![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
176 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two main causes of abdominal pain |
Conditions associated with inflammation Conditions associated with obstruction of a smooth muscle tube |
|
|
Describe the pain associated with inflammation in the abdomen |
Constant pain Made worse y any local or general disturbance Persists until the inflammation subsides |
|
|
Describe the pain associated with obstruction in the abdomen |
Colic- pain which fluctuates in severity at frequent intervals and feels gripping in nature Peaks are short and intermittent, but the pain seldom goes away completely during exacerbations |
|
|
What does prolonged obstruction in the abdomen feel like? |
It feels like constant stretching due to distension of the viscus (not colicky) |
|
|
Male 50 epigastric pain Vague mild discomfort Constant Radiates to back Relieved by eating, worse at night |
Peptic ulcer |
|
|
What drugs may exacerbate the symptoms of a peptic ulcer? |
NSAID's, steroids |
|
|
Which type of ulcer is relieved or worsened by eating? |
Peptic- made better by eating Duodenal- made worse by eating |
|
|
Female 45 Fairly sudden pain but H/O dyspepsia and pain after eating Pain in right hypochondrium Radiates to back and is continuous Exacerbated by movement and breathing Nausea and vomiting Anorexia |
Acute Cholecystitis |
|
|
What causes cholecystitis? |
Commonly caused by obstruction of the cystic duct by a small stone with proximal distension, statis and secondary inection |
|
|
What are the risk factors for Cholecystitis? |
Fair Fat Female Forty |
|
|
Male 55- Sudden onset colic across upper abdomen- Very severe- 10/10 Does not remit between exacerbation Severe pain lasts > 2 hours Nausea and occasional vomiting Long history of flatulence and dyspepsia |
Bilary colic |
|
|
What is bilary colic? |
Severe pain caused by spasm of the gall bladder as it trys to force a stone down the cystic duct |
|
|
Female 60 Severe LIF pain, constant, exacerbated by movement, feels distended Anorexia, nausea, no vomiting Diarrhea, hot and sweaty Dyuria and frequency |
Acute diverticulitis |
|
|
What are the risk factors for eptopic pregnancy? |
Previous PID, infertility, tubal surgery, IUCD, previous eptopic |
|
|
How would an eptopic pregnancy present? |
Lower abdo pain with PV bleed, cardiovasular collapse with shoulder tip pain Abdo and adnexal tenderness Postive pregnancy test U/S empty uterus, may show eptopic |
|
|
What are the causes of PID? |
Chlamydia 60% Nisseria gonorrhoea 30& |
|
|
How does PID present? |
Lower abdo pain and vaginal discharge Pelvic examination uncomftable |
|
|
Describe the presentation |
Sudden onset severe lower abdo pain May be palpable on bimanual |
|
|
What are the main causes of small bowel intestinal obstruction? |
Hernia, adhesion's, inflammation (eg crohns) radiation, intersuseption (meckels, poly) |
|
|
What are the main causes of large bowel intestinal obstruction? |
Carcinoma, volvulus, inflammation (diverticulus) |
|
|
What are the cardinal symptoms of bowel obstruction? |
Pain, vomiting, distension and absolute constipsation |
|
|
Describe the nature of the vomitus found with obstruction at different levels |
pyloric obstruction- watery acid High- small bowel- greenish, bile stained Distal small bowel- brown foul smelling 'faeculent' Large bowel- very late feature |
|
|
Describe the amount of abdominal distension seen with obstruction at different levels? |
High obstruction- not much distension Lower obstruction- more distension |
|
|
Where is AAA pain referred? |
Central back |
|
|
Where is gall bladder pain refered? |
Right scapular pain |
|
|
