![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What's the purpose in making dilutions of T4 virus ? |
to calculate # of phages in a sample; it's best to obtain a countable plate |
|
|
Describe what yeast looks like macroscopically |
moist, white pearls |
|
|
Describe what yeast looks like microscopically |
oval, large , seen at 400x |
|
|
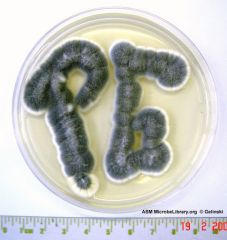
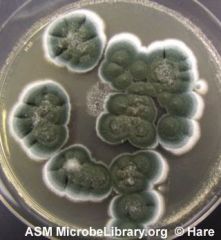
describe what penicillium looks like macroscopically |
green and wooley |
|
|
describe what penicillium looks like microscopically |
hand in the air |
|
|
describe what Rhizopus looks like macroscopically |
white, cotton-like |
|
|
describe Rhozopus microscopically |
lollipop looking |
|
|
describe aspergillus macroscopically |
black crushed velvet |
|
|
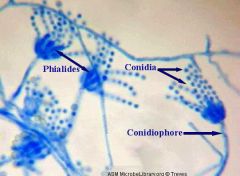
describe aspergillus microscopically |
Round head with mohawk / spiked hair |
|
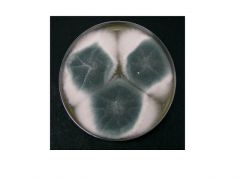
name
|
aspergillus - note velvety aerial hyphae
|
|
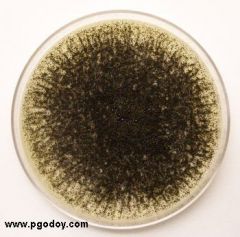
name |
aspergillus |
|
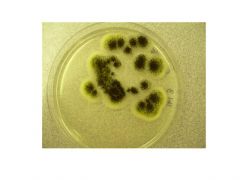
name |
aspergillus |
|

name |
aspergillus |
|
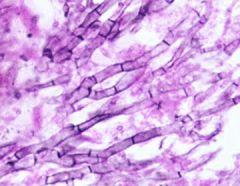
name |
aspergillus |
|
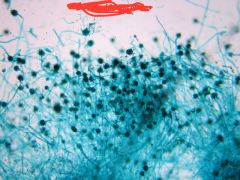
name |
aspergillus |
|
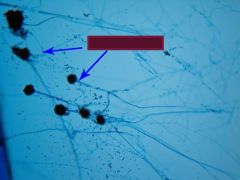
name |
aspergillus |
|

name |
aspergillus |
|

name |
aspergillus |
|
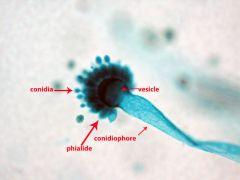
name |
aspergillus |
|
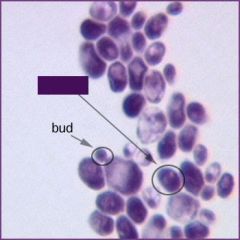
name |
yeast - candida albicans |
|
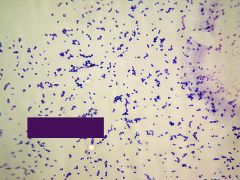
name |
yeast- candida albicans |
|

name |
Rhizopus |
|

name |
Penicillium |
|
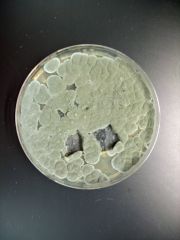
name |
Penicillium |
|
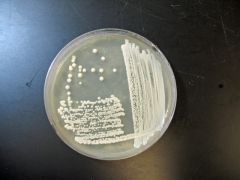
name |
yeast- candida albican |
|

name |
penicillium |
|
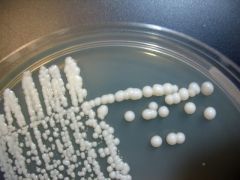
name |
yeast- candida albican |
|
name |
Penicillium |
|
name |
Penicillium |
|
name |
Rhizopus |
|
name |
penicillium |
|

