![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name one field of geology that people study.
|
Mineralogy
|
|
|
True or False: A theory is a scientific guess that does not have extensive evidence to support it.
|
False
|
|
|
Who is considered the father of geology?
|
James Hutton
|
|
|
True or False: The Earth's mantle is molten
|
False
|
|
|
Name one way that we know about the materials and properties of the Earth if we cannot directly observe it
|
Seismic waves
|
|
|
What type of igneous rock makes up the majority of the oceanic crust?
|
Basalt
|
|
|
Assuming it is cool enough that you wouldn't be injured and could actually observe the rocks around you, if you dug a hole into the mantle, what color would it be? Why?
|
Reddish-orange; The heat coming from the mantle. (The mantle is made up of rocks with higher portions of iron and magnesium)
|
|
|
Where on Earth does the thickest continental crust occur?
|
Himalayas
|
|
|
Which of Earth's layers is liquid?
|
Outer core
|
|
|
What are the main differences between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere?
|
The lithosphere is less dense but hard and behaves as brittle material and floats on top of the asthenosphere, where rock is in a plastic, semi molten state and so deforms in a ductile manner
|
|
|
At what type of boundary does subduction occur?
|
Convergent
|
|
|
What type of boundary occurs where tectonic plates slide past one another?
|
Transform
|
|
|
What type of boundary occurs where tectonic plates move away from each other?
|
Divergent
|
|
|
What type of boundary occurs where tectonic plates move toward each other?
|
Convergent
|
|
|
Name two of Alfred Wegener's four lines of evidence for Continental Drift
|
Glacial evidence and rock & mountain sequences
|
|
|
Name an example of a divergent plate boundary
|
East African Rift
|
|
|
Name an example of a hot spot
|
Hawaii or Yellowstone
|
|
|
Which of the following statements includes the absolute age of a rock formation?
A. The rocks that create the "head" on Camelback Mountain are approximately 15 million years old B. The clasts in a conglomerate were formed before the conglomerate was C. The dinosaurs died at the end of the Cretaceous Period D. The Coconino Sandstone is the youngest rock in the Grand Canyon because it is at the top |
A. The rocks that create the "head" on Camelback Mountain are approximately 15 million years old
|
|
|
You are analyzing a rock and find that it has 250 parent isotopes and 750 daughter isotopes.
A. How many parent isotopes were present when the rock initially formed? B. How many half-lives have occurred? |
A. 1000
B. 2 |
|
|
What subatomic particle is responsible for creating bonds?
|
Electrons
|
|
|
Bond created when two atoms share electrons
|
Covalent
|
|
|
Bond created when electrons are transferred and the charged atoms are attracted one another
|
Ionic
|
|
|
If the number of electrons in an atom varies, it creates a new _____
|
Ion
|
|
|
If the number of protons in an atom varies, it creates a new ______
|
Element
|
|
|
You are given four common but colorless minerals. What mineral properties would you test for to tell the difference between the four minerals?
|
Luster, cleavage, taste
|
|
|
To which mineral class does halite [NaCl] belong?
|
Halides
|
|
|
To which mineral class does diamond [C] belong?
|
Native elements
|
|
|
Why isn't color a reliable test for mineral identification?
|
A lot of minerals may have the same color
|
|
|
What are the five characteristics a substance must possess in order to be considered a mineral?
|
Inorganic, naturally occurring, crystalline structure, solid, definite chemical composition
|
|
|
What mineral on Bowen's reaction series forms at the lowest temperature?
|
Quartz
|
|
|
Why are non ferromagnesian silicates light in color?
|
Non ferromagnesian silicates are light in color because the lack substantial iron and magnesium in their crystalline structure
|
|
|
An igneous rock with a ______ texture has many holes from gas escaping from the magma
|
Vesicular
|
|
|
A rock that includes the minerals olivine, pyroxene, amphibole and biotite has what composition?
|
Ultramafic
|
|
|
Magma that cools deep below the crust is called ______
|
Intrusive
|
|
|
Why are the crystals in a phaneritic large while the crystals in an aphanitic rock small?
|
Phaneritic rocks have cooled slow enough so that the crystals could grow while aphanitic rocks cooled too fast and the crystals got too small to be seen by the unaided eye
|
|
|
Which of the following fluids as the lowest viscosity?