Where is LL pneumonia pain felt? |
Abdo pain |
|
|
Where does renal colic radiate |
The groin |
|
|
What signs would you see with generalised peritonitis? |
Rebound tenderness, guarding, fever, tachycardia, absent bowel sounds |
|
|
What are common causes of generalised peritonitis? |
Perforated GI tract Ruptured AAA Ischemic bowel |
|
|
How would bowel sounds sound if there is obstruction? |
Tinkling |
|
|
What are the causes of acute peritonitis? |
Gall stones Ethanol Trauma Steroids Mumps Autoimmune Scorpion bite Hyperlipidemia ERCP Drugs |
|
|
What risk factors are associated with developing GORD? |
Increased intra-abdominal pressure, inadequate cardiac sphincter, smoking, alcohol, fat, coffee, pregnancy, obesity, tight clothes, big meals, systemic sclerosis, hiatus hernia, drugs inc- TCA's anticholinergics, nitrates and calcium channel blockers |
|
|
Is H.Pylori associated with GORD? |
No |
|
|
What investigations can be done for suspected GORD? |
Endoscopy FBC to exclude anemia Barium swallow may show hiatus hernia Oesphageal pH monitoring to see if symptoms collide with when acid is in the osephagus |
|
|
What are your differential for GORD |
Oesophogitis from corrosive drugs eg NSAIDs Infection Peptic ulcer GI cancers Non-ulcer dyspepsia Oesphageal spasm |
|
|
What are the red flags for upper GI cancers? |
Dysphagia- food sticking Dyspepsia plus weight loss/ anemia/ vomiting FH of upper GI cancer Barretts oesphagus Pernicious anemia Peptic ulcer surgery known dysplasia, atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia Upper abdo mass |
|
|
What lifestyle advice is useful for patients with GORD? |
Reduce weight, stop smoking, reduce alcohol intake, sleep with more pillows, take small regular meals, avoid hot drinks/ alcohol/ eating three hours before bed, avoid drugs that affect oesphageal motility |
|
|
How do we treat GORD? |
PPI |
|
|
What are the causes of peptic ulcers? |
Hy. Pylori, NSAID's, pepsin, smoking, alcohol, bile acids, steroids, stress |
|
|
What are the symptoms of peptic ulcer disease? |
Epigastric pain Nausea Oral flatulence Heartburn |
|
|
What investigations should you do you a suspected peptic ulcer? |
FBC (anemia) H. Pylori testing- Carbon- 13 breath test/ stool antigen test/ lab serology Endoscopy |
|
|
What are the indications for endoscopy for suspected peptic ulcer disease? |
If a patient is presenting for the first time and is over 55 if there is: Iron deficiency anemia, chronic blood loss, weight loss, progressive dysphagia, persistent vomiting or an epigastric mass |
|
|
What lifestyle changes can be done to help manage peptic ulcer disease? |
medications review- adapting the way they take drugs like NSAID's/ asprin- after food/ stopping them Smoking caesation |
|
|
How do we treat H.Pylori postive ulcers? |
A 7 day course of a PPI and amoxicillin and either clarithromycin or metrondazole- all twice daily |
|
|
What complications are associated with peptic ulcers? |
Haematemesis or melaena or associated with erosion of a large blood vessel Perforated peptic ulcer can cause an acute abdomen Scaring of the duodenum may lead to pyloric stenosis |
|
|
Define constipation |
Defecation less than three times a week or straining on defecation at least 25% of the time |
|
|
What are the mechanical problems that may lead to constipation? |
Waste matter to hard to pass Movements infrequent Less frequent bowel movements than usual Sense of incomplete evacuation |
|
|
What people are my likely to be constipated? |
Older, female, poor socio-economic status, less exercise, less education, low calorie intake |
|
|
What are the causes of constipation |
