![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
113 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
1. "Warrior Vase" 2. Mycenae 3. Late Helladic 4. 1150 BC |
|
|
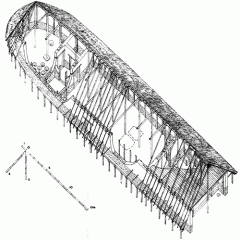
1. House and Tomb of Warrior or Chief ("Heroon") 2. Lefkandi 3. Protogeometric 4. 950 BC |
|

|
1. Dipylon Amphora 2. Athens 3. Late Geometric 4. ca. 760 BC |
|

|
1. Temple Model 2. Argos (actually near Argos) 3. Late Geometric 4. ca. 725-700 BC |
|

|
1. Mantiklos Apollo 2. Thebes 3. Late Geometric 4. ca. 700 BC |
|

|
1. Terracotta Centaur 2. Lefkandi 3. Protogeometric 4. 1000-900 BC |
|

|
1. Chigi Vase 2. Corinth 3. Orientalizing 4. ca. 640 BC |
|

|
1. Griffin Protome from a Bronze Cauldron 2. Olympia 3. Orientalizing 4. 650 BC |
|

|
1. Amphora by the Polyphemus Painter 2. Eleusis 3. Orientalizing 4. 650 BC |
|

|
1. Lady of Auxerre 2. Auxerre (France) 3. Orientalizing 4. 650 BC |
|

|
1. Nikandre Kore (possibly the goddess Artemis) 2. Delos 3. Orientalizing 4. 650 BC |
|
|
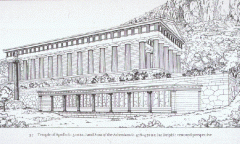
1. Reconstruction of Temple of Apollo 2. Isthmia 3. Orientalizing 4. 650 BC |
|

|
1. Pediment, Temple of Artemis 2. Confu 3. Archaic 4. 650 BC |
|

|
1. Metope with Perseus Beheading Medusa 2. Temple C, Selinous 3. Archaic 4. 550 BC |
|

|
1. Naxian Sphinx 2. Delphi 3. Archaic 4. 570 BC |
|
|
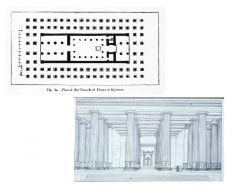
1. Plan and Reconstructed View, Temple of Artemis 2. Ephesos 3. Archaic 4. 560 BC |
|

|
1. Black-figure Eye Cup with Ship of Dionysos on Interior by Exekias 2. Athens 3. 540 BC |
|

|
1. Francois Vase by Kleitias and Ergotimos 2. Athens 3. Archaic 4. 570 BC |
|

|
1. Neck amphora by the Amasis Painter with Dionysos and maenads 2. Athens 3. Archaic 4. 540 BC |
|

|
1. New York Kouros 2. Attica 3. Archaic 4. 600-590 BC |
|

|
1. "Croesus" (AKA Anavysos Kouros) 2. Attica 3. Archaic 4. 530 BC |
|

|
1. The Peplos Kore 2. Athenian Acropolis 3. Archaic 4. 540-530 BC |
|

|
1. The Berlin Kore (AKA Berlin Goddess) 2. Attica 3. Archaic 4. 560 BC |
|

|
1. The Calf-Bearer 2. Athenian Acropolis 3. Archaic 4. 550 BC |
|

Look at Figure 7.3 to get a better aerial view |
1. Temple of Hera 2. Olympia 3. Archaic 4. 590 BC |
|
|
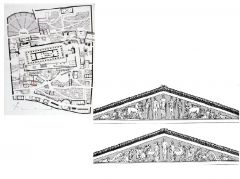
1. Temple of Apollo (plan & pediment) 2. Delphi 3. Archaic 4. ca. 515 BC |
|

|
1. "Kleobis and Biton" 2. Delphi 3. Archaic 4. 525 BC |
|
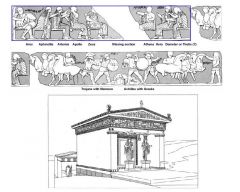
|
1. Siphnian Treasury 2. Delphi 3. Archaic 4. 525 BC |
|

