![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is deamination? |
The removal of an amino group from an organic compound. |
|
|
What is the nitrogenous waste formed from two molecules of ammonia and one molecule of carbon dioxide? |
Urea |
|
|
What is uric acid? |
A waste product formed from the breakdown of nucleic acids. |
|
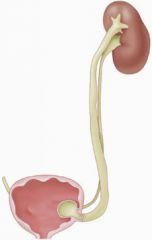
What is the tube that conducts urine from the kidney to the bladder? |
Ureter |
|
|
What is the urethra? |
The tube that carries urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body. |
|
|
What is the outer layer of the kidney called? |
The cortex |
|
|
What is the medulla? |
The area inside of the cortex |
|
|
What is the hollow area where the kidney joins the ureter? |
The renal pelvis |
|
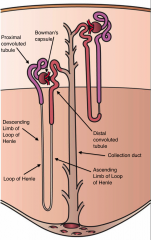
What is a nephron? |
A functional unit of the kidney |
|
|
What is a small branch of the renal artery that carries blood to the glomerulus? |
The afferent arteriole |
|
|
What is the high-pressure capillary bed that is the site of filtration? |
The glomerulus |
|
|
What is the efferent arteriole? |
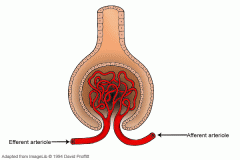
A small branch of the renal artery that carries blood away from the glomerulus to the peritubular capillaries. |
|
|
What is a member of the network of small blood vessels that surround the tubule of the nephron? |
The peritubular capillary. |
|
|
What is Bowman's capsule? |
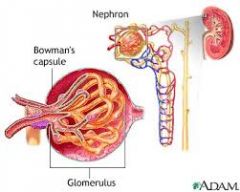
The cup like structure that surrounds the glomerulus. |
|
|
What is the section of the nephron joining the Bowman's capsule with the loop of Henle? |
The proximal tubule |
|
|
What is the loop of Henle? |
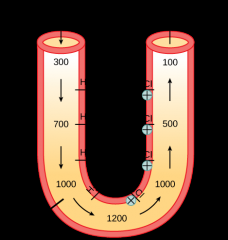
The section of the tubule that carries filtrate from the proximal tubule into the distal tubule. |
|
|
What conducts urine from the loop of Henle to the collecting duct? |
The distal tubule. |
|
|
What is the collecting duct? |
A tube that carries urine from nephrons to the renal pelvis. |
|
|
What is the maximum amount of a substance that can be moved across the nephron? |
Threshold level |
|
|
What is interstitial fluid? |
The fluid that surrounds body cells. |
|
|
What are the three functions of kidneys? |
Filtration, re absorption, and secretion. |
|
|
What is filtration due to? |
The pressure gradient within the glomerular apparatus. |
|
|
Is filtration selective? |
No. All solutes small enough to pass through the wall of the capillary will move to the Bowman's capsule. ie. water, salts, glucose, vitamins, nitrogenous waste (NOT RBCs) |
|
|
What is re absorption? |
The movement of small molecules from the tubules to the blood. |
|
|
Is re absorption selective? |
Yes. Ie. most sugars, vitamins, organic nutrients, and water. |
|
|
Where does re absorption take place? |
In the proximal, distal tubules, and the loop of Henle. |
|
|
What is secretion? |
The addition of plasm solutes to the filtrate within the tubule. |
|
|
What are the most common sites of secretion? |
Proximal and distal tubules. |
|
|
Is filtration selective? |
Yes. Very selective. Involves active and passive transportation. |
|
|
Explain the steps in which urine is formed. |
1. Blood is filtered in the glomerulus. 2. Ammonia, hydrogen ions, drugs and poisons are secreted into the proximal tubule. Bicarbonate is re absorbed to maintain pH of blood. 3. Water is re absorbed in the descending limb of the loop of Henle. 4. Thin part f the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to salt, and allows it to diffuse out of the tubule increasing the concentration of salt in the medula. The thick part secretes salts through active transportation, making the filtrate more dilute as it moves up to the cortex. 5. Secretion and re absorption continues to occur within the distal tubule. Potassium, salt, and pH levels are regulated further. 6. Filtrate is carried by the collecting duct back to the medulla and renal pelvis. Determines how much salt is being re absorbed or secreted. Water is further re absorbed, further concentrating the urine. |
|
|
What two hormones affect the kidneys? |
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), and Aldosterone |
|
|
Why and when is ADH released, and what does it do? |
The hypothalamus monitors the amount of water in the blood, and when the blood is too concentrated, the pituitary is stimulated to release ADH. ADH causes the distal tubules to become more permeable to water. More water is therefore reabsorbed from the urine into the blood. |
|
|
Why and when is aldosterone released, and what does it do? |
Within the kidneys, the adrenal gland releases aldosterone when the blood doesn't contain enough sodium. The tubules become more permeable to sodium and will set up a concentration gradient that allows water from the tubule to be reabsorbed into the blood. |
|
|
What is acute renal failure? |
The sudden failure of the kidney to filter waste products. Often reversible. |
|
|
What is dehydration due to? |
The environment, diuretics. or kidney failure. |
|
|
What are diuretics? |
Substances such as caffeine drinks and alcohol that decrease the secretion of ADH from the pituitary. |
|
|
What is insipidus diabetes caused by? |
Caused by damage to the hypothalamus or nerves leading to the pituitary. ADH is not released, and nephron is not stimulated to recover water. Symptoms include a large quantity of dilute urine, and a feeling of severe thirst. |
|
|
What is mellitus diabetes characterized by? |
A low/no secretion of the hormone insulin. Reduced/no insulin means ther is a lower absorption of glucose into the cells. This means greater glucose in the blood. If concentration is large enough, not all glucose is reabsorbed from nephron into the blood. This changes the osmotic gradient and water will not be reabsorbed. This loss of water increases urine output and decreases blood pressure. |
|
|
What organs are involved in the excretion of toxic materials? |
The lungs, the skin, the digestive tract, and the kidneys. |