Low fibre diet, inadequate fluid intake/ dehydration, immobility, old age, postoperative pain, hospital environment, |
|
|
What are the anorectal causes of constipation? |
Anal fissure, anal stricture, rectal prolapse |
|
|
What are the main causes of obstructive constipation? |
Abdominal mass- foetus/ fibroids Colonic carcinoma Strictures eg crohns Diverticulosis |
|
|
What are the neuromusclar causes of constipation? |
DM neuropathy, spinal pelvic injury, hirschsprungs disease, depression, PD |
|
|
What drugs can make you constipated? |
Antacids, anticholimergics, antidiarrhoeals, antiparkinsons, antidepressents, antihypertensives, metals eg bismuth/ iron, opiods, NSAID's |
|
|
What investigations should be done for constipation? |
U&E's, FBC, ESR, TSH, calcium Abdo x-ray Signmoidoscopy |
|
|
What are bulk laxatives? |
The increase in faecal mass stimulates peristalsis Need plenty of fluid so not for those with swallowing problems |
|
|
What are stimulant laxatives? |
Increase motility so not in obstruction Eg- Bisocodyl, docusate or Senna Used for rapid emptying of bowel Enema- glycerine |
|
|
What are osmotic agents? |
Hold fluid in the bowel Eg. lactulose, macrogols (movicol), magnesium salts Good oral fluid intake required |
|
|
What are Stool softeners? |
containing arachis oil, lubricate and soften impacted faeces and promote a bowel movement
|
|
|
What is IBS? |
A relapsing functional bowel disorder in which abdominal pain or discomfort is associated with defecation or a change in bowel habit Bloating and distension are often associated |
|
|
What is the aetiology of IBS? |
There is no structural lesion, however it seems to involve abnormal smooth muscle activity and sometimes viseral hypersensitivity and abnormal central processing of painful stimuli |
|
|
What are the three main types of IBS? |
IBS with constipation IBS with diarrhea IBS with diarrhea and constipation |
|
|
What is the diagnostic criteria for IBS? |
->6 months of: Abdominal pain or discomfort/ bloating/ change in bowel habit -Also, abdominal pain is either relieved by defecation or associated with altered stool frequency or form -And at least two of the following: altered passage of stool, abdominal bloating, aggravated by eating, passage of mucus rectally |
|
|
How is IBS managed? |
Reassurance and explanation Dietary advice- fibre and fluids Probiotics |
|
|
What is Crohns disease? |
It is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease of unknown aetiology, characterised by focal, asymmetrical, transmural and occasional granulomatous imflammation |
|
|
Where area of the bowel is affected by Crohns? |
Any part of the GI tract but particularly the terminal ileum and proximal colon There may be unaffected bowel between areas of active disease (skip lesions) unlike UC |
|
|
What are the risk factors for Crohns? |
Family history Smoking Interrecurrent infections NSAID's |
|
|
What are the symptoms of IBD? |
Diarrhoea, may be bloody/ chrionic Abdominal pain Weight loss Malasise, anorexia or fever |
|
|
How might children with crohns present? |
Poor growth Delayed puberty malnutrition bone deminerisation |
|
|
What might you find on examination of a patient with Cronhs? |
General ill health- weight loss, fluid depletion and anemia Hypotension/ tachycardia/ pyrexia Abdo tenderness/ distension/ palpable mass Anal and perianal lesions Mouth ulcers |
|
|
What extra-intestinal features might you find on a patient with cronhs? |
clubbing, erythema nordosm, conjuctivitis, episcleritis, iritis, large joint arthritis, ank spod, fatty liver, granulomata in the skin/ epiglottis/ mouth etc, renal stones, osteomalcia, malnutrition, amyloidosis |
|
|
What investigations are useful in a patient with suspected crohns?
