![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the chemical composition of a triglyceride
|
Ester of glycerol and three fatty acids
|
|
|
Outline the process of hydrogenation
|
addition of hydrogen gas to a unsaturated fat.
|
|
|
Name the catalyst used in hydrogenation
|
finely divided Cu or Ni
|
|
|
How does canning increase shelf life
|
Excludes air/oxygen to prevent oxidation.
Prevent decomposition by microbes |
|
|
State one function of sodium nitrite in food
|
Preservative
Fixes color prevent growth of microbes |
|
|
State the function of ascorbic acid or soidum ascorbate in food
|
antioxidant
|
|
|
Define a food
|
Any substance whether process, semi processed or raw that is intended for human conusmption.
|
|
|
Define a nutrient
|
A substance obtained form food and used by the body to provide energy, regulate growth, maintenance and repair the body's tissues.
|
|
|
List nutrients in order of increasing amounts needed for a balanced diet
|
vitamin & minerals > fats > protein > carbohydrates
|
|
|
Describe the chemical composition of carbohydrates
|
Contain one C=O group and at least two -OH groups and have the empirical formula CH2O. Simplest are monosaccharides. They are the building blocks of disaccharides and polysaccharides.
|
|

Name the type of browning and the conditions needed
|
enzymatic browning
foods containing the enzyme polyphenoloxidase |
|
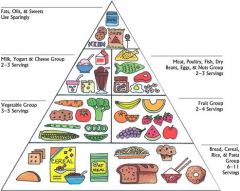
What does this pyramid represent
|
Relative amounts of nutrients needed for a healthy/balanced diet.
|
|
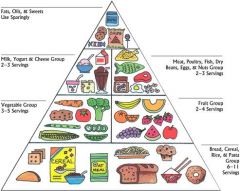
What does this pyramid represent
|
Relative amounts of nutrients needed for a healthy/balanced diet.
|
|
|
How does the melting point of a fatty acid change with increasing saturation and why.
|
Increases.
As number of carbon-carbon double bonds decreases the amount of kinking in the fatty acid chain decreases. The molecules can pack more closely and strength of van der Waals forces between them increases |
|
|
Distinguish between a cis and trans carbon-carbon double bond.
|
cis - hydrogen atoms of carbon-carbon double bond are on the same side.
trans - hydrogen atoms of the carbon-carbon double bond are on opposite sides. |
|
|
Which geometric isomer, cis or trans fatty acids have the higher melting point.
|
trans because the molecules are straighter and so can pack more closely together, increasing the strength of the van der Waals forces between the molecules, increasing the melting point.
|