name |
rhizopus |
|
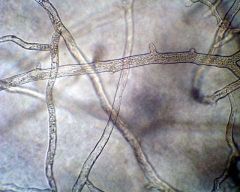
name |
rhizopus |
|

name |
rhizopus |
|
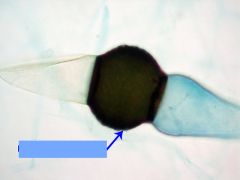
name |
rhizopus |
|
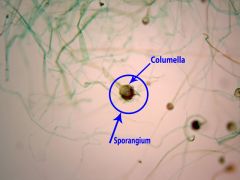
name |
rhizopus |
|
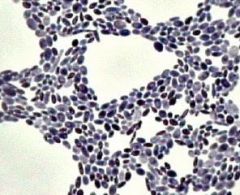
name |
yeast- candida albican |
|
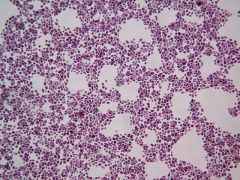
name |
yeast- candida albican |
|
|
Define Bacteriophage |
virus that infects bacteria |
|
|
Define Lytic |
burst open & kill bacterial host once appropriate # of viruses have been synthesized
|
|
|
Define Plaque |
area of clearing in a confluent lawn of bacterial growth |
|
|
Results of a Micrococcus luteus nitrate test |
negative , no color change after drops BUT color changes after zinc MEANS NEGATIVE FOR TURNING NITRATE INTO NITRITE |
|
|
Result of a Micrococcus roseus nitrate test |
positive ; two options First changes red after drops are places OR if no color change after drops & no color change after drops & zinc POSITIVE FOR TURNING NITRATE INTO NITRITE |
|
|
What happens when a bacteria is catalase (+) and which bacterias are those ? |
Bubbles when positive - positive bacterias are Staphylococcus & Micrococcus |
|
|
What happens when a bacteria is catalase (-) and which bacteria groups are those ? |
no bubbles - Streptococcus & Enterococcus |
|
|
KNOW HOW TO SPELL THE FOLLOWING CORRECTLY Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epidermidis Micrococcus roseus Micrococcus luteus |
|
|
|
How is mannitol salt agar both selective & differential |
selective- Staphylococcus by being salt-tolerant differential - media turns yellow for if mannitol is fermented |
|
|
SPELL CORRECTLY Enterococcus faecalis |
|
|
|
What is the Bile scullion test result for Enterococcus faecalis |
positive; very dark brown/black media |
|
|
What does the test result look like for a Beta hemolysis |
complete clearing of red blood cells |
|
|
What does the test result look like for a Alpha hemolysis
|
olive green |
|
|
What does the test result look like for a Gamma hemolysis
|
no damage to media |
|
|
why do we streak and stab on blood agar inoculations |
enhance appearance of hemolysis |
|
|
atmosphere to grow streptococcus |
|
|
|
How does CNA agar aid in identifying mixed unknowns |
gram positive grows |
|
|
How does McConkey agar aid in identifying mixed unknowns |
gram negative grows - hot pink for lactose fermentation |
|
|
What is the arrangement and gram stain for Staphylococcus and Micrococcus |
Gram (+) cocci in clusters |
|
|
Where are Staphylococcus and Micrococcus normally found in the body |
skin and mucous membranes |
|
|
define carrier |
harbor pathogen but show no symptoms |
|
|
Define MRSA |
resistant to PCN derivatives |
|
|
Define nosocomial |
healthcare acquired infections |
|
|
I DON'T HAVE THE CORRECT ANSSER FOR PRE ASSESSMENT EXERSIZE 17 #4 Name two substances that Staphylococcus aureus produce to cause disease - |
|
|
|
when do Staphylococcus epidermis and Micrococcus cause disease |
Opportunistic ? Pre assessment CH 17 #5 |
|
|
Explain why Coccidiodes immitis is considered to be a dimorphic fungus ? |
It is a yeast or mold depending on the environment |
|
|
what are the growth differences between fungus and bacteria ? |
Fungi grow slower, lower temp, lower PH than most bacteria |
|
|
Define blastospore |
newly asexually reproduced yeast cell |
|
|
define pseudohyphae |
yeast blastopore that remains attached to the original cell |
|
|
define septate hyphae |
fungi hyphal filaments separated by crosswall |
|
|
explain difference between vegetative hyphae and aerial hyphae |
vegetative - grow on or down the agar aerial - above agar surface |
|
|
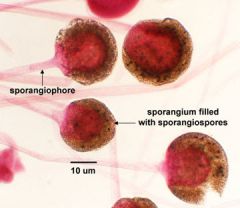
explain difference between sporangiospores and conidiospores |