|
Bloods- FBC, CRP U&E's, LFT's Stool culture and microscopy Antibodies to yeast- ASCA- high in Crohns, p-ANCA is higher in UC Microbiological testing for clostridium difficile toxin Iliocolonscopy- biopsys Small bowel follow through |
|
|
Discuss the managment of crohns |
Prophylatic Mesalazine Corticosteriods eg budesonide Enteral nutrition Antibiotics Anti-diarrheals- but not in acute flares Immunomodulators - eg Azathioprine, mercaptopurine or methotrexate Cytokine modulators- Infliximab or adalimumab Surgery |
|
|
How do you treat an acute flare of Crohns? |
1) systemic corticosteriods 2) Azothioprine, mercaptotopurine or methotrxate if intolerant 3) Infliximab 4) Surgery |
|
|
What complications might a patient with crohns get in the bowel? |
Strictures,- obstruction? Fistulae between different parts of the bowel, bladder, vagina or skin Perforation Crohns colitis- increased risk of colonic carcinoma |
|
|
Other than in the bowel, what other complications might you see in crohns? |
Oestoporosis- especially with steriod use Renal disease- secondary to obstruction iron/ folate/ B12 defiency Gall stonesand renal stones Delay in growth/ puberty if disease is active during preganancy- complictions such as still birth/ abortion |
|
|
What are the common disease distributions in UC? |
UC mostly starts at the rectum and moves proximaly with no skip lesions, |
|
|
What risk factors are associated with UC? |
Family history NSAID's- weak evidence Oral contraceptives- low risk Non-smokers- smoking is proctective |
|
|
What are the main symptoms of UC? |
Cardinal symtpom is bloody diarrhoea Colicky abdominal pain, urgency, tenesmus Constipation- if UC just in rectum Malise/ fever/ weight loss Extraintestinal- joint/cutaneous/eye involvement |
|
|
What investigations should be done for suspected UC? |
FBC, U&E's, LFT's, ESR, CRP, iron, B12 and folate Faecal calprotectin Microbiological testing for clostidium difficle Sigmoidoscopy AXR- if acute Colonscopy and biopsys USS/ C/ MRi |
|
|
What is mild UC? |
<4 stools daily, only small amounts of blood in the stool, no anemia, pulse <90, no fever, normal ESR and CRP |
|
|
What is moderate UC? |
4-6 stools a day with not much blood in them, no anemia, pulse <90, no fever, normal ESR/ CRP |
|
|
What is severe UC? |
6+ stools a day, visible blood in the stool, at least one feature of systemic upset- temp >37.8, pulse >90, anemia, ESR>30 |
|
|
What are the treatments for UC? |
Aminosalicylates- 5-ASA for induction and maintenance of remission Cortricosteriods- to induce relapsed Thiopurines- eg Azathioprine Ciclosporin Infliximab Stool bulking agents |
|
|
What are the main types of upper GI cancers? |
Oesphagus, GOJ, stomach |
|
|
What type is cancer do you find in the upper/ mid oesphagus? |
Squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
What type of cancer do you find in the lower oesphagus and below? |
Adenocarcinoma |
|
|
What age and gender is oesphageal cancer common in? |
Male: Female 2:1 Peak incidence 60-80 years |
|
|
What are the risk factors for oesphageal cancer? |
Smoking, alcohol, barretts, achalasia, obesity, diet |
|
|
What are the red flag symptoms of oesphageal cancer? |
Dysphagia, vomiting, anorexia, weight loss, GI blood loss |
|
|
What is a useful investigation in suspected oesphageal cancer? |
barium swallow Apple core lesion seen with distal oesphageal adenocarcinoma |
|
|
Describe the TNM staging system? |
T1- lamina propria/ submucosa T2- muscularis propria T3- Adventitia T4- Adjacent structures N1- 1/2 nearby nodes N2- 3-6 nearby nodes N3- >7 nearby nodes M1- distant metastases |
|
|
What investigations do we use to help stage oesphageal cancer? |
CT PET EUS Laparscopy |
|
|
What side effects are associated with chemo? |
GI- nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation Skin- hair loss Neurotoxicitiy- peripheral, tinnitus/ deafness Renal toxicity Fatigue Hematological- thrombocytonpenia, anemia, neuropenia Cardiovascular- angina/ MI, arrhythmias, cardiac failure |
|
|
