
Degarelix
|
GnRH antagonist:
- For prostate cancer - Competitive antagonist at pituitary GnRH receptor - Rapidly reduces gonadotropin & testosterone levels - These patients often need biphosphate therapy to guard against osteoporosis |
|
|
Blood flow in flaccid vs. erect penis:
|
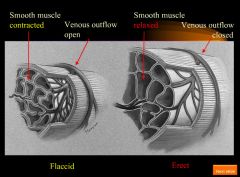
|
|
|
Nitric oxide and cGMP mechanism of penile erection:
|

|
|
|
Steps to an erection:
|

|
|
|
Steps to detumescence:
|

|
|
|
Testosterone deficiency can cause?
|
1. Loss of libido
2. Fatigue 3. Erectile dysfunction * When testing testosterone levels, evaluate morning and free testosterone. |
|
|
Requirements for an erection:
|

|
|
|
Requirements for an erection:
|

|
|
|
Erectile dysfunction can be classified in what 3 ways?
|
1. Organic
- Problems with blood flow - Medications - Nerve damage - Surgery - Systemic diseases - Lifestyle factors 2. Psychogenic - Lack of interest - Performance anxiety - Stress 3. Mixed |
|
|
Sildenafil, tadalafil (Viagra, Cialis); PDE5 inhibitors to treat impotence:
|

|
|
|
Direct vasodilators for impotence:
|

|
|
|
Treatment for premature ejaculation:
|

|
|
|
Fibrocystic and benign epithelial/proliferative changes:
|
- Most common disorder of the breast
- Most common cause of breast masses in women ages 25-50 years - Clinical: lumpy breasts (bilateral usually) with midcycle tenderness - Calcifications and densities on mammograms - Pathogenesis: may related to increased activity or increased sensitivity to estrogen - Nonproliferative versus proliferative |
|
|
Characteristics of non-proliferative fibrocystic change in breast tissue:
|
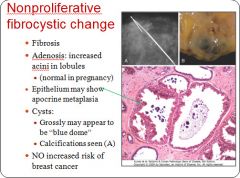
|
|
|
Characteristics of non-proliferative fibrocystic change in breast tissue:
|
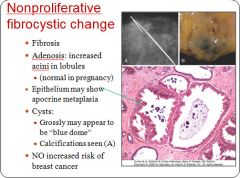
|
|
|
Characteristics of proliferative breast disease without atypia:
|
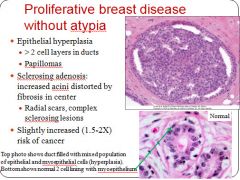
|
|
|
Sclerosing adenosis; a type of proliferative breast disease without atypia:
|
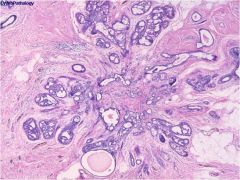
|
|
|
Characteristics of proliferative disease of the breast with atypia:
|
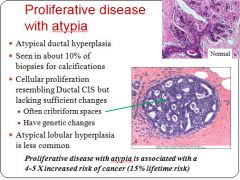
|
|
|
Characteristics of an intraductal papilloma:
|
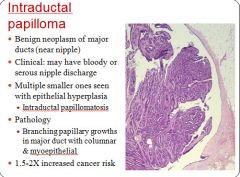
|
|
|
Characteristics of fibroadenoma:
|
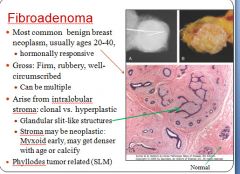
|
|
|
Over 95% of breast carcinomas are what type?
|
Adenocarcinomas
|
|
|
Characteristics of DCIS Comedocarcinoma type:
|
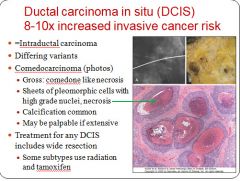
|
|
|
Characteristics of lobular carcinoma in situ:
|
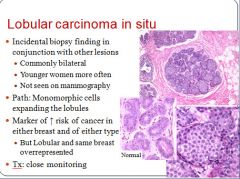
|
|
|
Molecular classifications of breast cancers:
|
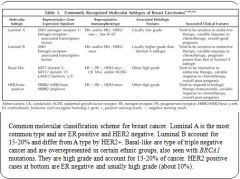
|
|
|
Characteristics of invasive lobular carcinoma:
|
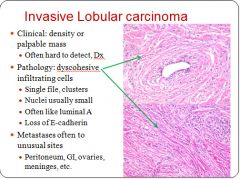
|

