![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Features of intracranial dural sinuses |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Total number of sinuses |
23 |
|
|
Unpaired sinuses enumerate |
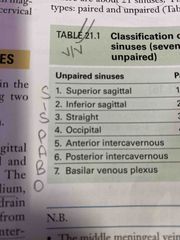
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Paired sinuses enumerate |
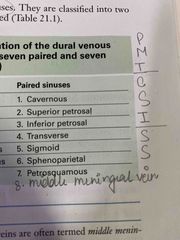
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Lateral sinus is formed by- |
Sigmoid and transverse sinus |
|
|
Middle meningeal vein is called |
Middle meningeal sinus |
|
|
Dural sinuses are formed by |
-Separation of two layers of cranial Dura -re-duplication of Meningeal layer |
|
|
Venous sinuses lie between |
Meningeal and endosteal layer |
|
|
Exceptional location of Venous sinuses is observed in |
Inferior sagittal and straight sinus |
|
|
Blood from dural venous sinuses is ultimately drained into |
Internal jugular vein |
|
|
Location of cavernous sinus |
Either side Body of sphenoid,sells turcica Middle cranial fossa |
|
|
Floor of cavernous sinus formed by which layer? |
Endosteal layer |
|
|
Later wall ,medial wall ,roof of cavernous sinus is formed by which layer? |
Meningeal layer |
|
|
Extent of cavernous sinus |
Anteriorly to medial end of Superior orbital fissure Posteriorly petrous temporal bone apex |
|
|
Structures present lateral wall of sinus |
O-Oculomotor nerve T-Trochlear nerve O-Ophthalmic nerve M-Maxillary nerve |
|
|
Tributaries of cavernous sinus from Brain |
Superficial middle cerebral vein Inferior cerebral veins |
|
|
Tributaries of cavernous sinus from meninges |
Sphenoparietal sinus Anterior or frontal trunk of middle meningeal vein |
|
|
Superior relations of cavernous sinus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Inferior relations of cavernous sinus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Medial relations of cavernous sinus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Location and drainage of Sphenoparietal sinus |
LoC-posterior free margin of lesser wing of sphenoid Drains into cavernous sinus anterior part |
|
|
Superior petrosal sinus |
Anterior part of attached margin of tentorium cerebelli and crosses above trigeminal nerve |
|
|
Inferior petrosal sinus location |
Location -petro-occipital suture |
|
|
Middle meningeal vein |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Superior sagittal sinus location |
Between two layers of Falx cerebri A long convexity of attached border Begins at Crista Galli Pass backward Reaches internal occipital protuberance Deviates right becomes continuous with right transverse sinus Further continues with the right sigmoid sinus Leave skull through jugular form and continue as right internal jugular vein Size becomes larger from CG to IOP |
|
|
Structures passing through cavernous sinus |
-internal carotid artery -abducent nerve |
|
|
Features of superior sagittal sinus |
Triangular Archnoid granulation project in to lumen Communicates with Venous lacunae on each side and sites of drainage of diploic in Meningeal veins |
|
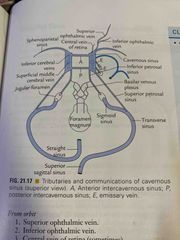
Communications of cavernous sinus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Inferior sagittal sinus |
Between two layers of lower free margin of Falx cerebri Ends by joining great cerebral vein to form straight sinus DrainsThe lower part of medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere |
|
|
Straight sinus |
Median plane within junction of falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli Continuation of inferior SS Terminates into left transfer sinus which at mastoid angle of parietal bone becomes continuous with left sigmoid sinus |
|
|
Occipital sinus |
Between two layers of attached margin of falx cerebri Runs downwards from internal occipital protuberance to posterior margin of forum in Magnum skirts the margin and drains into sigmoid sinus |
|
|
Transverse sinus |
Begins at internal occipital protuberance runs laterally between two layers of attached margin of tentorium cerebelli Courses horizontally grooving occipital bone and mastoid angle of parietal bone becomes continues as sigmoid sinus |
|
|
Sigmoid sinus |
Direct continuation of transverse sinus Sigmoid shape Grooves inner surface of mastoid part of petrous bone Terminal part curve is downward forward to posterior margin of jugular ForamenThrough which it passes to continue as internal jugular vein
|
|
|
Tributaries of sigmoid sinus |
Mastoid and condylar emissary veins Cerebellar veins Internal auditory vein |
|
|
What causes the expelling of blood from sinus cavernous |
Pulsation of internal carotid artery |
|
|
Lateral relations of your Cavernous sinus |
Temporal lobe (uncus) of cerebral hemisphere Cavum trigeminale containing trigeminal ganglion |
|
|
Anterior relations of cavernous sinus |
Superior orbital fissure Apex of orbit |
|
|
Posterior relations are cavernous sinus |
Crus cerebri of mid brain Apex of Petrus temporal bone |
|
|
From where do cavernous sinus receives blood |
Brain meninges orbit |
|
|
Tributaries of sigmoid sinus |
Mastoid and condylar emissary veins Cerebellar veins Internal auditory vein |
|
|
Anterior and posterior inter-cavernous sinus |
Interior and posterior inter-cavernous sinus connects the cavernous sinus They passed through diaphragma Sellae in front and behind the opening for infant the balm of pituitary gland respectively Inter cavernous sinus and the cavernous sinus together from the circular sinus |
|
|
Basilar Venous plexus |
Network of veins lying between two layers of Dura on Clivus Connects to inferior petrosal sinuses. And communicates with internal vertebral Venus plexus Receives blood from pons and medulla Thrombosis of basilar venous plexus is therefore fatal |
|
|
Confluence of sinuses(torcular herophili) |
Region where superior sagittal and straight sinus end and right and left transverse sinus begin. Occipital sinus also drains here located near internal occipital protuberance |
|
|
Thrombosis of sigmoid sinus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Thrombosis of superior sagittal sinus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Thrombosis of cavernous sinus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Arteriovenous communication |
Back (Definition) |