What are the contraindications for chemo? |
IHD Renal disease Performance status Patient choice |
|
|
What are the side effects of radiotheraphy? |
Fatigue, dyphagia, nausea, skin reaction |
|
|
What are the risk factors for stomach cancer? |
Diet, H.Pylori, smoking, familial adenomatous polyposis, barrets oespagus, pernicious anemia |
|
|
What type of cancer is gastric cancer? |
Adenocarcinoma 90% |
|
|
What environmental/ lifestyle factors are associated with bowel cancer? |
Obesity and inc BMI Inc red meat consumption low fibre Few fruits and vegs Physical inactivity Smoking Alcohol |
|
|
Describe the tumor spread spread of colon cancer? |
To adjacent organs Transcoelomic spread- peritoneal disease Reginonal lymph node involvement Heamatogenous- liver- lung- bone- brain |
|
|
What symptoms are associated with right sided colon cancer? |
Iron deficiency A palpable mass |
|
|
What symptoms are associated with left sided colon cancer? |
Change in bowel habit- looser more frequent stools and rectal bleeding |
|
|
What symptoms are associated with colorectal cancer? |
Rectal bleeding, tenesmus |
|
|
What investigations should you do for suspected colon cancer? |
FBC, U&E's, LFT, CEA- carcinoembryonic antigen |
|
|
What investigations help to stage colon cancer? |
CT PET MRI pelvis EUS laparoscopy |
|
|
Describe Dukes colon cancer staging |
A- In situ, in submucosa or muscosa propria but not through it B1- Into but not beyond muscluaris propria B2-through the muscluaris propria but no nodes C1- node postive but not apical node C2- Apical node positive D- metastatic |
|
|
What type of cancer is pancreatic cancer? |
Adenocarcinoma 90% infiltrating ductal adenocrdinomas |
|
|
What are the risk factors for pancreatic cancer? |
Smoking, diet, diabetes, alcohol intake Chronic or hereditary panceratitis FH Familial cancer syndromes eg BRAC1/2 |
|
|
What are the symptoms of pancreatic cancer? |
Epigastric discomfort, More than 2/3 occur in the head of the pancreas- and present with painless jaundice Tumors in the body and tail of the pancreas occur in patients presenting with non-specific pain and weight loss and are less likely to cause obstructive signs and symtpoms- presentation may be due to paraneoplastic processes |
|
|
What symptoms should you ask about in suspected pancreatic cancer? |
Abdo pain- eased when sitting forward Jaundice- also pale stools, puritis and dark urine Acute pancreatitis Weight loss/ anorexia Steatorrhoea- due to malabsorption Epigastric mass- late Haematemasis, melaena, iron deficiency anemia |
|
|
What is Couvoisers sign? |
It states that in the presence of an enlarged gallbladder which is nontender and accompanied with mild jaundice, the cause is unlikely to be gallstones. |
|
|
What blood tests will help you diagnose pancreatic cancer? |
FBC, LFT's Serum glucose Tumour markers |
|
|
What scans help to confirm the presence of pancreatic cancer? |
USS abdominal CT Endoscopic USS |
|
|
How is pancreatic cancer managed? |
Surgical resection Chemo Palliation |
|
|
What type of cancer is liver cancer? |
Hepatocellular cancer |
|
|
What are the risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma? |
90-95% of patients with HCC have cirrhosis HBV is the most common cause of HCC worldwide HCV is the most common cause of HCC in Europe Alcoholism, generic haemochromatosis, primary bilary cirrhosis, metabolic syndrome |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Hepatocellular carcinoma? |
Puritis, splenomegally, bleeding oesphageal varicies, weight loss, jaundice, confusion and hepatic encephalopathy, abdominal distension due to ascites, RUQ pain |
|
|
What signs are associated with HCC? |
Jaundice, Hepatomegally, ascites, spider naevi, peripheral oedema, anemia, periumbilical collateral veins, flapping tremor |
|
|
What populations should be screened for HCC? How do we screen? |
Cirrohtic HBV carriers, non-cirrotic patients with high HBV DNA concentration USS at 6/12 monthly intervals |
|
|
What conditions are associated with alcohol? |
