![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Financial statements communicate to external parties what info |
Results of operations, Financial position Cash flows |
|
|
FASB due process |
ID financial issues Technical agenda Deliberation at public meetings Exposure draft Public meeting Final draft |
|
|
Financial position helps understand |
Changes in resources and claims on them Evaluating potential cash inflows Determine how external factors effect resources |
|
|
Assumptions of financial accounting |
Economic entity- separate entity Gonna concentrate Monetary unit Periodicity- fiscal years |
|
|
Principals of financial accounting |
Revenue recognition and matching principal Historical cost-reported at cost Full disclosure - report everything |
|
|
Constraints of financial reporting |
Cost Industry practices Conservatism |
|
|
Funadamental qualitative characteristics |
Relevance Predictive value Confirmatory valve Material Faithful representation Completeness Neutrality Free from error Enhancing qualitative characteristics Comparability Verifuability Timeliness Understandibility |
|
|
A full set of financials should include |
Financial position at end of period Earnings for period Comparative income CASH FLOWS investments and distributions to shareholders |
|
|
Recognition criteria |
Definition of an element Measurable Relevant Reliable |
|
|
SEC regulations |
S-X reporting interim and annual S-K disclosures S-B small business issues S-T types of docs Financial Reporting Releases- updates Staff Accounting Bulleins - interpretations |
|
|
Basic info packet |
Financial statements 5 year of certain info MD&A Dividends and market value Description of business Location of properties Pending litigation Management Security holdings Matters up for shareholder approval Business relationships |
|
|
Transactions not reported |
Transactions with owners Error corrections Initially reported comprehensive income Transfers to/from retained earnings Accounting changes in prior years |
|
|
Discontinued operations are reported on the income statement |
Separately and net of tax Gains/losses are shown on face of Inc. Stmt or notes |
|
|
Earnings per share numerator |
Net income - dividends on preferred stock And Inc. From contin. Ops - divide on ps |
|
|
Earnings per share denominator |
Weighted average of shares Total number of shares x (time frame÷12) Then total all for the year Contingent issuable shares are included when conditions are met |
|
|
Diluted earnings per share |
Convertible securities Options/warrants Contingently |
|
|
Convertible bonds effect on diluted earnings per share |
Numerator Face amount x rate x (1-tax rate) added to top Denominator Face / par value added to bottom |
|
|
Convertible preferred stocks effect on diluted earnings per share |
Numarator #shares x par x % is added to top Denominator # of shares ÷ conversion ratio added to den. |
|
|
5 steps to recognize revenue from contract |
1 ID contract 2 ID performance obligations 3 determine price 4 allocate price to obligations 5 recognize revenue when performed obligation |
|
|
Treatment of costs to obtain a contract |
1 asset that is capitalized and amortized 2 if amort < 1 year expense 3 expensed as incurred if would have cost with or without contract as a result |
|
|
What are common policies required to be disclosed |
Basis of consolidation Depreciation method Amortization of intangibles Inventory pricing Rev recog. From contracts Rev recog. From leases |
|
|
3 characteristics of an operating segment |
1 a business component that earns revenue and incurs expenses 2operating regularly reviewed by operator 3 separate financial info is available |
|
|
Operating segments can be aggregated if... |
1 is consistent with with objective 2 similar economic characteristics 3 similar products, services, customers, distributions |
|
|
Quantitative thresholds for reporting segments |
1- 10% of internal and external sales 2- 10% of all assets 3- 10% of profit/loss Separate profit segments from loss segments Threshold = 10% of larger of total profits or total losses |
|
|
Disclosures for reporting segments |
Revenues from externals and internals Interest revenue interest expense Depreciations, deletion, amortization Unusual items Equity Income tax expense or benefit Other noncash items Reconciliation to consolidated |
|
|
