![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The purpose of the IS is to provide info about
the uses of funds in the income process - _________ , the uses of funds that will never be used to earn income - __________ , the sources of funds created by those expenses - __________, and the sources of funds not associated with the earnings process - __________ |
EXPENSES
LOSSES REVENUES GAINS |
|
|
|
The IS is useful in determining __________, _________ for investment purposes and credit__________.
|
PROFITABILITY
VALUE WORTHINESS |
|
|
|
Cost is the amount actually paid for something.
If COST is expensed immediately - it is ________ cost; if NOT expensed immediately - it is ________ |
PERIOD
CAPITALIZED = ASSET |
|
|
|
Unexpired cost is _________ because it can generate revenue in the future.
|
ASSET
|
|
|
|
_________ and _________ are normal reacuring operations , both separately reported at their ________ amounts
|
REVENUES AND EXPENSES
GROSS |
|
|
|
__________ and _________ are nonoperating income and reported at their _________ amounts.
|
GAINS AND LOSSES
NET |
|
|
|
COGS =
|
BI .
+ GOGM/purchases - EI . _________________ COGS . |
|
|
|
In the SINGLE STEP IS presentation of income from continuing operations, total _______ are subtracted form total ________ .
|
EXPENSES
REVENUES |
|
|
|
iDea - Discontinued operations
- are reported separately from continuing operations in the IS in the period in which they occur - anticipated losses NOT allowed. The loss form Discontinued operations can consist of an (3) |
1 impairment loss
2 G/L form actual operations 3 G/L on disposal |
|
|
|
A component of a business is classified as "Held for sale" in the period in which ALL criteria are met:(6)
|
1. Plan to sell
2 available for immediate sale 3 active to locate a buyer 4 expected to sell within ONE year 5 is being actively marketed 6 significant changes are unlikely |
|
|
|
Both of the following conditions must be met in order to report
income from DISCONTINUED operations : |
1 ELIMINATED FROM ONGOING OPERATIONS
2 NO SIGNIFICANT CONTINUING INVOLVEMENT |
|
|
|
Report the results of DISCONTINUED operations in period component is
DISPOSED OF or IS CLSSIFIED AS HELD FOR SALE. Types of items included : (3) |
1 revenues/expenses of the component - for that period
2 G/L on Disposal - in the period of sale 3 Impairment Loss and Subsequent increase in FV SP/NRV < BV, report immediately in the period HELD FOR SALE |
STAR
|
|
|
The results of DISCONTINUED operations, net of ________, are reported as a separate component of IS before the _________.
G/L disclosed in ______ or in ________ |
TAX
EXTRAORDINARY FACE OR NOTES |
STAR
|
|
|
idEa - EXTRAORDINARY ITEMS -
must be _____ AND _________ |
UNUSUAL AND INFREQUENT
|
|
|
|
MATERIAL Unusual OR Infriquent items shoul be reported as a separate line item as part or income from ___________________ at ____ amount.
|
CONTINUING OPERATIONS
GROSS |
|
|
|
INCOME STATEMENT
Normal reoccurring operations list the items for multiple step |
Net sales
Cost of sales ----------------------------------- Gross margin Selling expense G&A expenses Depreciation Expence ----------------------------------------- Income (loss) from operations |
|
|
|
INCOME STATEMENT
Non-operating list the items for multiple step |
OTHER revenues and gains:
Interest Income Gain on transactions in foreign currencies OTHER expenses and losses: Interest Expense Loss on sale of fixed assets INCOME before unusual items and income tax UNUSUAL or infrequent items Gain on litigation settlement Gain on sale of available-for-sale investments INCOME before income tax |
|
|
|
Net sales=
|
Net sales= Gross Sales - returns - discounts
|
|
|
|
Inventory cost =
Selling expense= G&A expenses= Non-operating = |

|
|
|
|
҉
Examples of extraordinary items: 1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. the abandonment of a plant due to an INFREQUENT earthquake.
2. An expropriation of a plant by the government. 3. A prohibition of a product line by a newly enacted law or regulation. 4. Certain gains or losses from extinguishment of long-term debt - must say unusual and infrequent. |
|
|
|
҉
Examples of NONEXTRAORDINARY items: 1.2.3.4.5. |
1. Gains or loss form sale or abandonment of property, plant or equipment used in the business
2. Large writedowns or writeoffs of: A/R, Inventory, Intangibles, Long-term securities 3. G/L from Foreign currency transactions of translation. 4. Losses from major strike by employees 5. Long-term debt extinguishments (not unusual and infrequent) |
҉
|
|
|
DISCOUNTINUED OPERATIONS – are reported separately from continuing operations in the _________. The loss from discontinued operations can consist of an Impairment loss, a Gain/loss from actual operations, and the Gain/loss on disposal. (in the period in which they occur) (iDea)
|
Income Statement
|
|
|
|
҉
CHANGE IN ACCOUNTING ESTIMATE - PROSPECTEVELY In the 3rd year of asset it estimated useful life was changed from 10 to 5. how to calc. the depreciation for current and future years? |
(BV- accum depr. ) / remaining useful life using new estimate (5-2)
|
|
|
|
IDE(A)
Accounting changes are broadly classified as (3) 1. Changes in accounting ESTIMATE - Prospective as Income from Cont. oper. 2. Changes in accounting PRINCIPLE - GR - Retrospective Change from GAAP to _________ Principal may be changed only IF new principal is _________ and _________ presents the information. 3. Changes in accounting ENTITY - Retrospective |
Change from GAAP to GAAP
preferable and more fairly |
|
|
|
҉
IDE(A) Accounting changes are broadly classified as (3) 1. Changes in accounting ESTIMATE - Prospective as Income from Cont. oper. 2. Changes in accounting PRINCIPLE - GR - Retrospective GR such changes should be recognized by adjusting _________ in the earliest period presented for the cumulative effect of the change. EXCEPTION TO GR: 1. if IMPRACTICABLE to estimate. EX: change from ______ to_______ 2. Change in the method of ________, _________and ___________ is concidered to be both a change in acct principle and change estimate. 3. Changes in accounting ENTITY - Retrospective |
beginning RE
1. LIFO to FIFO 2. Depr., Amort. and Depletion => PROSPECTEVELY |
|
|
|
Prior period adjustments are not considered ______________
|
ACCOUNTING CHANGES
|
|
|
|
Prior period adjustments:
1. Correction of __________ 2. new GAAP pronouncement 3. Changes from __________ method of accounting to ____________ |
1. ERROR
3. non-GAAP TO GAAP (from cash basis to accrual) |
|
|
|
STM of R/E ҉
|
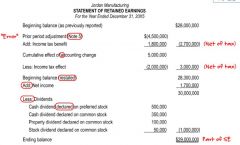
|
|
|
|
F/S prep under wich of the methods include andjustments for both
specific price ∆ and general price-level ∆ |
CURRENT COST, CONSTANT DOLLAR
|
|