Liver disease, pancreatitis, gastritis, arrhythmia & cardiomyopathy, cerebellar degeneration/ peripheral neuropathy, wernikes encephalopathy, withdrawal/ delirium tremens |
|
|
What conditions are indirectly related to alcohol? |
Hypertension, IHD, stroke, cancers inc oral, oesphageal and breast, trauma and violence, domestic violence, deliberate self harm |
|
|
What is the daily drinking guidelines? |
2-3 units |
|
|
Define hazardous drinking? |
Drinking above sensible levels but not yet experiencing harm A pattern of drinking that brings about the risk of harm |
|
|
Define harmful drinking |
Drinking above recognised sensible limits and experiencing harm |
|
|
Define dependent drinking |
Drinking above sensible levels and experiencing harm and also showing dependence |
|
|
Define alcohol dependence |
A craving for alcohol Difficult in controlling drinking A physiological withdrawal state Increased tolerance Centralization of drinking in lifestyle Continued drinking in spite of known harm |
|
|
How many units is classed as binge drinking |
>8 men >6 women |
|
|
What is the CAGE questionaire |
Cut down Annoyed Guilty Eye opener |
|
|
Features of alcohol withdrawal |
Shaking- sympathetic overactivity Delirium tremens Seizures Wernikes encephalopathy |
|
|
What are the symptoms of delirium tremens? |
Confusion, disorientation, agitation Aniexity, panic, paranoia Autonomic instability Hallcinations or illusions Visual or tactile formication |
|
|
What are the clinical features of cirrhotic decompensation? |
Hepatocellular failure Portal hypertension |
|
|
What are the main causes of compensated cirrhosis? |
Infection GI bleeding- Inc variceal Metabolic Drugs Heptoma |
|
|
How does hepatocellular failure manifest? |
Jaundice, hyperdynamic circulation, septicaemia, encephalopathy, ascities, coagulopathy |
|
|
What are the signs of portal hypertension? |
Ascities Varicies- oesphageal and rectal Spider naevi and caput medussa Encephalopathy |
|
|
What LFT's indicate s cholestatic picture? |
Alk Pos and gamma GT |
|
|
What LFT's indicate a hepatic picture? |
Raised ALT and AST |
|
|
What are the three main types of gallstones |
Cholesterol, black pigment and brown pigment |
|
|
What symptoms do gall stones present with? |
Bilary colic and atypical symptoms such as: chest pain, non-specific abdominal pain, belching, fullness after meals/ early, satiety, fluid regurgitation, abdominal distension/ bloating, epigastric or retrosternal burning |
|
|
What are the risk factors for developing gall stones? |
Older, FH, sudden weight loss, loss of bile salts, diabetes, oral contraception |
|
|
Describe bilary colic |
The pain starts suddenly in the epigastrium or RUQ and may radiate too the interscapular region, It often persists from 15 mins - 24 hours, nausea and vomiting often accompanies the pain |
|
|
What investigations are appropriate for suspected gall stones? |
CXR and ECG to rule out other causes USS to visualize stones |
|
|
What is the difference between bilary colic and cholecystitis? |
Biliary colic is just the presence of gall stones in the gall bladder and cholecystitis is when the gall stone gets stuck in the cystic duct |
|
|
How does cholecystitis present? |
It presents with bilary colic and is more inflammatory in nature- there is local peritonism, fever, raised WCC etc If the stone moves to the CBD- jaundice |
|
|
What is murphys sign? |
Lay two fingers on the RUQ, ask the patient to breath in, this causes pain and arrest of inspiration as the inflamed gall bladder impinges your fingers |
|
|
What investigations would you do for cholecyctitis? |
FBC- raised WCC liver enzymes- may be abnormal USS- thickened gall bladder/ presence of gall stones |
|
|
What is Charcots triad? |
Fever, jaundice and RUQ pain seen in Cholangitis |
|
|
How do people tend to present with liver disease? |
Incidental finding- LFT's, MCV, clotting etc Non-specific symptoms- anorexia, weight loss, lethargy Specific symptoms- eg jaundice, ascites etc |
|
|