Accounting method and influence on ownership of equity |
0-20 little or none, FM 20-50 significant, equity method or FM 50-100 control, consolidate method |
|
|
Equity method measurement of goodwill |
Cost - % ownership in net assets - % ownership in fv in excess of cost = good will. Not separately reported |
|
|
Change to and from equity method |
When significant control is obtained in steps apply prospective Investment = cost of addition shares+ current basis in previously owned shares When lost change to fmv method |
|
|
Held to maturity securities |
on balance sheet Reported at amortize cost - of premium of discount on balance sheetIncome statement for realised gains/losses and interestCashflows- investing activity Income statement for realised gains/losses and interest Cashflows- investing activity |
|
|
Trading securties |
Recorded at cost Income statement - unrealized holding gain/loss Cashflow- operating activity |
|
|
Available for sale securities |
Recorded at cost Unrealized gain/loss on oci Cashflow - investing activity |
|
|
Change in type of security |

|
|
|
Purchase of bond at premuim |
Present value = face x (PC of $1 at market rate for life of bond) Present value of interest = face x stated rate x pv of ordinary annuity Cost = pv of face + pv of interest Premium = cost - face |
|
|
Purchase of bond at discount |
Cost= face x of par amount |
|
|
Amortization of bond premium or discount |
Carry value x market rate = interest revenue Face value x purchase rate = interest received Difference = amortization Cash. Xxx Int. Rev. Xxx Investment. Disc. Prem. |
|
|
Bad debt expense calculation, income statement approach |
Matching principal, % of credit sales is calculated and that amount is the entry Bad debt expense. Xxx Allowance. Xxx |
|
|
Bad debt expense balance sheet approach |
Total allowance is calculated by % of accounts receivable Adjustment is made to make allowance account = the amount calculated |
|
|
Factoring |
Selling oc accounts receivable to a 3rd party Credit cards are common example Total receivables - reserve (1 - % advance) - factor fee = accruing to factor - interest = amounts received immediately |
|
|
COGS for manufavturing |
Begin materials + purchases, freight - returns, discounts - ending materials = direct materials used in production + direct labor, over head costs = total manufacturing costs for period + beginning WIP - ending WIP = COGS manufactured + beginning finished goods - ending finished goods = Cogs |
|
|
Inventory balance calculation using moving average method |
Recalculated for each purchase Begin inventory (100 units, 20 each) 2,000 + purchase 20 units for 32 each. 640 = 120 units. 2,640 or $22 each Every sale decreases inventory for most recent inventory price, so a sale for above would be for $22 each item. |
|
|
Weighted average inventory calculation |
Periodic method Begin inventory cost + cost of purchases ------------------------------------------- Units at begin + number purchased Begin inventory cost + purchases cost - ending inventory (count * weighted avg.) = COGS (units sold * weighted avg.) |
|
|
Inventory valuation lower of cost or market |
Ceiling = net realizeable value Floor = NRV - normal profit Market = replacement cost Market is the value unless goes above ceiling or below floor. |
|
|
Recognition of intangible goods, not goodwill |
External- purchase price or fair value Internal - legal fees, R& D is expensed as incurred |
|
|
Deferred tax liability/asset |
DTL- when gaap income > taxable income. Will owe more tax in the future DTA - when gaap income < taxable income. Will receive tax credit or pay less tax in future |
|
|
Switching from trading to available for sale securities |
Any fv adjustment only occurs due change in fv from date of conversion to year end or sale. |
|
|
Pension plans |
Defined contribution plan - benefits depend on contributions and earnings. - no guaranteed amount, only guaranteed contrib. - asset if contribute more than required. Defined benefit plan - defines amount of benefit employee receives - actuarial and investment risk - depend on life, employment, and compensation - complex |
|
|
Defined benefit pension plan expense calc. |
Service cost + interest cost = begin PBO x Discount Rate - expected return = fv x long term rate +/- amort of g/l +/- amort of prior service cost or credit = net periodic pension expense
