![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functions of Blood |
Transportation (gases, nutrients, hormones, waste), Regulation (body temp, pH level, fluid volume), protection (infection) |
|
|
Properties of Blood |
Liquid connective tissue, 8% total body mass, 20% of total ECF mass, pH 7.35 to 7.45. Volume 4-6L. |
|
|
Components of Blood |
Blood Plasma = 55% --> water 91.5%, proteins 7%, all other solutes 1.5%. Formed elements = 45% --> Red blood cells (99% of the formed elements), white blood cells and platelets (1% of the formed elements) |
|
|
Red Blood Cells |

Not real cells (no nucleus), responsible for transporting gases. Thye are biconcabe disks. Hemoglovin. Hematocrit. Life span 120 days |
|
|
Erythopoiesis |
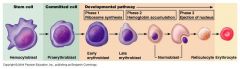
Formation of red blood cells. Stimulated by EPO (erythropoietin) secreted by the kidneys. |
|
|
Anemia |
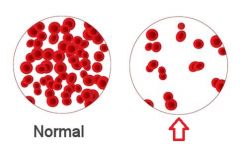
Abnormal low of RBCs or hemoglobins in the blood. Blood oxygen-carrying capacity is too low to support normal metabolism. |
|
|
Blood Doping |
Through erythropoietin (EPO), synthetic oxygen carriers, blood transfusions. Can cause increased risk of cardiovascular disease and blood contamination. |
|
|
White Blood Cells |
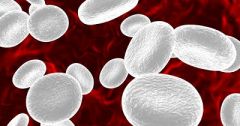
Real cells. 5,000 to 10,000 cells per microlitre. Five types, only know these 3: neutrophils, lymphoctytes, monoctyes. Life span is few hours to few days. Phagocytosis is key of defence. |
|
|
Leukemia |
Red bone marrow produces cancerous WBCs |
|
|
Platelets |

Not real cells, 150,000 to 400,000 per microlitre. Life span 5-9 days. |
|
|
Blood Types |
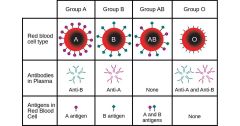
|
|
|
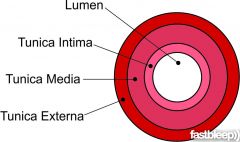
Tunica Interna, Media, Externa |
|
|
|
Artery |
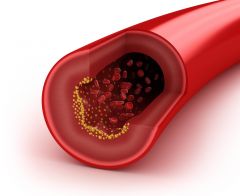
Most Muscular Vessels, deliver oxygenated blood from heart to body parts (except pulmonary arteries) |
|
|
Atherosclerosis |
Disease where plaque builds up inside your arteries. |
|
|
Veins |
Deliver deoxygenated blood from body parts back to the heart. 64% of blood is in systemic veins and venules. |
|
|
Capillary (Arteriole, Capillary, Capillary Bed, Muscular Venule |
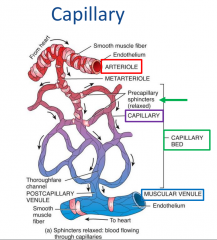
|
|
|
High Blood Pressure Ranges |

|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Facts |
Striated, branched, and shorten in length. Many mitochondria, involuntary control |
|
|
Intercalated Disks |
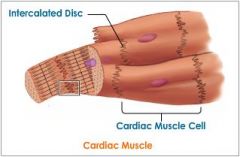
Connections between cardiac muscle. Contain desmosomes, gap junctions. |
|
|
Cardiac Conduction System |
Sinoatrial node -> Internodal tracts (SA to AV nodes) & Bachmann's bundle (SA to left atrium) -> Atrioventricular (AV) node -> Atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His) -> Right and left bundle branches -> Purkinje fibers |
|
|
Electrocardiogram |
Heart rate machine diagram |
|
|
Cardiac Cycle |
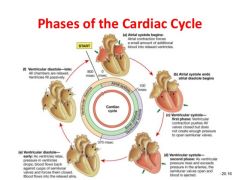
|
|
|
End Diastolic Volume (EDV) |
The volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole• 105 ml + 25ml |
|
|
End Systolic Volume (ESV) |
The volume of blood remaining in the ventricles at the endof systole (the volume not ejected from the ventricles)• 60 ml |
|
|
Stroke volume (SV) |
The volume of blood ejected from the ventricles witheach beat (SV = EDV – ESV)• 70 ml |
|
|
Ejection Fraction (EF) |
the percentage of End Diastolic Volume that is ejectedfrom the heart• 50 to 55% |
|
|
Cardiac Output (Q) |
The volume of blood ejected from the ventricles per minute• = SV × HR = 70ml/beat × 75 beats/min = 5.25 L/min |
|
|
Sickle Cell |
Abnormal Hemoglobin S |