A. Basalt B. Andesite C. Rhyolite |
A. Basalt
|
|
|
Match the volcano with the type of lava that is most commonly erupted. You will use one lava type twice.
Shield - Dome - Cinder cone - Composite/stratocone - A andesite B basalt C rhyolite |
Shield - Basalt
Dome - Rhyolite Cinder cone - Basalt Composite/stratocone - Andesite |
|
|
What type of volcano has the lowest viscosity lava?
|
Shield
|
|

What type of volcano is seen in the image?
|
Shield
|
|
|
What type of lava flow is erupted underwater?
|
Pillow basalt
|
|
|
What is the most abundant type of volcano?
|
Cinder cone
|
|

What type of lava is erupted by the volcano in the image?
|
Rhyolite lava
|
|
|
Hot ash and gas which moves down the slopes of >125 mph; major cause of death in Pompeii during the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 A.D. and by Mt. Pelee in the town of Saint-Pierre on the island of Martinique in 1902.
|
Pyroclastic flow
|
|
|
The iron minerals hematite and limonite result from the chemical weathering of iron-rich minerals by the process of...
|
Oxidation
|
|
|
Which of the following is/are most susceptible to chemical weathering by dissolution in water or the presence of acid?
A. Iron oxides B. Halite C. Quartz D. Clay minerals |
B. Halite
|
|
|
What two factors speed up rates of chemical reaction and weathering in rocks?
|
Warm temperatures; very moist areas
|
|
|
Which of the following statements concerning mechanical weathering is not true?
A. Is important in the formation of talus slopes B. Involves a major change in the mineral composition of the weathered material C. Reduces grain sizes of rock particles D. Allows for faster rates of chemical weathering |
D. Allows for faster rates of chemical weathering
|
|
|
Choose one of the mechanical weathering processes and explain how it works and the environment which it most likely occurs.
|
Frost heaving. Frost heaving occurs by pushing the rocks vertically from the soil by the formation of ice. This process occurs in the northern United States
|
|
|
Which mineral is very hard to weather?
A. Calcite B. Biotite C. Quartz D. Olivine |
C. Quartz
|
|
|
Which of the following minerals would weather the fastest? [Hint: Think Bowen's Reaction Series]
A. Plagioclase B. Olivine C. Potassium feldspar D. Biotite |
B. Olivine
|
|
|
What is the main difference between a conglomerate and a sedimentary breccia?
|
Breccia clasts are angular; conglomerate clasts are rounded
|
|
|
Which of the following correctly lists clastic sedimentary rocks in order from smallest clasts to largest clasts?
A. Shale, conglomerate sandstone B. Conglomerate, sandstone, shale C. Sandstone, conglomerate, shale D. Shale, sandstone, conglomerate |
D. Shale, sandstone, conglomerate
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a common cement in clastic sedimentary rocks?
A. Calcite B. Halite C. Silica D. Hematite |
D. Hematite
|
|
|
Pick one of the common cementing agents in the previous question and tell which chemical weathering process creates it
|
Calcite and it is created by the dissolution process
|
|
|
_____ and _____ are folds with the youngest rocks in the middle
A. Anticlines, domes B. Synclines, basins C. Synclines, domes D. Anticlines, basins |
B. Synclines, basins
|
|

What type of fault is depicted in the image?
|
Left-lateral strike-slip fault
|
|
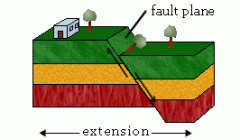
What type of fault is depicted in the image?
|
Normal fault
|
|
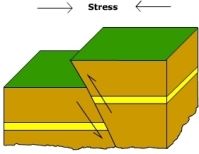
What type of fault is depicted in the image?
|
Reverse fault
|
|
|
What type of fault creates horsts and grabens?
|
Normal fault
|
|
|
Match the structure with the type of stress that creates it. Some stresses will be used for more than one structure
Syncline - Detachment fault - Anticline - Reverse fault - Normal fault - Strike-slip fault - Thrust fault - A tension B compression C shear |
Syncline - compression
Detachment fault - tension Anticline - tension Reverse fault - compression Normal fault - tension Strike-slip fault - shear Thrust fault - compression |
|
|
What type of earthquake wave moves the fastest?
|
P wave
|
|
|
What are the two ways that we measure earthquakes?