sporangiospores- usually produced @ end of aerial hyphae inside sac like structure conidiospores - formed on hyphae maybe 1 celled or multiple |
|
|
how are molds identified in the lab ? |
macroscopic appearance with naked eye & microscopic appearance |
|
|
Define obligate intracellular parasite |
can grow only inside another living host cell - Ex: viruses |
|
|
How does a medium used for bacterial growth differ from media for bacteriophage growth ? |
EXCERSIZE 15 NUMBER 2 |
|
|
What is a viral plaque and what does it represent |
clearing of bacterial growth- represents the spot where a virus has landed, infected the bacteria it encountered, and lysed them |
|
|
What enzyme helps differentiate all Staphylococci from Streptococci |
catalase |
|
|
How did Lancefield divide the beta-hemolytic streptococci into groups |
polysaccharide extracted from the cell walls |
|
|
what is the species name of lance field group a Streptococci |
S. pyogenes |
|
|
what is the species name of Lancefield Group B Streptococci |
S. agalactiae |
|
|
Where are Enterococcus normally found in the body |
GI tract |
|
|
Define VRE |
Vancomycin resistant Enterococcus |
|
|
define viridans streptococci |
PRE ASSESSMENT CH 18 # 6 |
|
|
Disease for Group A Strep |
Strep throat |
|
|
Disease from Group B Strep |
neonatal septicemia |
|
|
Disease for enterococcus |
urinary tract infection |
|
|
disease for Streptococcus pneumoniae |
community-acquired pneumonia |
|
|
disease for niridans streptococci |
dental cavities |
|
|
what type of organism grows on MacConkey agar |
Gram (-) |
|
|
what ingredient in the MacConkey agar will differentiate the organisms growing on the agar |
lactose ferment = hot pink |
|
|
what type of organism grows on CNA |
gram (+) |
|
|
how does the CNA medium inhibit the growth of gram negative rods ? |
antibiotics |
|
|
what ingredient in the CNA media allows differentiation of the organisms growing on the agar ? |
red blood cells |
|
|
why is the CNA media incubated in the candle jar |
some are microaerophilic |
|
|
why is a cotton swab used to obtain the sample from the original broth |
ensure enough is collected one over took another in the mixed unknown. |
|
|
why is T. soy agar used to grow the "stock cultures" |
it's a "non-inhibitory" media that will allow the organisms to produce enzymes and metabolize the ingredients |
|
|
why do we develop two flow charts for our mixed unknowns ? |
one for Gram (+) one for Gram (-) |
|
|
what are the two major groups of gram negative rods and the common characteristics of each group ? |
Enterobacteria ceae - -gram (-) rods ferment glucose do not produce oxidase reduce nitrate to nitrite nonfermenters all gram (-) do not ferment glucose many but not all are oxidase (+) |
|
|
which carbohydrate is used to determine whether a game (-) rod is a "nonfermenter" or "enterobacteriaceae" |
clucose |
|
|
what carbohydrates are in the Kligler Iron Agar media |
lactose and glucose |
|
|
What carbohydrate is in MacConkey agar |
lactose |
|
|
Why is MacConkey agar considered tone selective and differential media |
selective for gram (-) rods bile salts and crystal violet inhibit gram (+) growth differential by the ability to ferment lactose |
|
|
what is an enteric organism |
Enterobateriaceae normal flora GI tract |
|
|
how are culture media designed to detect if a bacteria can produce a specific enzyme |
substrates |
|
|
what is the purpose of the Durham tube in the carbohydrate fermentation tubes ? |
collect gas |
|
|
name the specific tests that are part of the IMViC test ? |
Indole, Methyl red, Voges-proskauer & citrate |
|
|
name three Enterobacteriaceae normally found in the GI tract |
E. coli, E. aerogenes, P. vulgaris |
|
|
Name two Enterobacteriaceae that are major pathogens and state the disease each cause |
Salmonella - gastroenteritis & ty |