Difference between ending calc and pbo ending value = liability loss (positive) or liability gain (negative) Asset gain/loss is the difference between expected and actual. Net gain/loss = liability gain/loss +/- asset gain/loss |
|
|
4 types of bonds |
Mortgage- backed by assets like real estate Debentures- backed by borrowers credit Collateral trust- backed by securities Guaranteed- guaranteed by a 3rd party |
|
|
Pv and fv of annuities |
Use the pv and fv factor tables to calculate an ordinary annuity. Take the ordinary annuity x (1 + interest rate) for annuity due |
|
|
Calc of bond pv |
Must separate to 2 parts PV of face amount ($1) Pv of interest (face x stated rate) (annuity) |
|
|
Amortization of bond premium or discount |
Carry value of bond X market rate = interest expense - cash paid = amortization Into. Exp. Xxxx Premium amort. xxxx Discount anort. Xxxx Cash. Xxxx |
|
|
One of the 4 indicators of a capital lease |
1) provides for transfer of ownership 2) bargain purchase option 3) term is at least 75% of useful life 4) Pv of payments at least 90% of fair value |
|
|
Pv of leased property |
2 parts 1) Pv of minimum rental payments 2) pv of bargain purchase option or pv of residual value |
|
|
Property dividends |
Date of declaration - revalue property to fv Loss on revaluation. Xxxx Inventory. Xxxx Retained earnings. Xxxx Dividends payable. Xxxx Date of distribution Dividend payable. Xxxx Inventory. Xxxx |
|
|
Asset acquisition vs business combination |
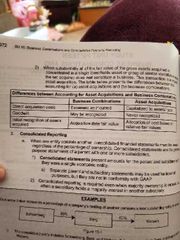
|
|
|
Recognition of business combination costs |
Acquisition costs - expenses incurred Direct issue of stock costs - expenses to APIC Indirect issue of stock costs - expenses as incurred Debt issue costs - direct deduction from carry amount of debt |
|
|
Business combination- acquisition method |
Fmv at acquisition date
Also consider contingent consideration - promises from acquirer to the former owners also at fmv of acquisition date. If with assets revalued each statement date. If with equity no revaluation. Equity account of aquiree are irrelevant. Which includes non-controlling ownership which is recorded separately in the balance sheet |
|
|
Goodwill calculation |
Consideration transferred + noncontrolling interest Consideration transferred + noncontrolling interest- carrying amount of net assets (assets-liabilities) - excess fair value of assets = goodwill Consideration transferred + noncontrolling interest- carrying amount of net assets (assets-liabilities) - excess fair value of assets = goodwill - carrying amount of net assets (assets-liabilities) - excess fair value of assets = goodwill |
|
|
Quick ratio |
Acid test- more conservative than current ratio Cash&equivalents + marketable securities + net receivables ‐--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Current liabilities |
|
|
AR turnover ratio |
Number of times a year receivables is cashed
Net sales / average balance in receivables Average collection period Days in year / ar turnover ratio |
|
|
Inventory ratios |
Inventory turnover Cogs/ avg inventory balance Days sales in inventory Days in year / inventory turnover ratio |
|
|
Cycle ratios |
Operating cycle = time between inventory received and when cash collected on sale Days in sales + days in inventory |
|
|
Operating activities |
Income: Receipts from sales or services Royalties, fees, commissions other revenue Interest or dividends Receipts from sale of debt or equity for the purpose of resale Outflows: Goods or services Employees Taxes, duties, fees Interest |
|
|
Investing activities |
PPE, intangibles, long live assets sales or purchases Held to maturity sales or purchases Cash advances or loans to other parties |
|
|
Financing activities |
Inflows: Issuing shares or equity Issuing loans notes Outflows: Repayments or borrowed amounts Cash dividend payments Cash paid to acquired own shares |
|
|
Governmental funds |
General Special revenue - restricted or committed Capital projects - capital projects Debt service- paying principal and interest Permanent - where funds are restricted to earnings not principal |
|
|
Proprietary funds |
Enterprise funds Internal service funds |
|
|
Fiduciary funds |
Pension and trust - employee benefits Investment trust - trusts on behalf of other govs Private purpose - benefit individuals, private orgs. Agency - held for custodial, like tolls |