|
Magnitude and intensity
|
|
|
At what type of plate boundary do the most numerous, destructive and deep earthquakes occur?
|
Subduction zones
|
|
|
Which type of earthquake body wave does not travel through Earth's liquid outer core?
|
S wave
|
|
|
What town experienced three of the largest earthquakes in U.S. history over the winter of 1811-1812?
|
New Madrid, Missouri
|
|
|
What city experienced an earthquake in 1906 in which 90% of the damage was due to fire?
|
San Francisco
|
|
|
Extensive damage during the 1964 Nigita, Japan and the Good Friday, Alaska earthquakes was caused due to water-bearing sediment being shaken. This geologic hazard is called _____
|
Liquefaction
|
|
|
What was the largest recorded earthquake in the world? Give the date and location.
|
9.5M; Chile; 1960
|
|
|
What mainland U.S. city has been damaged due to tsunamis numerous times (1964 Good Friday and 2011 Japan earthquakes both caused extensive damage)?
|
Crescent City, California
|
|
|
What was the largest recorded earthquake in the U.S.? Give the date and location.
|
Alaska; 9.2M; 1964
|
|
|
What is one way we can map the ocean floor?
|
Seismic reflection
|
|
|
Which U.S. coast is an active margin?
|
Pacific
|
|
|
Name one region in the United States that was a subduction zone, but is not currently
|
West coast; California
|
|
|
Put the following location in order of degree of ocean development. (1- earliest phase of development, youngest type of ocean; 5- last phase of development, oldest type of ocean)
___ East Africa ___ Atlantic Ocean ___ Pacific Ocean ___ Red Sea ___ Himalayas |
1 - East Africa
2 - Red Sea 3 - Atlantic Ocean 4 - Pacific Ocean 5 - Himalayas |
|
|
The _____ are a geologically old mountain range folded and deformed during the formation of Pangaea.
|
Appalachians in the eastern United States
|
|
|
The _____ are a young, currently rising mountain range that resulted from continental collision.
|
Himalayas of India and Asia
|
|
|
An episode of mountain building is known as a(n) ____.
|
Orogeny
|
|
|
Match the sedimentary rock with environment it forms in
____ Conglomerate ____ Shale ____ Breccia ____ Travertine ____ Halite ____ Limestone ____ Sandstone A fast moving river bottom B lake, river flood plain, off-shore marine C coral reef D talus slopes beneath a cliff E beach F cave G dried lake bed |
Conglomerate - fast moving river bottom
Shale - lake, river flood plain, off-shore marine Breccia - talus slopes beneath a cliff Travertine - cave Halite - dried lake bed Limestone - coral reef Sandstone - beach |
|
|
Which metamorphic rock reacts with acid?
|
Marble
|
|
|
Match the metamorphic rock with the correct parent rock
___ schist ___ slate ___ quartzite ___ marble ___ gneiss A sandstone B slate C limestone D granite E shale |
Schist - slate
Slate - shale Quartzite - sandstone Marble - limestone Gneiss - granite |
|
|
Which of the following is the correct order of metamorphic parent rocks from lowest grade to highest grade?
A. Slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss B. Gneiss, schist, phyllite, slate C. Slate, gneiss, schist, phyllite D. Phyllite, gneiss, slate, shcist |
A. Slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss
|
|
|
Name three agents of metamorphism.
|
Heat, pressure, fluid activity
|
|
|
What metamorphic rocks are non foliated from this list?
Phyllite Slate Marble Quartzite Gneiss Schist |
Marble and Quartzite
|
|
|
True or False: Metamorphic rocks are created by the recrystallization of minerals by melting them.
|
False
|
|
|
A debris/mudflow on a volcano is known as a _____
|
Lahar
|
|
|
Which type of mass movement is most common in the spring months?
|
Rock slide
|
|
|
All of the following are factors that control or trigger mass wasting except for ____
A. slope angle B. geologic age C. removal of vegetation D. water |
B. geologic age
|
|
|
Give two ways in which water can affect the stability of a slope.
|
Way #1: It can make it steeper
Way #2: It can make it more dense |
|
|
Which type of mass movement is the slowest and yet the most expensive?
|
Creep
|
|
|
Below is the equation for discharge on a river. Use it to answer the following questions.
