![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
List the Structure of the Earth |
Inner Core- Solid iron and nickel Outer Core- Liquid iron and nickel Mantle- Semi-molten Rock Crust- Tectonic plates (thin rock) |
|
|
|
Name the two types of tectonic plate |
Continental plate Oceanic plate |
|
|
|
Name the differences between the oceanic and continental crust |
Continental crust- less dense, thicker. Oceanic crust- more dense, thin. |
|
|
|
Explain why tectonic plates move |
Convection currents in the mantle due to radioactive decay in the core causes heat to rise in so moving currents which move the plates, creating different types of plate boundaries. |
|
|
|
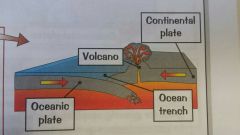
Explain destructive plate margins |
Plates moving towards each other. When an Oceanic meets a Continental plate, the denser Oceanic plate is subducted into the mantle. This creates earthquakes where pressure builds between the plates. This boundary makes volcanoes and ocean trenches. |
|
|
|
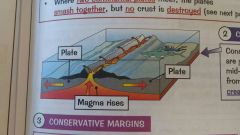
Explain a Constructive plate boundary |
Where two plates are moving apart. Magna rises from the mantle to fill the gap and cools, making a new crust or sometimes a shield volcano. |
|
|
|
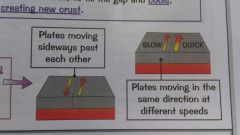
Explain a Conservative plate boundary |
Two plates moving last each other in either opposite or the same direction but at different speeds. No crust is created or destroyed but earthquakes are very common due to the high tension between plates as a result of friction. |
|
|
|
Explain how Fold Mountains are formed |
Sedimentary rocks are pushed up when plates (destructive or collision) push towards each other and are folded and forced upwards. Fold mountains are rocky and have steep slopes, there are valleys between them and often snow on their peaks. |
|
|
|
How people use Fold Mountains |
Farming- high land is used to graze animals. -low land is terraced to grow crops. Mining- metal ores are found in the mineral rich ground.HEP- High lakes and steep land are ideal for generating power from water. HEP- High lakes and steep land are ideal for generating power from water. Forestry- grow specific tree types to make fuels and paper.Tourism- scenery and skiing or hiking is common. Forestry- grow specific tree types to make fuels and paper.Tourism- scenery and skiing or hiking is common. paper. Tourism- scenery and skiing or hiking is common. |
|
|
|
How people in Fold Mountain ranges have adapted |
Tunnels- for better travel. Roads- in zig-zag to make accessible. Terracing- to grow crops. Animals- to farm as they are adapted better, grazing soil. Satelites- better communications for earthquakes and so on. |
|
|
|
Describe volcano formation |
-magma pool forms -Magma rises through vents -Magma erupts making lava and forms a volcano. |
|
|
|
Composite volcano |
Made of ash and lava cooled into layers. Thick lava that flows slowly. Hardens to form a steep sides volcano. |
|
|
|
Shield volcano |
Made of only lava Lava is runny and flows quickly Low and flat. |
|
|
|
Dome volcano |
Only lava Lava is thick Hardens quickly making it steep sided |
|
|
|
Predicting volcanic eruptions |
Tiltmometers to detect shape change. Seismometers to detect earthquakes. Chemical sensors to detect gases. Thermal imagery to detect temperature. |
|
|
|
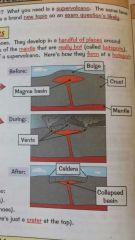
Super volcano differences to a normal volcano. |
Flat. Cover a larger area. Much more serious effects. Have a caldera. Don't just form on boundaries |
|
|
|
Supervolcanic eruptions |
|
|
|
|
Effects of a supervolcanic eruption. |
-Ash will cover hundreds of square kilometeres. -volcanic winter. -larger pyrcoclastic flow killing everything |
|
|
|
Earthquakes |
Tension builds, causing shock waves to be released. They spread from the focus out wards, losing their strength the further away they go. |
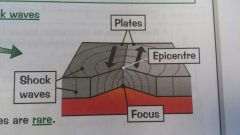
|
|
|
Measuring earthquakes |
Richter scale- measures magnitude through seismometer readings. As the numbers increase this means they are 10 times more powerful. Major earthquakes are above 5. Minor are below 2. Mercalli scale- measures effects of an earthquake. 12 being the worst 1 being not felt by humans. |
|
|
|
Tsunami causes |
When an earthquake happens under the ocean it can cause a fault line, this is where one plate jolts up and sends masses of displaced water at a high speed and high height towards land. |
|