What symptoms indicate a patient may have live disease |
Jaundice, bleeding varicies, ascites/ oedema, encephalopathy, pruritis |
|
|
What questions are important to ask in a history of liver disease? |
PMH- Previous surgery- transfusions? DH- Medications, over the counter, herbal, ilicit SH- alcohol, illicit drug use FH- Wilson's, haemochromatosis |
|
|
How many units of alcohol indicate hazardous drinking/ harmful/ binge drinking? |
Hazardous: 15-35 p/week Harmful: >35 units p/week Binge: >7 units a session |
|
|
What dos Glossitis indicate? |
Nutritional deficiency: B12, Iron Syphillis Inhaled burns Ingestion of corrosive materials |
|
|
Give some examples of causes of splenomegally> |
Infections eg TB, EBV, CMV, malaria Cirrhosis and portsal hypertension Myeloproliferative disorders eg CML Lymphoproliferative disorders Congestive cardiac failure Haemolytic anemias Hereditary spherocytosis Haemoglobinopathies Collagen diseases- eg RA or SLE |
|
|
What are the symptoms of acute hepatitis? |
N&V, RUQ pain, jaundice, fever |
|
|
What are the signs of acute hepatitis? |
jaundice, dark urine, tender RUQ |
|
|
What would you see in the blood results of a patient with acute hepatitis? |
Very high ALT, high Bilirubin Imflammation |
|
|
What are the infectious causes of hepatitis? |
Hep A, B, C, D and E EBV and CMV Yellow fever Bacteria- brucella, mycobacteria etc Parasites- schistosoma etc |
|
|
What is Hep A? |
RNA virus Faecal-oral Incubation period 2-5 weeks |
|
|
Describe the serology of Hep A |
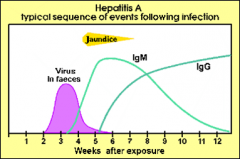
|
|
|
What is Hep E |
Faecal-oral Large outbreaks Commonest cause of acute hepatitis |
|
|
How many Hep B infections become chronic? |
5-10% |
|
|
What investigations would you do in someone with suspected Hep B infection? |
Bloods- LFT's, platelets, clotting Serology Hep B core DNA liver USS Fibroscan- assess liver stiffness Liver biopsy |
|
|
hat screening do you do in patients with cirrhosis? |
Alpha fetaorotein- to screen for HCC Abdominal USS OGD to assess for varicies |
|
|
How many of those infected with Hep C will go on to develop cirrhosis? And how many of these will develop HCC? |
80% 1/3 |
|
|
What is HsAg |
Hepatitis B surface antigen Protein part of the vaccine, present during acute infection |
|
|
What is anti-HBs? |
Hep B surface antibody The body is fighting off an acute Hep B infection or the person has been infected |
|
|
What is anti- HBc |
Hep B core antibody Indicates previous infection with Hep B |
|
|
What is AgM anti-HBc |
IgM antibody to hep B core antigen It indicated a recent infection with hep B |
|
|
What are the components of LFT's? |
Bilirubin ALP ALT Total protein Albumin (GGT is an extra) |
|
|
What are the causes of raised bilirubin? |
Gilberts Stress/ fasting drugs Haemolytic diseases Dubin-Johnson syndrome Rotors syndrome |
|
|
What are the causes of high ALT |
Alcohol Viral hepatitis Steatosis Medications/ toxins (Also small raises seen in coeliac diease, strenuous exercise, muscle disease and thyroid disease) |
|
|
What would a AST:ALT ratio of >2.1 |
May be suggestive but not diagnostic of alcohol related liver diease |
|
|
WHat would a AST: ALT ratio of <2.1 indicate |
Suggests hepatic steatosis or chronic viral hepatitis |
|
|
What are the physiological causes of high ALP? |
Third trimester of pregnancy Adolescents due to bone growth Benign/ familial |
|
|
What are the pathological causes of high ALP? |
Bile duct obstruction, primary bilary cirrosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, drug induced cholestasis, metastatic liver disease, bone disease- eg pagets, heart failure |
|
|
What are the causes of raised GGT |
Hepatobilary disease Pancreatic disease Alcoholism COPD Renal failure Diabities MI Drugs |
|
|
When might we see low albumin? |
Decreased synthesis- eg sereve liver disease Haemodiultion Altered distribution- injury, infection etc Loss from body- burns etc Increased catabolism |
|
|
What sizes is normal on abdo x-ray for the following: Small bowel Large bowel Sigmoid |
3cm 6cm 9cm |