|
1. Athenian Treasury 2. Delphi 3. Archaic 4. 480 BC |
|
|
Kerameikos |
The potters' quarter in Athens; also used of a major cemetery in the same area |
|
|
Single inhumations
|
Single burials
|
|
|
Cist graves |
Small pit, often lined with stone and provided with a lid, used for burial |
|
|
Structure |
LOOK IN BOOK FOR DEFINITION |
|
|
Flux |
Calcium in limestone |
|
|
Slag |
Silicate impurities |
|
|
Amphora |
Jar with upright handles on either side of the neck, used for storing wine and oil |
|
|
Multiple-Brush Compass
|
Technique used by painters to paint amphoras
|
|
|
Oinochoe
|
A wine jug
|
|
|
Sintering
|
Formed into a mass of iron by heat and pressure
|
|
|
Apse; apsidal (architecture) |
The curved part of any building shaped roughly like a horseshoe; a building with an apse is "apsidal" |
|
|
"Bomos" (Greek word) |
"Alters" |
|
|
Masseboth |
Standing stones |
|
|
"Toumba" (Greek word) |
Artificial mounds of earth |
|
|
Krater |
Large, deep bowl for mixing wine and water |
|
|
Prothesis
|
A credence table
|
|
|
Polis |
City state |
|
|
Protome |
Projecting, separately made attachment to a vessel or other object, in the shape of a head (human, animal, or supernatural) |
|
|
"Polites" (Greek word) |
Only free adult males were regarded as "citizens" |
|
|
"Ekklesia" (Greek word) |
Assembly of all citizens |
|
|
"Archons, kosmoi" (Greek word) |
Executive officials serving limited terms |
|
|
"Gerousia, boule" (Greek word) |
Older men serving as advisory body |
|
|
"Helots" (Greek word) |
Serfs without political rights ruled by relatively few full citizens |
|
|
"Agora" (Greek word) |
Marketplace |
|
|
"Politis" (Greek word) |
Free-born adult native women |
|
|
"Kurios" (Greek word) |
A male guardian |
|
|
"Hieron" (Greek word) |
Sanctuary |
|
|
"Temenos" (Greek word) |
Enclosed sacred area |
|
|
"Naos" (Greek word) |
Temple |
|
|
Votive |
Gift for a god, usually placed in a sanctuary; includes anything from flowers to small buildings |
|
|
Sphyrelaton (plural: sphyrelata) |
Statues of hammered bronze sheets on wooden core |
|
|
Peripteral |
Having columns on all sides |
|
|
"Hekatompedon" (Greek word) |
"Hundred-footer" |
|
|
"Hoplites" (Greek word) |
Heavily armed infantrymen |
|
|
"Hoplon" (Greek word) |
Shield |
|
|
"Aspis" (Greek word) |
Round shield |
|
|
"Phalanx" (Greek word) |
Infantry formation used in hoplite battles; men standing in parallel rows and marching in unison towards an enemy |
|
|
Metropolis (Greek word: oikistes) |
Each colony had an independent polis; relationships with local indigenous people varied |
|
|
"Orientalizing" |
Extensive use of motifs drawn from Near East (Oriental) |
|
|
Incision, incised |
Line made by scratching with a sharp point; commonly used in ceramics and metalworking |
|
|
Black-figure technique |
Technique using dark, silhouette figures with incised detail and use of added red paint for details |
|
|
Animal friezes |
A horizontal zone running along the length of a building immediately above the architrave (the horizontal blocks resting atop the columns); sometimes portrayed as animals |
|
|
Iconography |
The images or symbols traditionally associated with a particular subject or story |
|
|
Sphinx |
Creature with a lion body, eagle wings, and a woman's head |
|
|
Griffin |
Creature with a lion body, and an eagle's head and wings (sometimes with a rooster's comb as well) |
|
|
"Dipinti" (Greek word) |
Painted inscription |
|
|
Kore |
Young woman |
|
|
"Agalma" (Greek word) |
Statue dedicated to a god; literally a "delight" or treat for the god |
|
|
"Sema" (Greek word) |
Statues, tombs, letters, omens, and other meaningful things |
|
|
Kouros |
Young man |
|
|
Dipteral |
Double colonnade all the way around |
|
|
Distyle-in-antis |
Two columns between the antae in front |
|
|
Prostyle |
A projecting colonnade in front only |
|
|
Amphiprostyle |
A projecting colonnade in front and back |
|
|
Stylos |
Column |
|
|
Distyle |
Two colums |
|
|
Tetrastyle |
Four columns |
|
|
Hexastyle |
Six columns |
|
|
Octastyle |
Eight columns |
|
|
Pan tile |
Flat roof tile |
|
|
Cover tile |
Curved or angled roof tile which covers ("caps") the gaps between pan tiles |
|
|
Antefix |
Upright element along a roof line which keeps the roof tiles in place |
|
|
Laconian system |
LOOK AT LECTURE 16, SLIDE 27 |
|
|
Conrinthian system |
LOOK AT LECTURE 16, SLIDE 27 |
|
|
Pentastyle |
Five columns |
|
|
Apotropaic |
Having the power to prevent evil or bad luck |
|
|
Hypaethral |
Interior open to sky |
|
|
Dentil course |
Substitutes for frieze |
|
|
"Turannos" (Greek word) |
Tyrant |
|
|
Numismatics |
Study of coins |
|
|
Staters |
Cities minting gold or electrum coins in units |
|
|
"Trite" (Greek word) |
"One-third" |
|
|
Obol |
"Rod"; same value as iron rods that previously served as currency |
|
|
Drachma |
"Handful"; 6 obols |
|
|
Didrachm |
2 drachmas |
|
|
Tetradrachm |
4 drachmas |
|
|
Mina |
100 drachmas |
|
|
Talent |
6,000 drachmas or 60 minas |
|
|
"Perioikoi" (Greek word) |
Free non-citizens |
|
|
Late Helladic IIIC and Submycenaen periods
|
1200-1050 BC
(Submycenaen was ca. 1100-1050 BC if it was valid) |
|
|
Protogeometric period
|
1050-900 BC
|
|
|
Geometric period
|
900-ca.700 BC
(Late Geometric period: 760-700 BC) |
|
|
Orientalizing period
|
ca. 700- ca. 600 BC
(Two major regional styles: Protocorinthian [730-620 BC; Corinthian Orientalizing] and Protoattic [700-620/600 BC; Attic Orientalizing]) |
|
|
Archaic period
|
ca. 600-480 BC
|