Q(discharge)=width x depth x velocity A. If the width of the channel decreases, how does the velocity of the water change? B. If the discharge increases but the channel size remains constant, how does the velocity change? |
A. The velocity increases
B. The velocity doesn't change |
|
|
Location on a meandering stream where lateral erosion occurs.
|
Cutbank
|
|
|
Which of the following is an indicator of a drop in base level?
A. incised meanders B. formation of an oxbow C. increased deposition D. decrease in stream gradient |
A. incised meanders
|
|
|
Drainage pattern most likely to occur on the slopes of a stratovolcano.
|
Radial
|
|
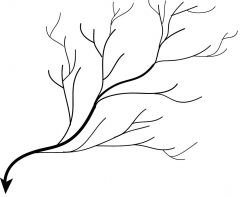
Drainage pattern depicted in the image.
|
Dendritic
|
|
|
Describe the geology that underlies a dendritic drainage pattern
|
They are the most common form of drainage system. In a dendritic system, there are many contributing streams (analogous to the twigs of a tree), which are then joined together into the tributaries of the main river (the branches and the trunk of the tree, respectively). They develop where the river channel follows the slope of the terrain. Dendritic systems form in V-shaped valleys; as a result, the rock types must be impervious and non-porous.
|
|

Drainage pattern depicted in the image.
|
Rectangular
|
|
|
_____ is the percentage of total volume of rock or sediment that consists of pore spaces.
|
Porosity
|
|
|
The ability to transmit a fluid is called ____.
|
Permeability
|
|
|
The lowering of the water table around a well due to overuse of groundwater is a(n) _____.
|
Cone of depression
|
|
|
The lowering of the ground surface due to over-pumping of groundwater is called ______.
|
Subsidence
|
|
|
What hazard, found in the Basin and Range topographic region (and the Phoenix Valley specifically), is caused by groundwater withdrawal?
|
Earth fissures
|
|
|
Name a rock or mineral that dissolves in water or weak acid and creates karst landscapes.
|
Limestone
|
|
|
Name two sources of groundwater contamination.
|
Source #1: Chemical spills
Source #2 Air pollution |
|
|
The ice ages are caused by:
A. the drift of the continents B. the eruption of supervolcanoes C. the sunspot cycle D. minor changes in Earth's rotation and orbit E. variations in solar output |
D. minor changes in Earth's rotation and orbit
|
|
|
Process that occurs where a glacier enters the sea.
|
Calving
|
|
|
What type of rock is glacial ice?
|
Metamorphic
|
|
|
Deserts are caused by:
A. location on latitude belt where dry air sinks B. high mountains that force air to lose moisture C. neither of the above D. both of the above |
B. high mountains that force air to lose moisture
|
|
|
In a desert environment, what does the most erosional work?
|
Running water
|
|
|
What type of sand dune is created in an area with highly variable winds?
|
Longitudinal
|
|
|
Most beach sand derives from _____
|
Rivers
|
|
|
Wave energy is derived from ______
|
Wind
|
|
|
Waves get _____ and _____ as they approach land.
|
Shorter and faster
|
|
|
Cyclone Bhola hit Bangladesh in 1970 and killed up to 500,000 people. The landfall occurred during high tide that was higher than average. This type of tide is called a _____.
|
Neap tide
|
|
|
Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the _____ and to a lesser degree, the ______
|
Moon and the Sun
|
|
|
The most common Precambrian fossils are ______, layered mounds of calcium carbonate that are formed by single-celled organisms.
|
Stromatolites
|
|
|
During which mass extinction did the largest percentage of the world's living organisms become extinct?
|
Permian
|
|
|
Put the following events in order from the first (#1) to the most recent (#10)
____ humans ____ amphibians ____ world's largest mass extinction ____ fish ____ formation of the moon ____ oxygen in the atmosphere ____ reptiles ____ flowers ____ extinction of the dinosaurs ____ formation of the solar system |
Formation of the solar system - 1
Formation of the moon - 2 Oxygen in the atmosphere - 3 Fish - 4 Amphibians - 5 Reptiles - 6 World's largest mass extinction - 7 Extinction of the dinosaurs - 8 Flowers - 9 Humans - 10 |
|
|
What evidence do we have that indicates that Arizona was a desert during the Jurassic?
|
Marine invertebrate fossils
|

